北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 83-87. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.013
应用于无牙颌种植修复设计的三维面部扫描配准方法的对比
国丹妮1,潘韶霞1,Δ( ),衡墨笛2,屈健2,魏秀霞2,周永胜1
),衡墨笛2,屈健2,魏秀霞2,周永胜1
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 修复科, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,义齿加工中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Comparison of the registration methods for the three-dimensional facial scans applied to the design of full-arch implant supported restoration
GUO Dan-ni1,PAN Shao-xia1,Δ( ),HENG Mo-di2,QU Jian2,WEI Xiu-xia2,ZHOU Yong-sheng1
),HENG Mo-di2,QU Jian2,WEI Xiu-xia2,ZHOU Yong-sheng1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Dental Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
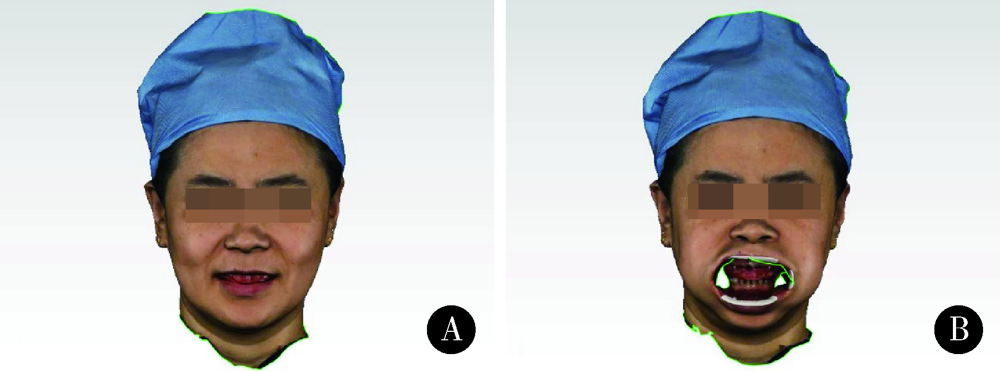
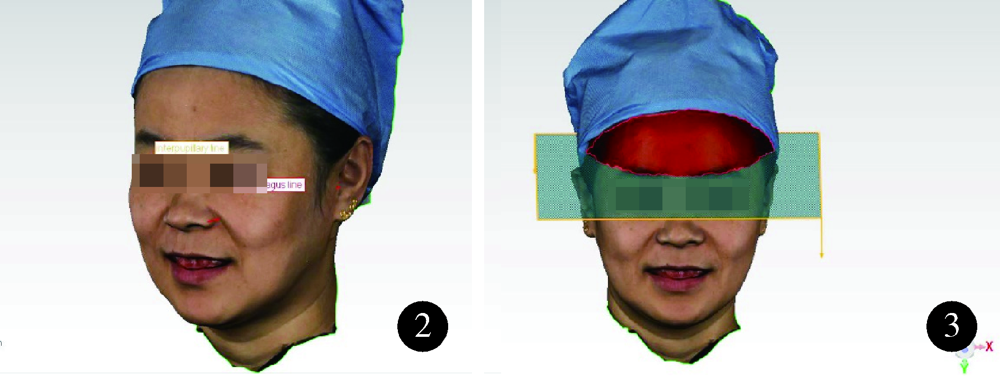
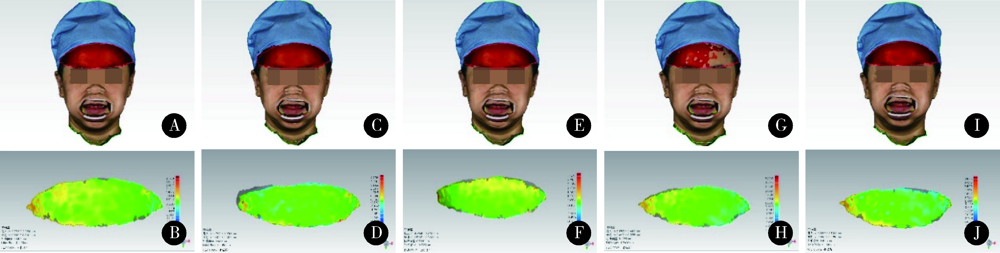
目的: 比较无牙颌种植修复设计三维面部扫描配准的5种方法的配准精度,探究适宜的配准方法。方法: 依据标准共纳入10名受试者,每位受试者戴有具有特征标志点的蜡堤。利用FaceScan三维面部扫描仪获取10位拟行无牙颌种植修复患者的自然大笑位和开口器牵拉暴露口内蜡堤的三维面部扫描数据,将扫描数据导入数字化分析软件Geomagic Qualify 2012中,建立局部坐标系,分别利用面部解剖标志点对齐、面部不动区域对齐、面部点对齐与区域对齐结合、增加面部特征点对齐、增加面部和口内特征标记对齐5种方法将两个面部扫描数据重合,计算同一选定区域的三维偏差,三维偏差越小代表配准精度越高。采用SPSS22.0软件进行统计学分析,面部解剖标志点对齐、面部不动区域对齐、面部点对齐与区域对齐结合3组间差异进行Frideman检验,是否增加面部特征点对齐和是否增加口内特征标记对齐的两组进行配对t检验比较。结果: 直接选择面部解剖标志点对齐[(1.501 2±0.406 1) mm],面上1/3选中区域三维偏差平均值显著大于面部不动区域对齐[(0.629 1±0.150 6) mm]及两种方法相结合[(0.603 5±0.493 4) mm]的偏差(P<0.001);增加面部特征点可显著减小配准后偏差(t=1.001 3, P<0.001),其余组间差异无统计学意义。结论: 面上1/3不动区域应用于无牙颌种植修复设计的三维面部扫描配准是临床可行的,面部扫描操作时可尽量暴露前额区域,增加面部特征点,并利用面部不动区域最佳拟合对齐提高配准精度。
中图分类号:
- R783.4
| [1] |
Wong JY, Oh AK, Ohta E, et al. Validity and reliability of craniofacial anthropometric measurement of 3D digital photogrammetric images[J]. Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 2008,45(3):232-239.
doi: 10.1597/06-175 pmid: 18452351 |
| [2] |
Knoops PG, Beaumont CA, Borghi A, et al. Comparison of three-dimensional scanner systems for craniomaxillofacial imaging[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2017,70(4):441-449.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2016.12.015 pmid: 28161205 |
| [3] |
