北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 46-53. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.008
3种自酸蚀粘接系统和轻度唾液污染对乳牙釉质及牙本质粘接耐久性的影响
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,儿童口腔科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Effects of three self-etch adhesives and mild salivary contamination on the bonding durability of deciduous teeth
LUO Chi-yi,PENG Chu-fang,YANG Yuan,QIN Man,WANG Yuan-yuan( )
)
- Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Disease & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
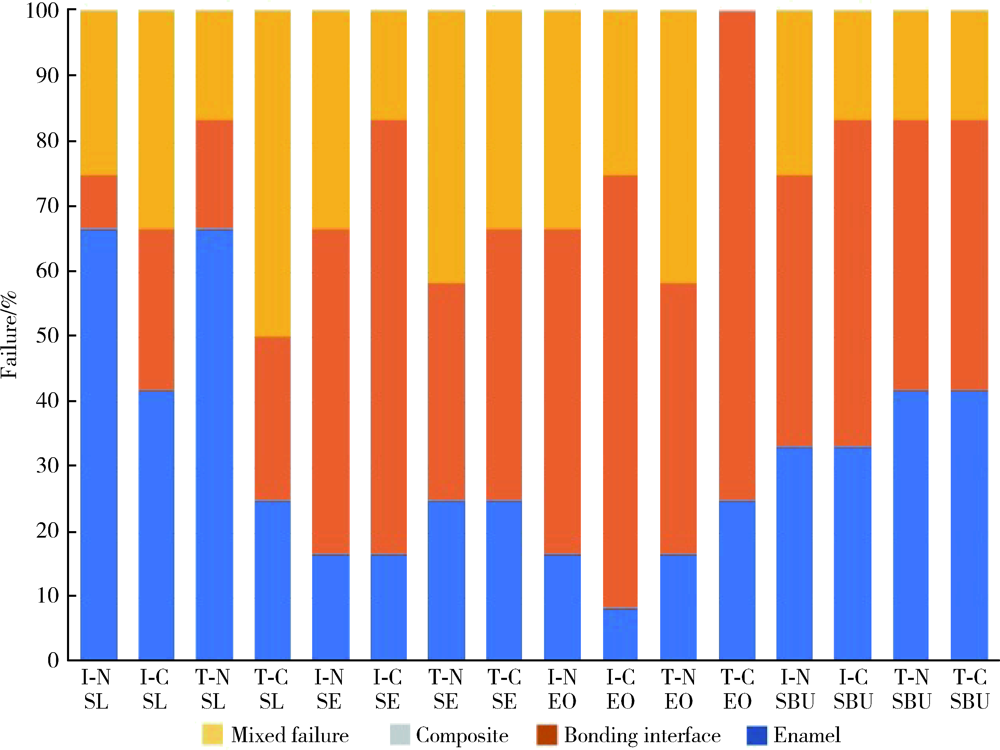
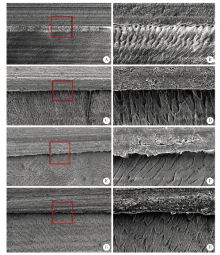
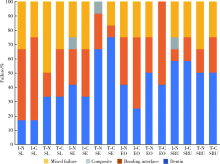
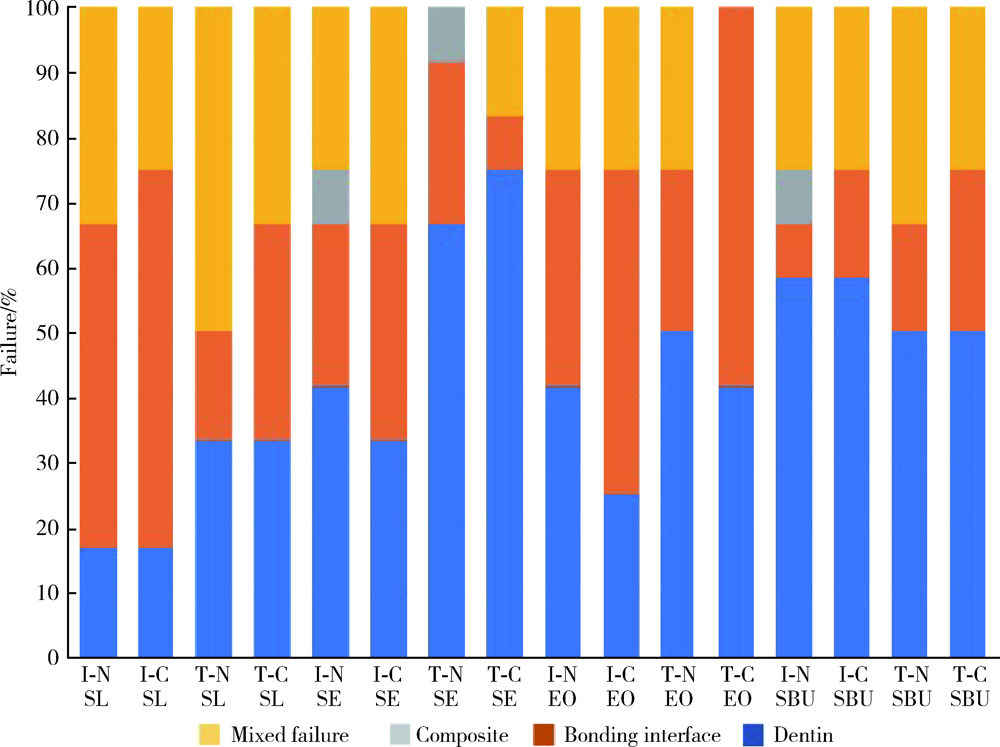
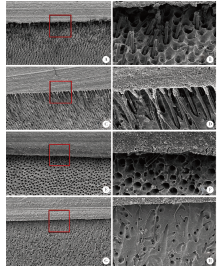
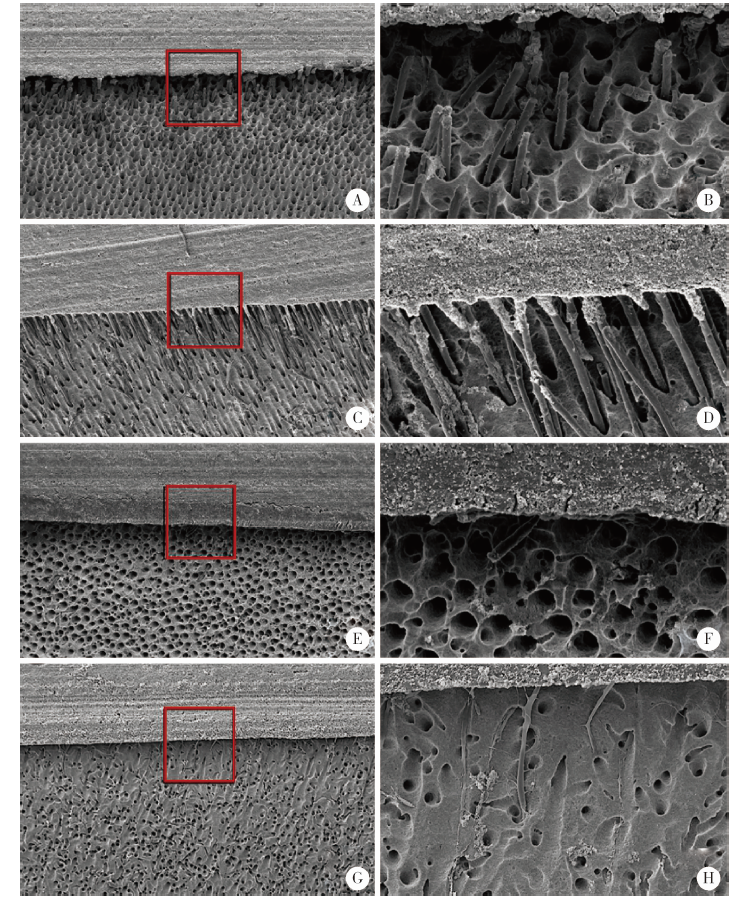
目的: 比较Clearfil SE Bond(SE)、AdperTM Easy One(EO)、Scotchbond Universal(SBU)3种自酸蚀粘接系统对乳牙釉质和牙本质粘接耐久性的影响,以及粘接界面轻度唾液污染后即刻吹干对粘接耐久性的影响。方法: 将240个乳牙釉质及240个牙本质样本随机分为16组(n = 15个/组), 实验组选用SE、EO、SBU等3种不同自酸蚀粘接系统,对照组选用AdperTM Single Bond Plus(SL)全酸蚀粘接系统,在无污染或有唾液污染、蒸馏水储存(水浴储存24 h)或水浴循环老化(5 ℃和55 ℃水浴中循环5 000次)等两种不同储存条件下,测量每组中12个试样的剪切粘接强度,用扫描电子显微镜观察分析剩余3个试样的粘接界面情况。