北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 523-529. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.014
北京市通州区和顺义区747例2型糖尿病患者生存质量影响因素
樊理诗1,高敏1,Edwin B.FISHER2,孙昕霙1,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学公共卫生学院社会医学与健康教育系, 北京 100191
2.Department of Health Behavior, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599-7440, USA
Factors associated with quality of life in 747 patients with type 2 diabetes in Tongzhou District and Shunyi District of Beijing
FAN Li-shi1,GAO Min1,Edwin B. FISHER2,SUN Xin-ying1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Social Medicine and Health Education, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Health Behavior, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599-7440, USA
摘要:
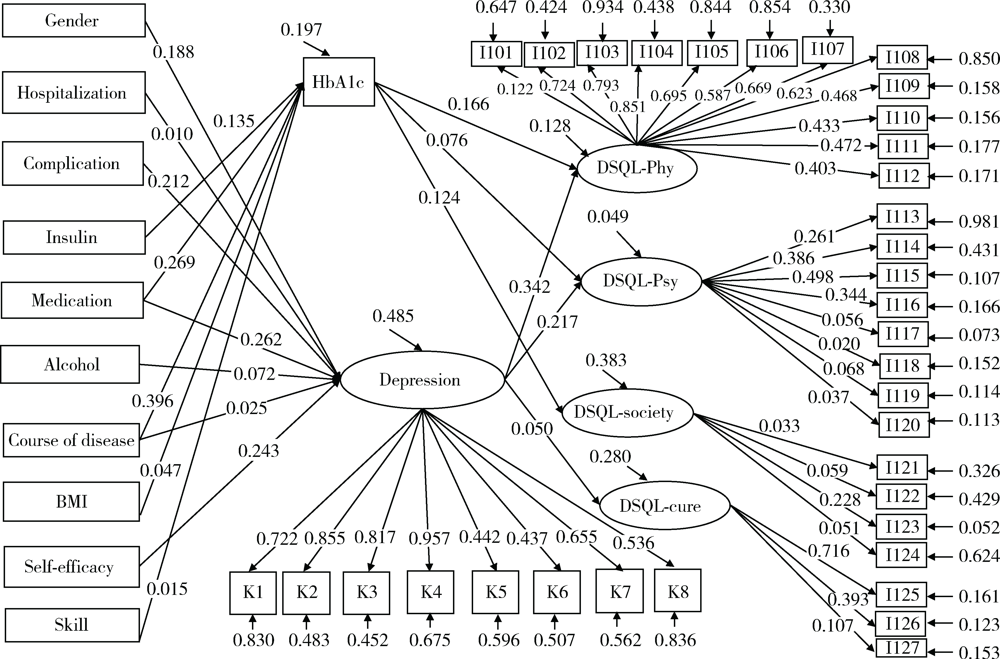
目的: 探讨北京市通州区和顺义区747例2型糖尿病患者的生存质量现状及影响因素。方法: 对纳入研究的747例2型糖尿病患者进行问卷调查和抽血实验室血生化检查。以糖化血红蛋白(hemoglobin A1c,HbA1c)作为血糖控制指标,以糖尿病患者特异性生存质量量表(diabetes specific quality of life scale,DSQL)评分为患者生存质量指标,采用多元线性回归和结构方程模型(structural equation modeling,SEM)分析生存质量的影响因素。结果: 调查747例患者,HbA1c平均水平(7.1±1.2)%,血糖控制达标率为35.1% (262/747)。血糖控制好和血糖控制差两组患者的病程、服药和使用胰岛素、吸烟情况及体重指数(body mass index,BMI)差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。DSQL总分为(44.92±13.32)分,生理维度条目平均分最高,其次是心理维度。多元线性回归结果显示,家庭月收入、并发症、抑郁、病程时间、胰岛素、住院及自我效能是DSQL总分的影响因素(P<0.05)。SEM结果显示,血糖对于生存质量的生理维度(标准化效应值为0.166)、心理维度(0.076)及社会维度(0.124)存在影响,抑郁对于生存质量的生理维度(0.342)、心理维度(0.217)及治疗维度(0.050)存在影响,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论: 北京市通州区和顺义区2型糖尿病患者HbA1c控制水平欠佳,生存质量尚可,仍有非常大的提升空间。应提高对男性、病程长、处于不服药状态、不使用胰岛素、吸烟、处于抑郁状态、糖尿病技能得分水平低的患者的关注和管理,同时应在临床治疗中提高对患者心理需求的重视,加强对患者及其家属的心理健康教育,采取相应的心理干预措施,以达到有效控制血糖的目的,从而提高患者的生活质量。
中图分类号:
- R587.1
| [1] |
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018,14(2):88-98.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151 pmid: 29219149 |
| [2] | Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: national cross sectional study[J]. BMJ, 2020,369:m997. |
| [3] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2021,37(4):311-398. |
| [4] | 高蕾莉, 纪立农, 陆菊明, 等. 2009—2012年我国2型糖尿病患者药物治疗与血糖控制状况调查[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2014,22(7):594-598. |
| [5] | Bajaj S. RSSDI clinical practice recommendations for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017[J]. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries, 2018,38(Suppl 1):1-115. |
| [6] | 许燕川, 马米果, 黄小碟. 543例糖尿病患者生活质量及其影响因素调查分析[J]. 预防医学情报杂志, 2020,36(9):1222-1227. |
| [7] | 王冯彬, 高敏, 陈雪莹, 等. 社区2型糖尿病患者家庭支持与饮食行为的相关性研究[J]. 中国健康教育, 2020,36(4):300-304. |
| [8] | 高敏, 陈雪莹, 孙信, 等. 2型糖尿病患者的抑郁症状与人格特质和运动行为的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2021,35(4):271-276. |
| [9] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会, 中华医学会内分泌学分会. 中国成人2型糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白控制目标及达标策略专家共识[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2020,12(1):1-12. |
| [10] | 庄鵷, 田冰洁, 王绮, 等. 老年2型糖尿病患者生存质量现状及影响因素研究[J]. 上海护理, 2021,21(2):30-34. |
| [11] | 汪爱茹, 唐婷婷, 周珈瑀, 等. 2型糖尿病患者心理状况和生存质量的相关性研究[J]. 四川医学, 2020,41(4):407-411. |
| [12] | 姜乾金. 应激(压力)系统模型:理论与实践[C]// 中国心理学会. 第十七届全国心理学学术会议论文摘要集. 北京: 中国心理学会, 2014: 1. |