Artopoulos A, Buytaert JA, Dirckx JJ, et al. Comparison of the accuracy of digital stereophotogrammetry and projection moiré profilometry for three-dimensional imaging of the face[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014,43(5):654-662.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.10.005 pmid: 24225265 |
| [4] |
Secher JJ, Darvann TA, Pinholt EM. Accuracy and reproducibility of the DAVID SLS-2 scanner in three-dimensional facial imaging[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2017,45(10):1662-1670.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.07.006 pmid: 28847623 |
| [5] |
Sforza C, de Menezes M, Ferrario V. Soft- and hard-tissue facial anthropometry in three dimensions: what’s new[J]. J Anthropol Sci, 2013,91:159-184.
doi: 10.4436/JASS.91007 |
| [6] |
Zhao YJ, Xiong YX, Wang Y. Three-dimensional accuracy of facial scan for facial deformities in clinics: a new evaluation method for facial scanner accuracy[J]. PLoS One, 2017,12(1):e0169402.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169402 pmid: 28056044 |
| [7] |
Jang KS, Bayome M, Park JH, et al. A three-dimensional photogrammetric analysis of the facial esthetics of the miss Korea pageant contestants[J]. Korean J Orthod, 2017,47(2):87-99.
doi: 10.4041/kjod.2017.47.2.87 pmid: 28337418 |
| [8] | 刘云松, 叶红强, 谷明, 等. 患者参与的数字化设计在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014,46(1):90-94. |
| [9] |
Hassan B, Gimenez Gonzalez B, Tahmaseb A, et al. A digital approach integrating facial scanning in a CAD-CAM workflow for complete-mouth implant-supported rehabilitation of patients with edentulism: A pilot clinical study[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2017,117(4):486-492.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.07.033 pmid: 27881321 |
| [10] |
Coachman C, Calamita MA, Coachman FG, et al. Facially generated and cephalometric guided 3D digital design for complete mouth implant rehabilitation: a clinical report[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2017,117(5):577-586.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.09.005 pmid: 27836143 |
| [11] |
Hassan B, Greven M, Wismeijer D. Integrating 3D facial scanning in a digital workflow to CAD/CAM design and fabricate complete dentures for immediate total mouth rehabilitation[J]. J Adv Prosthodont, 2017,9(5):381-386.