采用三因素方差分析法和Tukey检验对数据进行统计学分析。结果: 对于乳牙牙釉质粘接,全酸蚀粘接剂的即刻剪切粘接强度(28.92±1.83) MPa和老化后剪切粘接强度(27.27±3.03) MPa均显著高于其他组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);EO组有唾液污染时即刻剪切粘接强度(11.88±3.17) MPa或老化后剪切粘接强度(11.90±3.98) MPa均显著低于其无唾液污染时的即刻剪切粘接强度(19.57±3.89) MPa或老化后剪切粘接强度(19.01±5.03) MPa,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。对于乳牙牙本质的粘接,老化处理后全酸蚀粘接剂的剪切粘接强度(14.31±1.97) MPa显著低于其他粘接剂组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);EO组有唾液污染时的即刻剪切粘接强度(12.99±2.66) MPa显著低于其无唾液污染时剪切粘接强度(18.63±3.61) MPa,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);EO组的无/有污染状态下的剪切粘接强度[(14.41±2.68) MPa和(10.93±2.18) MPa]均显著低于SE组[(21.10±4.40) MPa和(19.56±3.64) MPa]和SBU组[(22.27±5.43) MPa和(20.60±5.11) MPa], 差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。结论: 全酸蚀粘接剂对乳牙釉质粘接耐久性更佳;SE和SBU对乳牙牙本质有更好的粘接耐久性;粘接界面轻度唾液污染后即刻吹干处理可恢复SE和SBU的粘接强度,但对EO的粘接性能影响较大,无法恢复其粘接耐久性。
中图分类号:
- R788.4
| [1] | Perdigao J, Sezinando A, Monteiro PC. Laboratory bonding ability of a multi-purpose dentin adhesive[J]. Am J Dent, 2012,25(3):153-158. |
| [2] |
Munoz MA, Luque-Martinez IV, Malaquias P, et al. In vitro longe-vity of bonding properties of universal adhesives to dentin[J]. Oper Dent, 2015,40(3):282-292.
doi: 10.2341/14-055-L pmid: 25405904 |
| [3] |
Lawson NC, Robles A, Fu CC, et al. Two-year clinical trial of a universal adhesive in total-etch and self-etch mode in non-carious cervical lesions[J]. J Dent, 2015,43(10):1229-1234.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2015.07.009 pmid: 26231300 |
| [4] |
Vermelho PM, Reis AF, Ambrosano GMB, et al. Adhesion of multimode adhesives to enamel and dentin after one year of water storage[J]. Clinical Oral Investigations, 2016,21(5):1707-1715.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1966-1 pmid: 27714528 |
| [5] |
Santschi K, Peutzfeldt A, Lussi A, et al. Effect of salivary contamination and decontamination on bond strength of two one-step selfetching adhesives to dentin of primary and permanent teeth[J]. J Adhes Dent, 2015,17(1):51-57.
