北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1033-1038. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.012
新型血栓四项联合常规凝血指标预测抗磷脂综合征患者血栓形成的价值
洪丽荣1,2,陈雨佳2,江庆来2,贾汝琳1,*( ),李春1,冯亮华2,*(
),李春1,冯亮华2,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
2. 厦门市第五医院风湿免疫科, 福建厦门 361101
Predictive value of four items of new thrombus markers combined with conventional coagulation tests for thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome
Li-rong HONG1,2,Yu-jia CHEN2,Qing-lai JIANG2,Ru-lin JIA1,*( ),Chun LI1,Liang-hua FENG2,*(
),Chun LI1,Liang-hua FENG2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Xiamen Fifth Hospital Rheumatology Department, Xiamen 361101, Fujian, China
摘要:
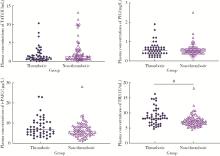
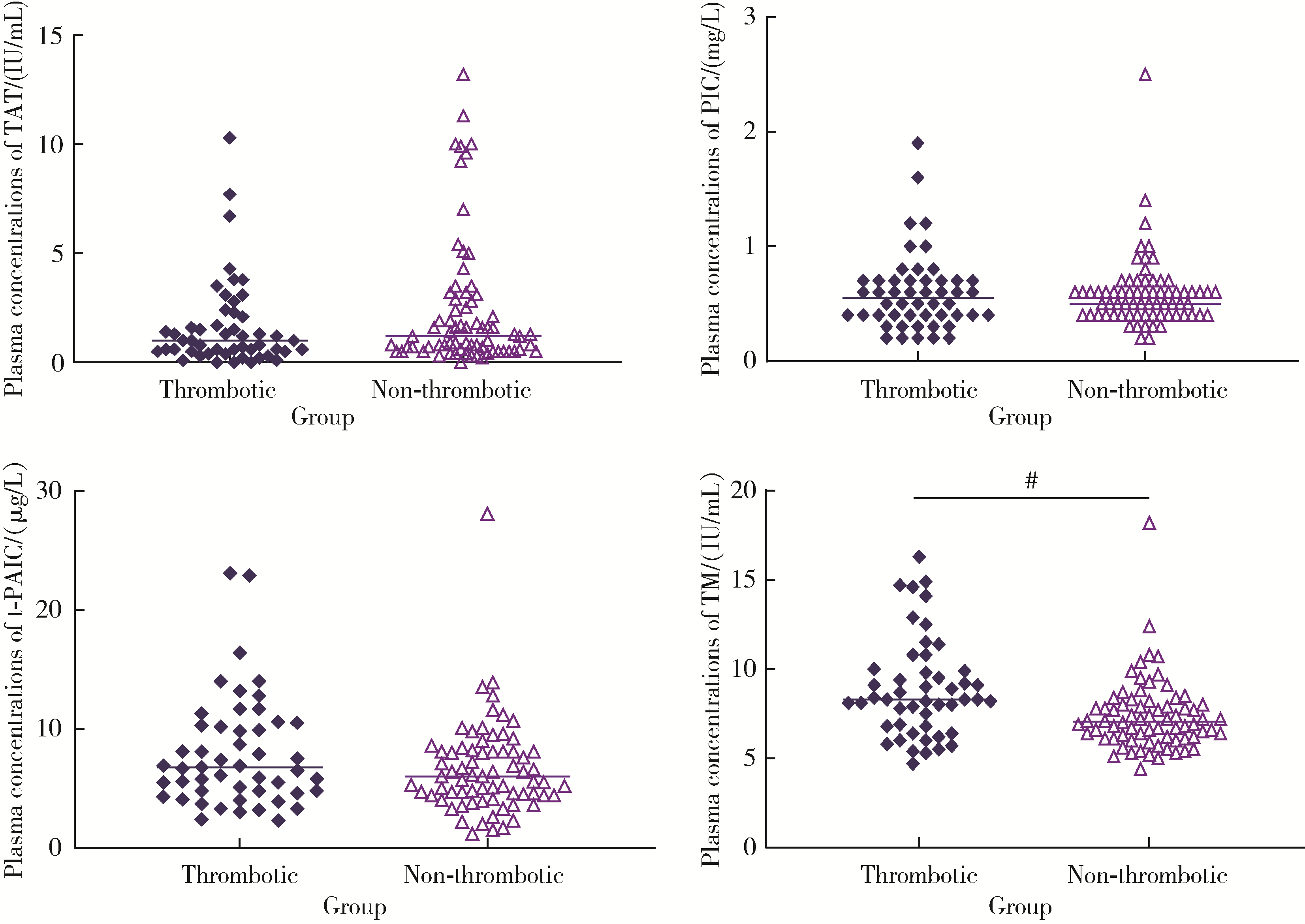
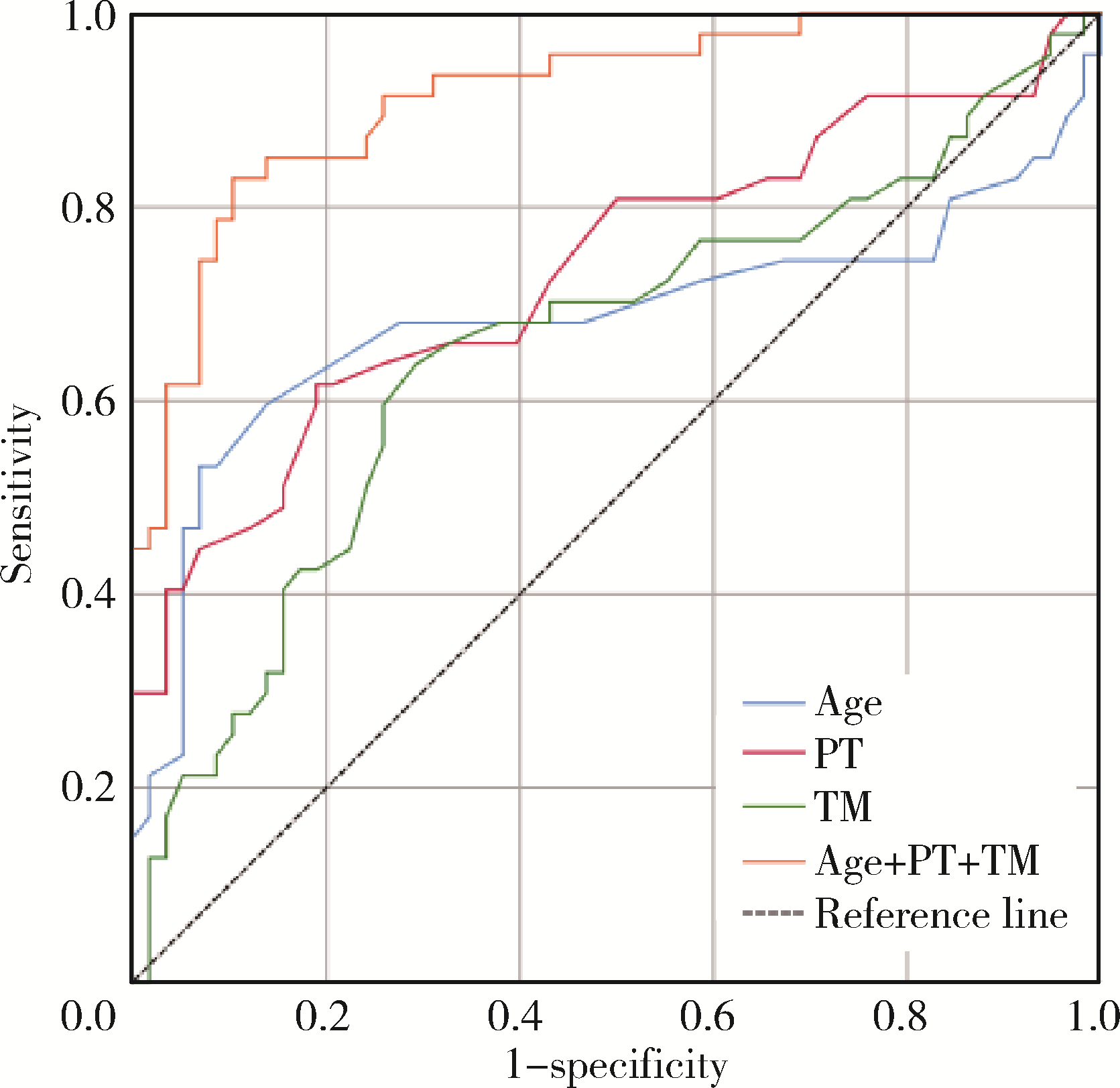
目的: 探讨新型血栓四项联合常规凝血指标在预测抗磷脂综合征(antiphospholipid syndrome, APS)患者血栓形成的早期诊断价值。方法: 选择2022年3月至2023年1月北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科就诊的APS患者121例进行回顾性分析,根据是否发生血栓将患者分为血栓组(50例)和非血栓组(71例)。比较血栓组和非血栓组患者包括抗磷脂抗体(antiphospholipid antibodies,aPL)在内的实验室指标的差异,采用化学发光免疫分析法检测其静脉血浆中新型血栓四项[包括凝血酶调节蛋白抗原(thrombomodulin,TM)、凝血酶抗凝血酶复合物(thrombin-antithrombin complex,TAT)、血浆纤溶酶抗纤溶酶复合物(plasmin-α2 plasmin inhibitor complex,PIC)、组织纤溶酶原激活物抑制物复合物(tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor complex,t-PAIC)]水平。