doi: 10.4047/jap.2017.9.5.381 pmid: 29142646 |
| [12] |
Ritschl LM, Wolff KD, Erben P, et al. Simultaneous, radiation-free registration of the dentoalveolar position and the face by combining 3D photography with a portable scanner and impression-taking[J]. Head Face Med, 2019,15(1):28.
doi: 10.1186/s13005-019-0212-x pmid: 31767030 |
| [13] |
Bohner L, Gamba DD, Hanisch M, et al. Accuracy of digital technologies for the scanning of facial, skeletal, and intraoral tissues: a systematic review[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2019,121(2):246-251.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.01.015 pmid: 30017156 |
| [14] | 赵一姣, 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 等. 2种三维颜面部扫描仪测量精度的定量评价[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2016,32(1):37-42. |
| [15] | 苏莉, 王红梅, 白玉兴. 基于激光扫描的面部软组织三维模型的重叠和分析方法的建立[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2015,23(3):135-140. |
| [16] |
熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 等. 两种评价面部三维表面数据不对称度方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(2):340-343.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2015.02.030 |
| [17] | Pérez-Giugovaz MG, Park SH, Revilla-León M. Three-dimen-sional virtual representation by superimposing facial and intraoral digital scans with an additively manufactured intraoral scan body [J/OL]. J Prosthet Dent, 2020[2020-09-25]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.07.012. |
| [18] | Lepidi L, Galli M, Grammatica A, et al. Indirect digital workflow for virtual cross-mounting of fixed implant-supported prostheses to create a 3d virtual patient [J/OL]. J Prosthodont, 2020 [2020-8-31]. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.13247. |
| [19] | 彭菊香, 江久汇, 赵一姣, 等. 结构光扫描对骨性Ⅲ类错牙合正畸正颌联合治疗前后软组织三维变化的初步评价[J], 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(1):98-103. |
| [20] |
Germec-Cakan D, Canter HI, Nur B, et al. Comparison of facial soft tissue measurements on three-dimensional images and models obtained with different methods[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2010,21(5):1393-1399.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181ec6976 pmid: 20856027 |
| [21] |
Hajeer MY, Ayoub AF, Millett DT, et al. Three-dimensional imaging in orthognathic surgery: the clinical application of a new method[J]. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg, 2002,17(4):318-330.
pmid: 12593004 |
| [22] | 苏莉, 曹丽, 龚宇田. 基于激光扫描的面部软组织三维模型三种重叠方法的对比[J], 北京口腔医学, 2018,26(1):33-36. |
| [23] |
Revilla-León M, Campbell HE, Meyer MJ, et al. Esthetic dental perception comparisons between 2D- and 3D-simulated dental discrepancies[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2020[2020-01-22]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.11.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.09.060 pmid: 33455728 |
| [24] |
Ghoddousi H, Edler R, Haers P, et al. Comparison of three methods of facial measurement[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2007,36(3):250-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.10.001 pmid: 17113754 |
| [25] |
Knoops PG, Beaumont CA, Borghi A, et al. Comparison of three-dimensional scanner systems for craniomaxillofacial imaging[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2017,70(4):441-449.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2016.12.015 pmid: 28161205 |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [4] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [5] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [6] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [7] | 张晗,秦亦瑄,韦帝远,韩劼. 牙周炎患者种植修复维护治疗依从性的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [8] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [9] | 李穗,马雯洁,王时敏,丁茜,孙瑶,张磊. 上前牙种植单冠修复体切导的数字化设计正确度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [10] | 刘晓强,周寅. 牙种植同期植骨术围术期高血压的相关危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [11] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [12] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [13] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [14] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [15] | 刘想,谢辉辉,许玉峰,张晓东,陶晓峰,柳林,王霄英. 人工智能对提高放射科住院医生诊断胸部肋骨骨折一致性的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
|
||