doi: 10.3290/j.jad.a33514 pmid: 25625136 |
| [6] |
Soares FZM, Rocha RdO, Raggio DP, et al. Microtensile bond strength of different adhesive systems to primary and permanent dentin[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2005,27(6):457-462.
pmid: 16532885 |
| [7] |
Ozmen B, Koyuturk AE, Tokay U, et al. Evaluation of bond strength of self-etching adhesives having different pH on primary and permanent teeth dentin[J]. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater, 2015,13(3):e274-e279.
doi: 10.5301/jabfm.5000234 pmid: 26391869 |
| [8] |
Osorio R, Yamauti M, Ruiz-Requena ME, et al. MMPs activity and bond strength in deciduous dentine-resin bonded interfaces[J]. J Dent, 2013,41(6):549-555.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2013.02.008 pmid: 23454331 |
| [9] |
Soares FZ, Lenzi TL, de Oliveira Rocha R. Degradation of resin-dentine bond of different adhesive systems to primary and permanent dentine[J]. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent, 2017,18(2):113-118.
doi: 10.1007/s40368-017-0282-z pmid: 28271448 |
| [10] |
Yaguchi T. Layering mechanism of MDP-Ca salt produced in demineralization of enamel and dentin apatite[J]. Dent Mater, 2017,33(1):23-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2016.09.037 pmid: 27773341 |
| [11] | Kulkarni AS, Kokate S, hegde V, et al. The effect of saliva con-tamination on shear bond strength of two universal bonding agents: an in vitro study[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2018,12(4):6-10. |
| [12] |
Cobanoglu N, Unlu N, Ozer F, et al. Bond strength of self-etch adhesives after saliva contamination at different application steps[J]. Oper Dent, 2013,38(5):505-511.
doi: 10.2341/12-260-L |
| [13] |
Loguercio AD, Munoz MA, Luque-Martinez I, et al. Does active application of universal adhesives to enamel in self-etch mode improve their performance?[J]. J Dent, 2015,43(9):1060-1070.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2015.04.005 pmid: 25908573 |
| [14] |
Cardenas AFM, Siqueira FSF, Bandeca MC, et al. Impact of pH and application time of meta-phosphoric acid on resin-enamel and resin-dentin bonding[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2018,78:352-361.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.11.028 pmid: 29202298 |
| [15] |
Gong HH, Guo XW, Cao DF, et al. Photopolymerizable and moisture-curable polyurethanes for dental adhesive applications to increase restoration durability[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2019,7(5):744-754.
doi: 10.1039/c8tb01716f pmid: 32254848 |
| [16] |
Antoniazzi BF, Nicoloso GF, Lenzi TL, et al. Selective acid etching improves the bond strength of universal adhesive to sound and demineralized enamel of primary teeth[J]. J Adhes Dent, 2016,18(4):311-316.
doi: 10.3290/j.jad.a36154 pmid: 27419240 |
| [17] | Memarpour M, Shafiei F, Razmjouei F, et al. Shear bond strength and scanning electron microscopy characteristics of universal adhesive in primary tooth dentin: An in vitro study.[J]. Dent Res J (Isfahan), 2018,15(4):264-270. |
| [18] |
Porto IM, Saiani RA, Chan KL, et al. Organic and inorganic content of fluorotic rat incisors measured by FTIR spectros-copy[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 2010,77(1):59-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2010.04.024 pmid: 20547096 |
| [19] |
Silverstone LM, Saxton CA, Dogon IL, et al. Variation in the pattern of acid etching of human dental enamel examined by scanning electron microscopy[J]. Caries Res, 1975,9(5):373-387.
doi: 10.1159/000260179 pmid: 1055640 |
| [20] |
Sumikawa DA, Marshall GW, Gee L, et al. Microstructure of primary tooth dentin[J]. Pediatr Dent, 1999,21(7):439-444.
pmid: 10633518 |
| [21] |
Lenzi TL, Guglielmi Cde A, Arana-Chavez VE, et al. Tubule density and diameter in coronal dentin from primary and permanent human teeth[J]. Microsc Microanal, 2013,19(6):1445-1449.