| [13] | 许国敏, 程煜. 动态血糖监测联合心理疏导对2型糖尿病患者血糖控制、负性情绪及生活质量的影响[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2020,28(12):1797-1802. |
| [14] |
Wong MC, Wu CH, Wang HH, et al. Association between the 8-item Morisky medication adherence scale (MMAS-8) score and glycaemic control among Chinese diabetes patients[J]. J Clin Pharmacol, 2015,55(3):279-287.
doi: 10.1002/jcph.v55.3 |
| [15] | 曹昭春. 上海市社区2型糖尿病患者血糖控制现况及影响因素分析[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019. |
| [16] | 李玉东. 南阳地区空巢老年糖尿病患者自我管理水平与生活质量相关性研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2019,34(13):1228-1230, 1243. |
| [17] | 蒋明晖, 张桥, 朱汝霞, 等. 南宁城乡2型糖尿病患者生存质量及其影响因素分析[J]. 右江民族医学院学报, 2018,40(4):359-362. |
| [18] | 李黎, 黄少冰, 陈焕萍, 等. 珠海市某基层医院2型糖尿病患者生活质量调查及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国当代医药, 2020,27(12):156-158. |
| [19] | 刘芳, 张英娴, 卫海燕. 1型糖尿病儿童血糖控制及生活质量状况调查[J]. 滨州医学院学报, 2019,42(1):24-26. |
| [20] | 王吉英, 肖光青, 王彦, 等. 社区糖尿病患者自我管理现状和护理指导需求的影响因素分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2020,26(15):2061-2065. |
| [21] | 姚静静, 孙强, 李奇, 等. 2型糖尿病患者自我效能与服药依从性关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2019,35(11):1471-1473. |
| [22] |
van Dooren FE, Denollet J, Verhey FR, et al. Psychological and personality factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus, presenting the rationale and exploratory results from The Maastricht Study, a population-based cohort study[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2016,16:17.
doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-0722-z pmid: 26817600 |
| [1] | 王敏, 李倩. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性影响因素的路径分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 809-814. |
| [2] | 陈敬,单蕊,肖伍才,张晓蕊,刘峥. 青春期和成年早期自制力与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联:基于全国调查的十年前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 397-402. |
| [3] | 汤华萌,袁典琪,王明星,杨晗冰,郭超. 数字融入和健康生活方式对社会经济状况与老年人抑郁关系的序列中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [4] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [5] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [6] | 王婷,李乔晟,刘皓冉,简伟研. 人格特征、城乡差异与抑郁症状变化的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [7] | 袁雯,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,陈曼曼,刘婕妤,马涛,马奇,崔孟杰,郭桐君,王鑫鑫,董彦会,马军. 儿童青少年身体脂肪分布与抑郁和社交焦虑的关联:基于双能X线检测的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 429-435. |
| [8] | 张紫薇,花语蒙,刘爱萍. 中国中老年人群抑郁症状、缺血性心血管疾病10年风险对心血管疾病的联合影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 465-470. |
| [9] | 李志华,黄燕波,庞秋颖,于书慧,陈宇珂,李德润. 膀胱阴道瘘修补术后患者生存质量和心理状态调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 190-193. |
| [10] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [11] | 陆林,刘晓星,袁凯. 中国脑科学计划进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 791-795. |
| [12] | 王佳文,刘敬超,孟令峰,张威,刘晓东,张耀光. 间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征患者生活质量及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 653-658. |
| [13] | 耿研,宋志博,张晓慧,邓雪蓉,王昱,张卓莉. 银屑病关节炎抑郁和焦虑患病情况及相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1048-1055. |
| [14] | 王一帆,范稹,成姚斌,金月波,霍阳,何菁. 原发性干燥综合征患者睡眠障碍的相关影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1063-1068. |
| [15] | 易端,朱薇,孟秀丽,刘晓光,李水清,祝斌,贾东林. 慢性腰腿痛患者微创术前焦虑,抑郁状态及相关影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 285-289. |
|
||