北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 302-307. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.012
炎症生物标志物对输尿管尿路上皮癌患者预后预测的临床价值
- 河北北方学院附属第一医院泌尿外科,河北张家口 075061
Clinical value of inflammatory biomarkers in predicting prognosis of patients with ureteral urothelial carcinoma
CHEN Huai-an,LIU Shuo( ),LI Xiu-jun,WANG Zhe,ZHANG Chao,LI Feng-qi,MIAO Wen-long
),LI Xiu-jun,WANG Zhe,ZHANG Chao,LI Feng-qi,MIAO Wen-long
- Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Hebei North Univercity, Zhangjiakou 075061, Hebei, China
摘要:
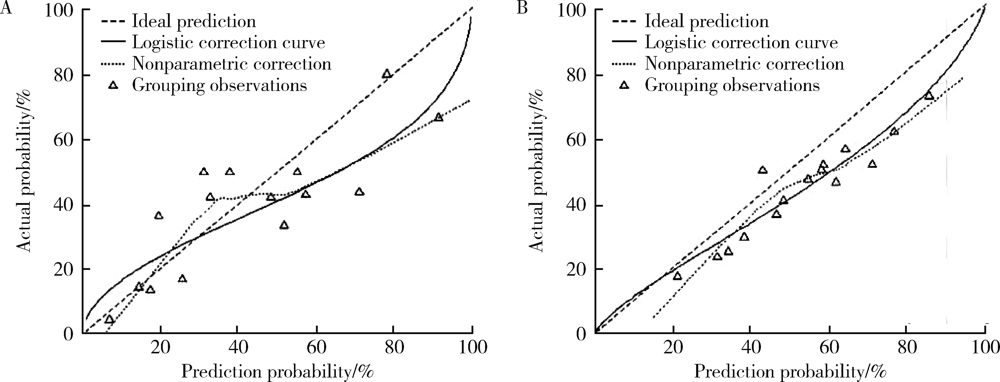
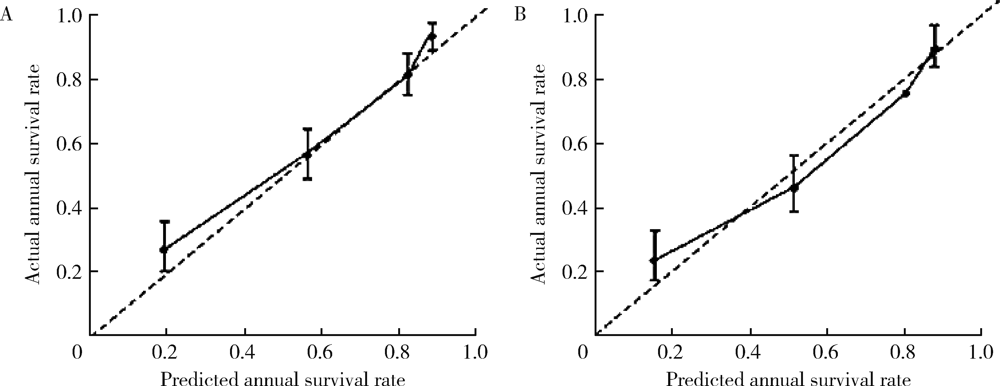
目的: 评估炎症相关标志物对输尿管尿路上皮癌患者预后预测的临床价值。方法: 采用分割样本验证将200例输尿管尿路上皮癌患者随机分为建模组和验证组,回顾患者石蜡病理标本,免疫组织化学法检测肿瘤组织浸润中性粒细胞(tumor-infiltrating neutrophil,TIN)(CD66b+标记)、肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)(CD163+标记)及淋巴细胞(CD+、CD4+、CD8+标记)计数,以及外周血中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值(neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio,NLR)、肿瘤组织中性粒细胞/单核细胞比值(neutrophil/monocyte ratio,NMR),按病理分期结果将患者分成非肌层浸润性和肌层浸润性输尿管尿路上皮癌组,分别建立预后预测列线图模型。对模型进行分辨度评价,分别建立仅包含外周血参数和包含全部参数的预后列线图模型,比较两种模型对输尿管尿路上皮癌患者预后判断的准确性。结果: 患者中位随访时间36个月,无进展生存时间40个月,3年内出现肿瘤进展42例(21.0%)。肿瘤大小、病理分期、病理分级等指标均为预测输尿管尿路上皮癌术后3年首次复发的单因素变量,肿瘤大小、病理分期、病理分级、TIN、TAM、NLR、NMR是预测输尿管尿路上皮癌术后3年首次复发的多因素变量。非肌层浸润性输尿管尿路上皮癌104例,术后3年首次复发10例(9.6%),肌层浸润性输尿管尿路上皮癌96例,术后3年首次复发32例(33.3%),两组比较差异有统计学意义(χ2=15.53,P<0.05)。建立两组无进展生存率的预测列线图模型发现,非肌层浸润组和肌层浸润组一致性指数分别为0.722(95%CI:0.70~0.78)和0.725(95%CI:0.71~0.79),与实际观察到的3年生存率一致性较佳。区分度测试结果显示,输尿管尿路上皮癌的全参数预后预测模型一致性指数为0.726,高于输尿管尿路上皮癌的外周血参数预后预测模型(一致性指数0.672),尿路上皮癌肿瘤组织的免疫微环境提高了模型的预测准确性。结论: 以免疫炎症相关标志物为基础的全参数预后预测模型可以作为现有病理分级和分期系统的完善和补充,为输尿管尿路上皮癌患者的精准个体化治疗提供了依据;以外周血标本相关指标为基础的预后预测模型标本易于获取,检测方法简单、经济,更利于临床推广应用。
中图分类号:
- R737.13
| [1] | 陆健伟, 吴佩琪. 非前哨淋巴结转移预测模型对中国乳腺癌患者的验证价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2018,41(2):212-218. |
| [2] | 苄晓洁, 沈益君, 朱耀, 等. 预测去势抵抗性前列腺癌患者总生存期Halabi风险列线图的验证研究[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2017,22(4):334-338. |
| [3] | 张燕, 孙晓, 赵桐, 等. 术中快速预测乳腺癌非前哨淋巴结转移模型的建立与验证研究[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2017,27(5):368-375. |
| [4] | 王枭杰, 池畔, 林惠铭, 等. 建立影像学无远处转移结肠癌患者发生腹膜转移的列线图预测模型[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2017,20(12):1387-1392. |
| [5] | 王枭杰, 池畔, 林惠铭, 等. 建立非转移性结直肠癌患者预后的列线图预测模型[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2017,20(6):654-659. |
| [6] | 黄纲, 董忠信, 谢显彪, 等. 骨肉瘤预后个体化预测模型列线图的建立[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(2):133-141. |
| [7] | 赵芳, 徐斌, 蒋敬庭, 等. 未转移结直肠癌患者术后转移风险预测列线图的构建[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2018,36(5):388-391. |