doi: 10.1017/S1431927613012725 |
| [22] | Ye Q, Wang Y, Spencer P. Nanophase separation of polymers exposed to simulated bonding conditions[J]. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater, 2009,88(2):339-348. |
| [23] |
Werle SB, Steglich A, Soares FZM, et al. Effect of prolonged air drying on the bond strength of adhesive systems to dentin.[J]. Gen Dent, 2015,63(6):68-72.
pmid: 26545278 |
| [24] |
Landuyt KLV, Snauwaert J, Munck JD, et al. Origin of interfacial droplets with one-step adhesives[J]. J Dent Res, 2007,86(8):739-744.
doi: 10.1177/154405910708600810 pmid: 17652202 |
| [25] |
Pragasam AX, Duraisamy V, Nayak UA, et al. Evaluation of sealing ability two self-etching adhesive systems and a glass ionomer lining LC under composite restoration in primary tooth: An in vitro study[J]. J Pharm Bioallied Sci, 2015,7(Suppl 2):518-523.
doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.163525 |
| [26] |
Angker L, Nockolds C, Swain MV, et al. Quantitative analysis of the mineral content of sound and carious primary dentine using BSE imaging[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2004,49(2):99-107.
doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2003.08.006 |
| [27] |
van Meerbeek B, de Munck J, Yoshida Y, et al. Buonocore memorial lecture adhesion to enamel and dentin: current status and future challenges[J]. Oper Dent, 2003,28(3):215-235.
pmid: 12760693 |
| [1] | 仲若情,朱梦倩,李应龙,潘洁. 低温等离子体对牙本质小管内粪肠球菌的抗菌效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 38-43. |
| [2] | 郭若兰,黄桂彬,龙赟子,董艳梅. 新型生物活性玻璃促进人工牙本质龋再矿化的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 82-87. |
| [3] | 冯莎蔚,国慧,王勇,赵一姣,刘鹤. 乳牙数字化参考牙冠模型的初步构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 327-334. |
| [4] | 田靖,秦满,陈洁,夏斌. 失活剂烧伤致乳磨牙早失及恒牙胚丧失2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 381-385. |
| [5] | 马欣蓉,朱晓鸣,李静,李德利,李和平,谭建国. 新型大气压冷等离子体射流处理对牙本质胶原纤维交联化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 83-88. |
| [6] | 李秋菊,宫玮玉,董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃预处理对牙本质粘接界面耐久性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 931-937. |
| [7] | 谢静,赵玉鸣,饶南荃,汪晓彤,方滕姣子,李晓霞,翟越,李静芝,葛立宏,王媛媛. 3种口腔颌面部来源的间充质干细胞成血管内皮分化潜能的比较研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 900-906. |
| [8] | 潘怡湘,李秀花,田福聪,王晓燕. 髓腔内压对树脂水门汀与牙本质粘接强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 321-326. |
| [9] | 周琼,彭楚芳,秦满. 近红外光透照技术诊断乳磨牙早期邻面龋[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 59-64. |
| [10] | 游文喆,窦桂丽,夏斌. 乳牙间接牙髓治疗两年疗效观察及影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 65-69. |
| [11] | 李芳,刘洋,刘浩辰,冯海兰. 乳光牙本质患者的基因变异分析及患牙的组织学观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 666-671. |
| [12] | 汪晓彤,饶南荃,方腾姣子,赵玉鸣,葛立宏. 乳牙牙髓干细胞CD146阳性/阴性细胞亚群生物学特性的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 284-292. |
| [13] | 臧海玲,王月,梁宇红. 有机溶剂对牙本质表面残留根管封闭剂的清除效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 63-68. |
| [14] | 贾维茜,赵玉鸣,葛立宏. 人重组转化生长因子β1促进牙髓干细胞的增殖和矿化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 680-681. |
| [15] | 李皓,刘玉华,罗志强. 生物活性玻璃用于缓解活髓牙全冠预备后敏感的效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 709-713. |
|
||