通过二元Logistic回归分析,筛选APS患者血栓发生的独立危险因素,应用受试者工作特征(receiver operator characteristic, ROC)曲线分析评估各指标预测血栓风险的效能。结果: 血栓组APS患者年龄显著高于非血栓组APS患者[49(32, 64)岁vs. 36(32, 39)岁,P < 0.05],血栓组APS患者中男性、吸烟、高血压、全面抗磷脂综合征评分(global antiphospholipid syndrome score,GAPSS)≥10分的比例均高于非血栓组APS患者(P均 < 0.05)。血栓组APS患者中抗心磷脂抗体(anticardiolipin antibcdy, aCL)、狼疮抗凝物(lupus anticoagulant, LA)阳性率更高(P均 < 0.05),凝血酶原时间(prothrombin time,PT)、活化部分凝血活酶时间(activated partial thromboplastin time,APTT)、纤维蛋白原降解产物(fibrin degradation product,FDP)水平更高(P均 < 0.05)。血栓组静脉血栓19例(38.00%),其中深静脉血栓16例(84.21%),肺栓塞5例(26.32%);动脉血栓35例(70.00%),其中心肌梗死6例(17.14%),脑梗死30例(85.71%)。血栓组患者的TM水平明显大于非血栓组(P<0.05),两组间TAT(Z=-1.420,P=0.156)、PIC(Z=-0.064,P=0.949)和t-PAIC(Z=-1.487,P=0.137)血浆浓度差异无统计学意义。对相关变量进行单因素及二元Logistic回归分析,发现高龄[OR=1.126,P=0.002]、TM升高[OR=1.325,P=0.048]、PT延长[OR=4.127,P=0.008]是APS患者血栓形成的独立危险因素,对上述3个独立危险因素进行ROC曲线分析,发现年龄、PT、TM三项联合检测对APS血栓形成的诊断性能最佳[AUC为0.916(0.862, 0.969)],具有最高的约登(Youden)指数(0.727)和敏感性(83.0%),特异性为89.7%。结论: TAT、PIC、TM和t-PAIC可以从凝血系统、纤溶系统和内皮系统反映血栓形成。TM、PT联合年龄优于单一标志物的应用,对APS血栓形成的早期识别具有诊断价值。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Miyakis S , Lockshin MD , Atsumi T , et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2006, 4 (2): 295- 306.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01753.x |
| 2 |
Galli M , Luciani D , Bertolini G , et al. Anti-β2-glycoprotein Ⅰ, antiprothrombin antibodies, and the risk of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. Blood, 2003, 102 (8): 2717- 2723.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-11-3334 |
| 3 |
Cervera R , Serrano R , Pons-Estel GJ , et al. Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: A multicentre prospective study of 1 000 patients[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015, 74 (6): 1011- 1018.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204838 |
| 4 | 徐文龙, 沙宇. 血栓分子标志物联合Caprini评分预测创伤性下肢骨折后深静脉血栓形成风险研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2023, 33 (2): 245-248, 257. |
| 5 | Zhao X , Yang S , Lei R , et al. Clinical study on the feasibility of new thrombus markers in predicting massive cerebral infarction[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13, 942887. |
| 6 |
Tonello M , Mattia E , Favaro M , et al. IgG phosphatidylserine/prothrombin antibodies as a risk factor of thrombosis in antiphospholipid antibody carriers[J]. Thromb Res, 2019, 177, 157- 160.
