北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 954-960. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.05.024
儿童直立不耐受和坐位不耐受的疾病谱及治疗方式十年回顾
崔雅茜1,杜军保1,2,张清友1,廖莹1,刘平1,王瑜丽1,齐建光1,闫辉1,徐文瑞1,刘雪芹1,孙燕1,孙楚凡1,张春雨1,陈永红1,金红芳1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院儿科, 北京 100034
2. 教育部分子心血管学重点实验室, 北京 100191
A 10-year retrospective analysis of spectrums and treatment options of orthostatic intolerance and sitting intolerance in children
Ya-xi CUI1,Jun-bao DU1,2,Qing-you ZHANG1,Ying LIAO1,Ping LIU1,Yu-li WANG1,Jian-guang QI1,Hui YAN1,Wen-rui XU1,Xue-qin LIU1,Yan SUN1,Chu-fan SUN1,Chun-yu ZHANG1,Yong-hong CHEN1,Hong-fang JIN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatrics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Key Laboratory of Molecular Cardiovascular Sciences, Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
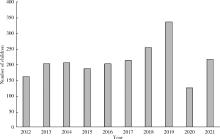
目的: 分析儿童直立不耐受(orthostatic intolerance, OI)和坐位不耐受(sitting intolerance, SI)的基础疾病谱, 并了解其在临床上采用的经验性治疗方式。方法: 选择北京大学第一医院儿科2012年1月至2021年12月十年期间所有患儿的病例资料(包括病史、体格检查、实验室检查和影像学检查)进行回顾性分析, 将符合OI和SI诊断标准的患儿纳入研究, 分析患儿OI和SI的基础疾病谱, 并总结分析其治疗方式。结果: 共纳入OI和SI病例资料2 110例, 其中男943例(44.69%), 女1 167例(55.31%), 年龄4~18岁, 平均(11.34±2.84)岁。十年间总体OI和SI患儿例数呈逐渐增多趋势。OI疾病谱中占比最高的是体位性心动过速综合征(postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, POTS), 共826例(39.15%); 其次为血管迷走性晕厥(vasovagal syncope, VVS), 共634例(30.05%)。而SI疾病谱中占比最高的是坐位性心动过速综合征(sitting tachycardia syndrome, STS), 共8例(0.38%); 其次为坐位性高血压(sitting hypertension, SHT) 2例(0.09%); 此外, OI和SI合并疾病中占比最多的是POTS合并STS, 共36例(1.71%)。在OI和SI治疗方式中, 主要为自主神经功能锻炼757例(35.88%), 其次为口服补液盐(oral rehydration salts, ORS) 687例(32.56%), 美托洛尔307例(14.55%), 盐酸米多君142例(6.73%), ORS联合美托洛尔138例(6.54%)和ORS联合盐酸米多君79例(3.74%)。POTS合并VVS的患儿相对于POTS或VVS患儿, 接受药物治疗者更多(41.95% vs. 30.51% vs. 28.08%, χ2= 20.319, P < 0.01), 而POTS和VVS患儿的药物治疗占比没有统计学差异。结论: 儿童POTS及VVS是OI的主要基础疾病, SI是近年来新发现的疾病。OI和SI患儿的人数整体呈逐渐增加的趋势, 其主要治疗方式为自主神经功能锻炼和口服ORS。POTS合并VVS的患儿相对于单纯POTS或VVS患儿, 更倾向于接受药物治疗。
中图分类号:
- R725
| 1 |
魏红芳, 董湘玉, 肖要. 儿童直立不耐受与微观营养素和体质指数相关性研究进展[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2019, 14 (6): 473.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2019.06.017 |
| 2 |
Anderson JB , Willis M , Lancaster H , et al. The evaluation and management of pediatric syncope[J]. Pediatr Neurol, 2016, 55, 6- 13.
doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2015.10.018 |
| 3 | Jug J , Lovrić Benčić M , Bradić L , et al. Depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with syncope[J]. Psychiatr Danub, 2020, 32 (3/4): 442- 443. |
| 4 |
Kara A , Doǧan MT . The psychopathology, depression, and anxiety levels of children and adolescents with vasovagal syncope: A case-control study[J]. J Nerv Ment Dis, 2021, 209 (8): 547- 551.
doi: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000001334 |
| 5 |
Zhao J , Han Z , Zhang X , et al. A cross-sectional study on upright heart rate and BP changing characteristics: Basic data for estab-lishing diagnosis of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome and orthostatic hypertension[J]. BMJ open, 2015, 5 (6): e007356.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007356 |
| 6 |
Lin J , Wang Y , Ochs T , et al. Tilt angles and positive response of head-up tilt test in children with orthostatic intolerance[J]. Cardiol Young, 2015, 25 (1): 76- 80.
doi: 10.1017/S1047951113001601 |
| 7 | 尚丽丽, 彭宇阁, 刘佳, 等. 直立倾斜试验在儿童不明原因晕厥诊断中的应用[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2019, 22 (18): 2026- 2031. |
| 8 |
王利平, 杜忠东, 柴晓敏, 等. 舌下含服硝酸甘油直立倾斜试验对儿童血管迷走性晕厥的诊断价值[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2006, 24 (5): 364- 366.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3606.2006.05.007 |
| 9 |
张清友, 杜军保, 李万镇. 舌下含化硝酸甘油直立倾斜试验对儿童不明原因晕厥的诊断研究[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2004, 42 (5): 371- 374.
doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0578-1310.2004.05.016 |
| 10 |
Tao C , Han Z , Yan Y , et al. Sitting-induced hemodynamic changes and association with sitting intolerance in children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10 (1): 13921.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70925-y |
| 11 |
Wang C , Li Y , Liao Y , et al. 2018 Chinese pediatric cardiology society (CPCS) guideline for diagnosis and treatment of syncope in children and adolescents[J]. Sci Bull, 2018, 63 (23): 1558- 1564.