| [8] | 张怡, 钱萍. 转移性淋巴结比率在淋巴结转移胆囊癌患者中的预后意义及预后模型建立[J]. 浙江医学, 2018,40(20):2216-2219. |
| [9] | 王葵, 邹奇飞, 李征, 等. 肝细胞癌个体化治疗的临床预测模型[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018,34(7):1382-1386. |
| [10] | 孙奎霞, 闫存玲, 李志艳, 等. 基于前列腺健康指数建立的预测前列腺癌列线图模型的验证研究[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2018,41(7):536-540. |
| [11] | 张彩祥, 丰琅, 田野. 上尿路尿路上皮癌患者输尿管全长切除术后再发膀胱癌的危险因素分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2016,37(7):488-492. |
| [12] | 刘彬, 李文贤, 肖慧敏, 等. 上尿路尿路上皮癌根治术后尿路外复发的临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2016,37(10):740-744. |
| [13] | 邢云超, 熊耕砚, 方东, 等. 非肌层浸润性上尿路尿路上皮癌5年随访生存分析及其预后相关因素研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2016,37(3):190-194. |
| [14] | 冯炳富, 罗勇, 魏德超, 等. 根治术联合化疗对高风险上尿路尿路上皮癌患者生存预后的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2019,99(2):115-119. |
| [15] | 关豹, 曹振朋, 彭鼎, 等. T2N0M0期上尿路尿路上皮癌患者预后相关因素分析:单中心235例患者回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017,49(4):603-607. |
| [16] | 赵芳, 徐斌, 蒋敬庭, 等. 肾移植受者上尿路尿路上皮癌术后膀胱复发的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(4):605-610. |
| [17] | 王跃, 贺慧颖. 上尿路尿路上皮癌368例根治标本的临床病理特点及预后分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2016,45(10):681-686. |
| [18] |
Shankar A, Patil J, Sethi N, et al. Urinary dysfunction assessment in long-term survivors of carcinoma cervix using LENT SOMA scale: An Indian study addressing quality of life issues[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2019,20(2):383-389.
pmid: 30803196 |
| [19] |
Yaegashi H, Izumi K, Kadomoto S, et al. High serum CA19-9 concentration indicates high chemosensitivity and better survival in advanced urothelial carcinoma[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019,39(1):375-380.
doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13122 pmid: 30591483 |
| [20] | 邢云超, 熊耕砚, 方东, 等. 上尿路尿路上皮癌术前预后相关因素分析及初步风险分层模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016,48(6):1032-1037. |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | 马会超,李军,王永清. 妊娠合并炎症性肠病的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 260-266. |
| [8] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [9] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [10] | 殳畅,韩烨,孙雨哲,杨再目,侯建霞. Ⅲ期牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗前后炎症性贫血相关指标的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 45-50. |
| [11] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [12] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [13] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [14] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [15] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
|
||