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2019.03.006 |
| 7 |
Schaller J , Gerber SS . The plasmin-antiplasmin system: structural and functional aspects[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2011, 68 (5): 785- 801.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0566-5 |
| 8 |
Salet DM , Bekkering S , Middeldorp S , et al. Targeting thromboinflammation in antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2023, 21 (4): 744- 757.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2022.12.002 |
| 9 | Zhou K , Zhang J , Zheng ZR , et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of TAT, PIC, TM, and t-PAIC in malignant tumor patients with venous thrombosis[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2020, 26, 1- 10. |
| 10 |
Wang L , Zhong J , Xiao D , et al. Thrombomodulin (TM), thrombin-antithrombin complex (TAT), plasmin-α2-plasmininhibitor complex (PIC), and tissue plasminogen activator-inhibitor complex (t-PAIC) assessment of fibrinolytic activity in postpartum hemorrhage: A retrospective comparative cohort study[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10 (23): 1273.
doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5221 |
| 11 |
Loghmani H , Conway EM . Exploring traditional and nontraditional roles for thrombomodulin[J]. Blood, 2018, 132 (2): 148- 158.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-768994 |
| 12 | Pletsch-Borba L , Grafetstatter M , Husing A , et al. Vascular injury biomarkers and stroke risk: A population-based study[J]. Neurology, 2020, 94 (22): e2337- e2345. |
| 13 |
Kamtchum-Tatuene J , Mwangalika Kachingwe G , Mwandumba HC , et al. Endothelial dysfunction and carotid atherosclerosis in Malawian adults: A cross-sectional study[J]. eNeurologicalSci, 2020, 20, 100252.
doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100252 |
| 14 | Gosselin RC . An acute need inspiration: Autoneutralization of lupus anticoagulants in affected prothrombin times (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin times (APTT)[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2023, 2663, 289- 295. |
| 15 | Fei Y , Tang N , Zhang H , et al. Significantly prolonged prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time with no bleeding tendency: A patient with lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia syndrome positive for immunoglobulin M anti-phosphatidylserine/prothrombin complex antibodies[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2020, 46 (4): 507- 511. |
| 16 | Erzen B , Sabovic M . In young post-myocardial infarction male patients elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 correlates with insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction[J]. Heart Vessels, 2013, 28 (5): 570- 577. |
| 17 | Nordenhem A , Leander K , Hallqvist J , et al. The complex between tPA and PAI-1: Risk factor for myocardial infarction as studied in the SHEEP project[J]. Thromb Res, 2005, 116 (3): 223- 232. |
| 18 | Winter MP , Kleber ME , Koller L , et al. Prognostic significance of tPA/PAI-1 complex in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2017, 117 (3): 471- 478. |
| 19 | Lundbech M , Krag AE , Christensen TD , et al. Thrombin generation, thrombin-antithrombin complex, and prothrombin fragment F1+2 as biomarkers for hypercoagulability in cancer patients[J]. Thromb Res, 2020, 186, 80- 85. |
| 20 | Tao J , Guo X , Li D , et al. Increased level of thrombomodulin is associated with endothelial injury in patients with sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation[J]. Clin Lab, 2021, 67 (8): 1863- 1870. |
| 21 | Asanuma K , Nakamura T , Okamoto T , et al. Do coagulation or fibrinolysis reflect the disease condition in patients with soft tissue sarcoma[J]. BMC cancer, 2022, 22 (1): 1075. |
| 22 | Guo X , Tao H , Li D , et al. The α2-plasmin inhibitor-plasmin complex is a potential biomarker of venous thromboembolism in orthopedic trauma patients[J]. Clin Lab, 2021, 67 (4): 1065- 1072. |
| [1] | 卢情怡,艾尼扎提·哈斯木,李宇菲,李春. 抗神经酰胺抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的分布及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1139-1143. |
| [2] | 侯玉珂,蔡青猛,刘香君,贠泽霖,李春,张学武. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1117-1122. |
| [3] | 王玉华,张国华,张令令,罗俊丽,高兰. 系统性红斑狼疮合并自发性肾上腺出血1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1178-1181. |
| [4] | 顾婕昱,陆翠,石慧,杨程德. 14例恶性抗磷脂综合征病例报道及临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1033-1038. |
| [5] | 李记,郑莉,石连杰,徐婧,舒建龙,张学武. 可溶性内皮糖蛋白在抗磷脂综合征患者的血清水平及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1027-1032. |
| [6] | 郑晓娟, 邓晓莉, 刘湘源. 54例抗磷脂综合征患者的妊娠结局[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 323-328. |
| [7] | 李茹*, 周云杉*, 贾园, 栗占国. 抗磷脂综合征患者血栓事件的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 788-791. |
|
||