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.09.019 |
| 12 |
宋婧媛, 王圆圆, 李红霞, 等. 儿童血管迷走性晕厥发病机制研究进展[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2018, 33 (6): 478- 480.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-428X.2018.06.020 |
| 13 |
Magkas N , Tsioufis C , Thomopoulos C , et al. Orthostatic hypotension: From pathophysiology to clinical applications and therapeutic considerations[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2019, 21 (5): 546- 554.
doi: 10.1111/jch.13521 |
| 14 |
Zhang Q , Li J , Xie Y , et al. Orthostatic hypertension in children and adolescents with postural tachycardia syndrome[J]. J Trop Pediatr, 2014, 60 (6): 461- 466.
doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmu055 |
| 15 |
Brignole M , Moya A , de Lange FJ , et al. 2018 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39 (21): 1883- 1948.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy037 |
| 16 | 蔺婧, 王瑜丽, 张清友, 等. 儿童青少年晕厥疾病谱近30年变化及卫生经济学分析单中心报告[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2016, 31 (5): 350- 355. |
| 17 |
杜军保, 李万镇. 基础直立倾斜试验对儿童不明原因晕厥的诊断研究[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 1997, 35 (6): 309- 312.
doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0578-1310.1997.06.008 |
| 18 |
张清友, 杜军保, 李万镇. 儿童体位性心动过速综合征的临床特征及随访研究[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2005, 43 (3): 165- 169.
doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0578-1310.2005.03.002 |
| 19 | 钟睛. 儿童直立不耐受559例临床分析[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019. |
| 20 |
Cai H , Wang S , Zou R , et al. Comparison of the active sitting test and head-up tilt test for diagnosis of postural tachycardia syndrome in children and adolescents[J]. Front Pediatr, 2021, 9, 691390.
doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.691390 |
| 21 |
Kanjwal K , Sheikh M , Karabin B , et al. Neurocardiogenic syncope coexisting with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in patients suffering from orthostatic intolerance: A combined form of autonomic dysfunction[J]. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 2011, 34 (5): 549- 554.
doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2010.02994.x |
| 22 |
Tao C , Jin H , Du J . Management of orthostatic intolerance in children: the state of the art[J]. World J Pediatr, 2020, 16 (6): 543- 548.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00329-0 |
| 23 |
Kaufmann H , Norcliffe-Kaufmann L , Palma JA . Baroreflex dysfunction[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382 (2): 163- 178.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1509723 |
| 24 |
Iacoviello M , Guida P , Forleo C , et al. Impaired arterial baroreflex function before nitrate-induced vasovagal syncope during head-up tilt test[J]. Europace, 2008, 10 (10): 1170- 1175.
doi: 10.1093/europace/eun217 |
| 25 | 肖要, 张小华, 魏红芳, 等. 儿童直立不耐受发病机制研究进展[J]. 兰州大学学报(医学版), 2021, 47 (6): 82- 88. |
| 26 |
Mitro P , Mudráková K , Micková H , et al. Hemodynamic parameters and heart rate variability during a tilt test in relation to gene polymorphism of renin-angiotensin and serotonin system[J]. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 2008, 31 (12): 1571- 1580.
doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.01228.x |
| 27 |
Stewart JM , Medow MS , Sutton R , et al. Mechanisms of vasovagal syncope in the young: reduced systemic vascular resistance versus reduced cardiac output[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2017, 6 (1): e004417.
doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004417 |
| 28 |
Bai W , Chen S , Jin H , et al. Vascular dysfunction of postural tachycardia syndrome in children[J]. World J Pediatr, 2018, 14 (1): 13- 17.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-017-0104-8 |
| 29 |
Mosqueda-Garcia R , Furlan R , Tank J , et al. The elusive pathophysiology of neurally mediated syncope[J]. Circulation, 2000, 102 (23): 2898- 2906.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.23.2898 |
| 30 |
Liao Y , Du J . Pathophysiology and individualized management of vasovagal syncope and postural tachycardia syndrome in children and adolescents: An update[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2020, 36 (6): 667- 681.
doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00497-4 |
| [1] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [2] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [4] | 费秀文,刘斯,汪波,董爱梅. 成人及儿童组织坏死性淋巴结炎临床特征及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [5] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [6] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | 弭小艺,侯杉杉,付子苑,周末,李昕璇,孟召学,蒋华芳,周虹. 中文版童年不良经历问卷在学龄前儿童父母中应用的信效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [8] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [9] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [10] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [11] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [12] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [13] | 马涛,李艳辉,陈曼曼,马莹,高迪,陈力,马奇,张奕,刘婕妤,王鑫鑫,董彦会,马军. 青春期启动提前与儿童肥胖类型的关联研究: 基于横断面调查和队列调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [14] | 杜燕燕,王健,贺兰,季丽娜,徐樨巍. 儿童川崎病合并轻微脑炎/脑病伴可逆性胼胝体压部病变综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [15] | 刘云飞,党佳佳,钟盼亮,马宁,师嫡,宋逸. 1990—2019年中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡率分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 498-504. |
|
||