北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 17-24. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.004
不同种类聚合物对猪小肠黏膜下层支架仿生矿化的影响
陈晓颖1,张一2,李雨柯1,唐琳1,*( ),刘玉华1,*(
),刘玉华1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院修复科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院综合二科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Effects of different polymers on biomimetic mineralization of small intestine submucosal scaffolds
Xiaoying CHEN1,Yi ZHANG2,Yuke LI1,Lin TANG1,*( ),Yuhua LIU1,*(
),Yuhua LIU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of General Dentistry Ⅱ, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
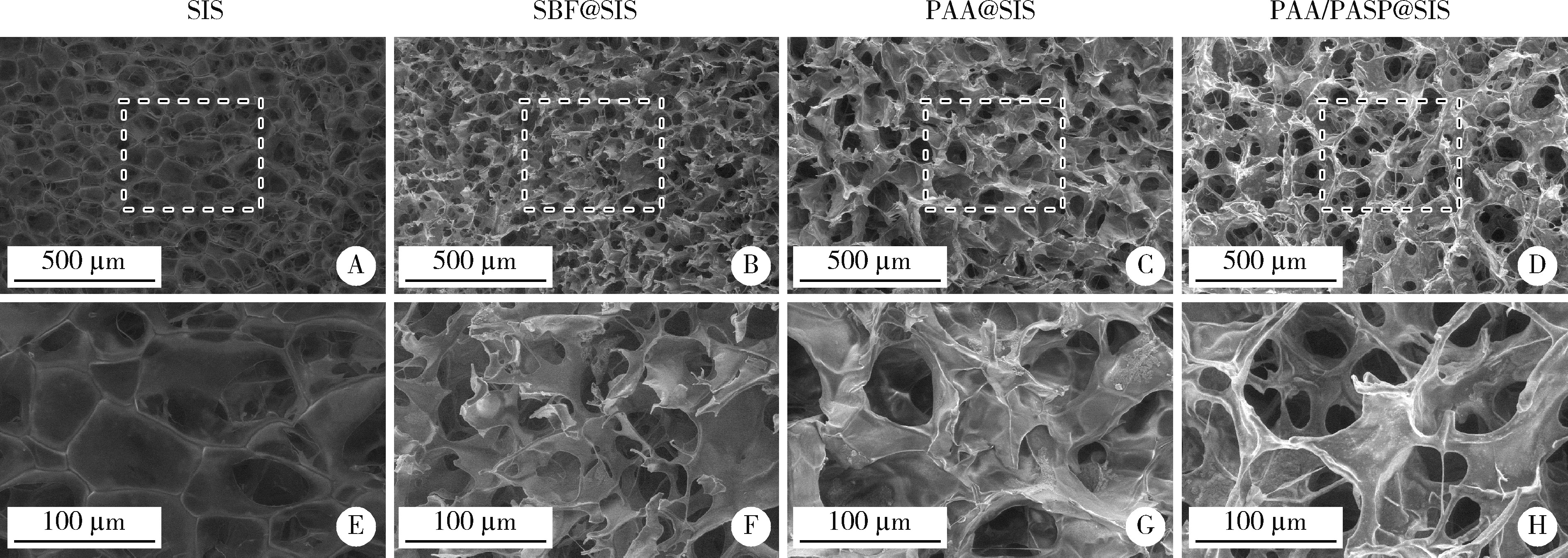
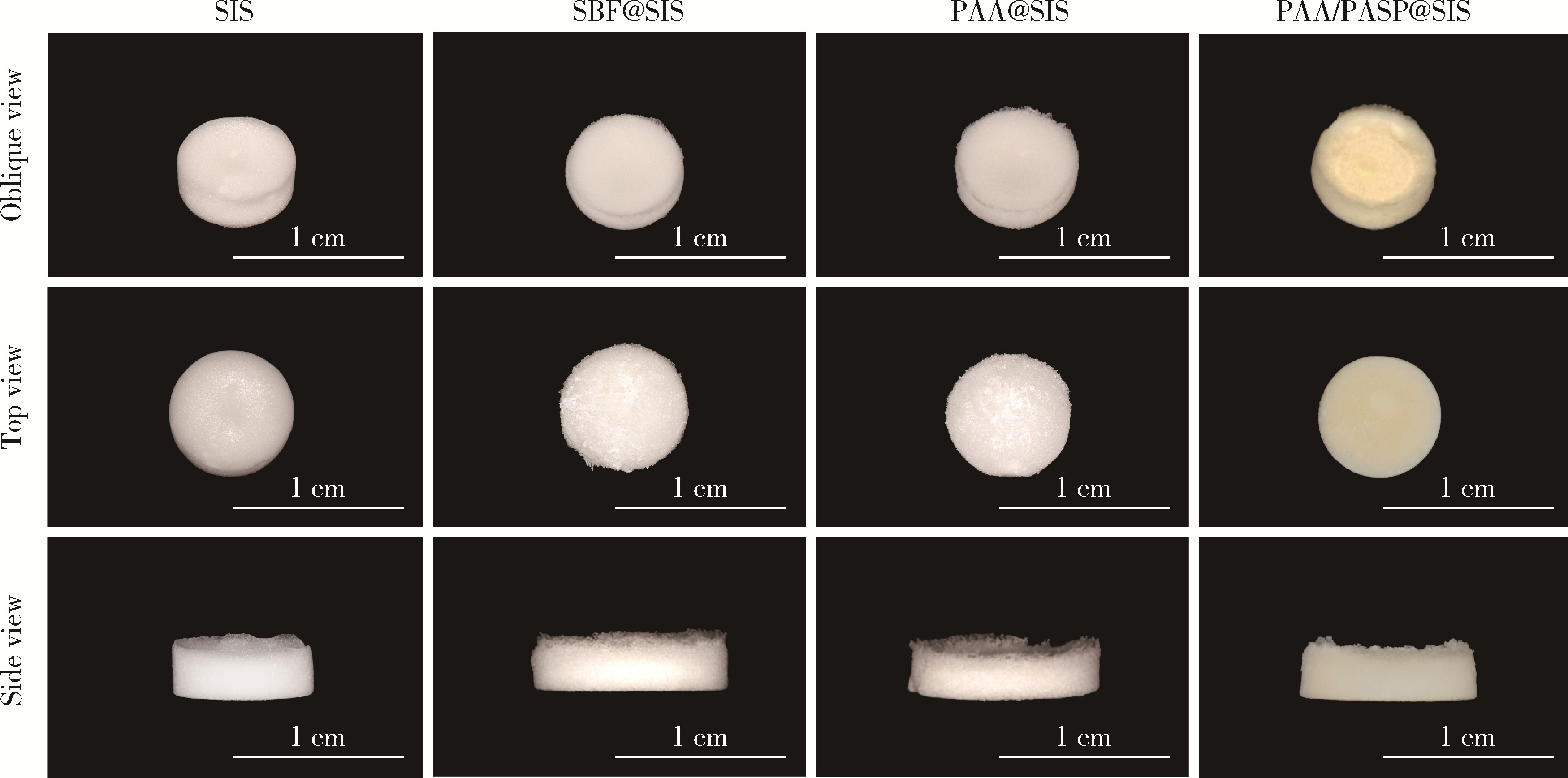
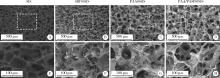
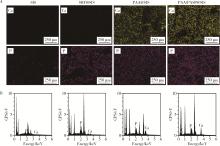
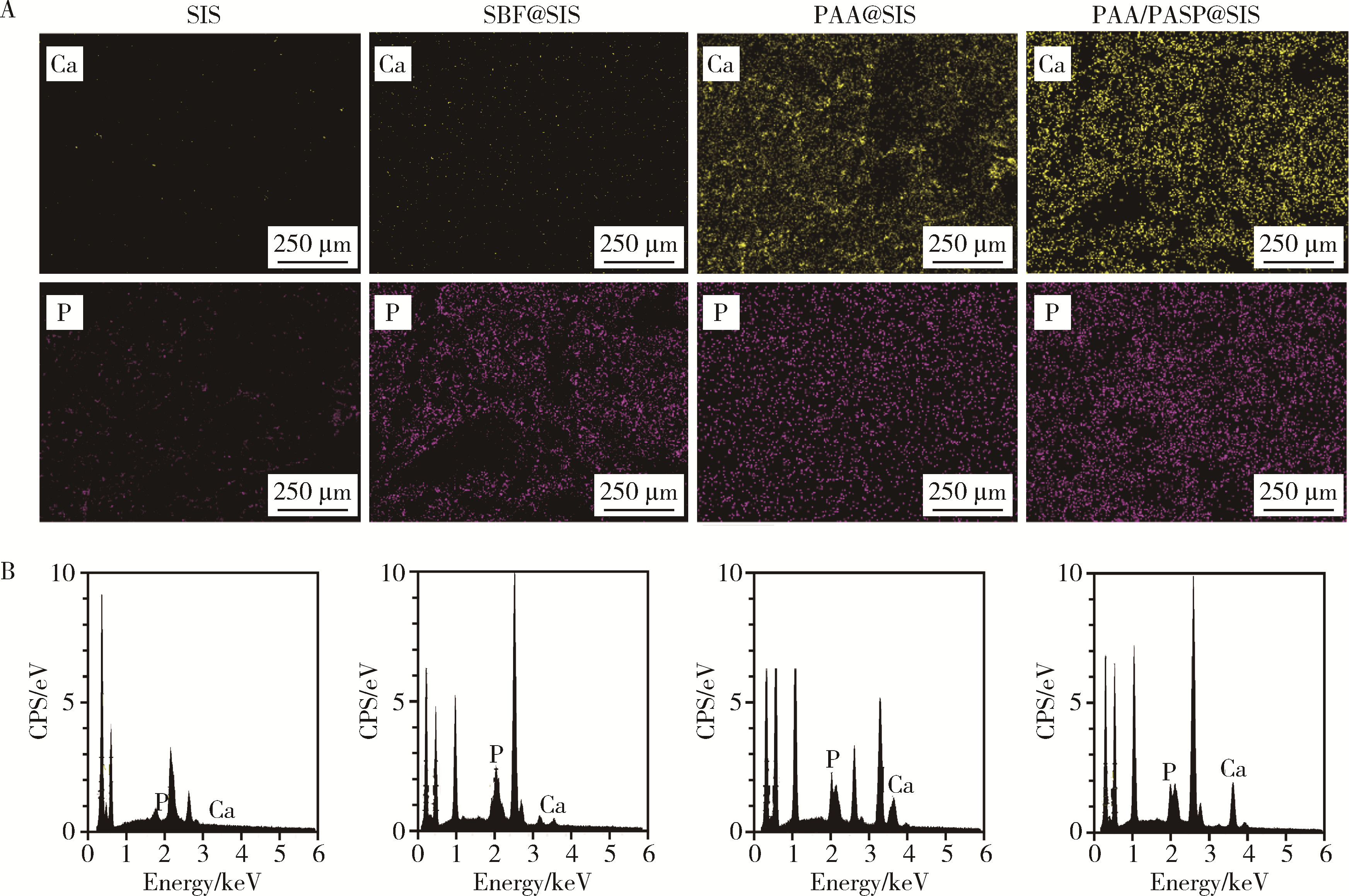
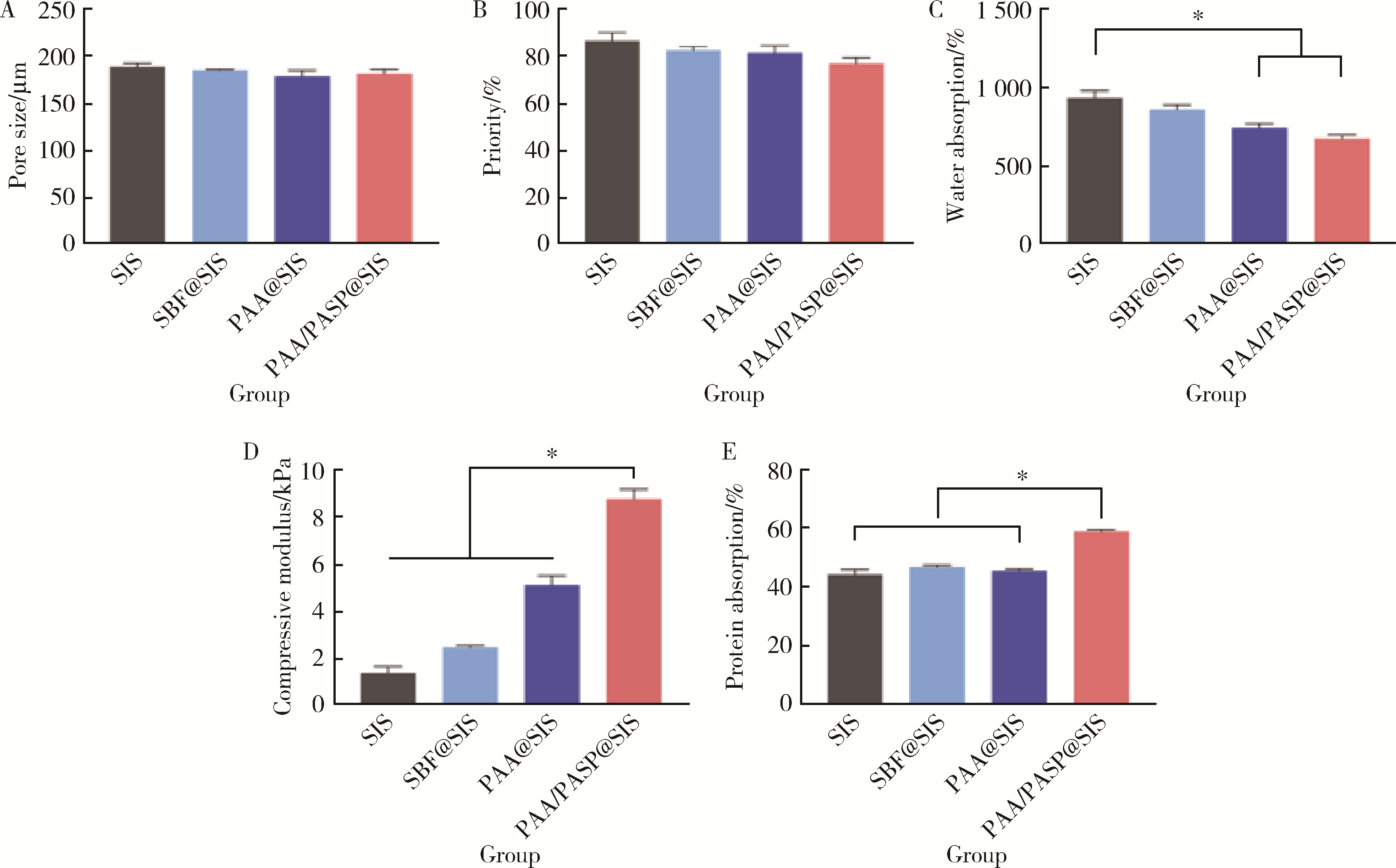
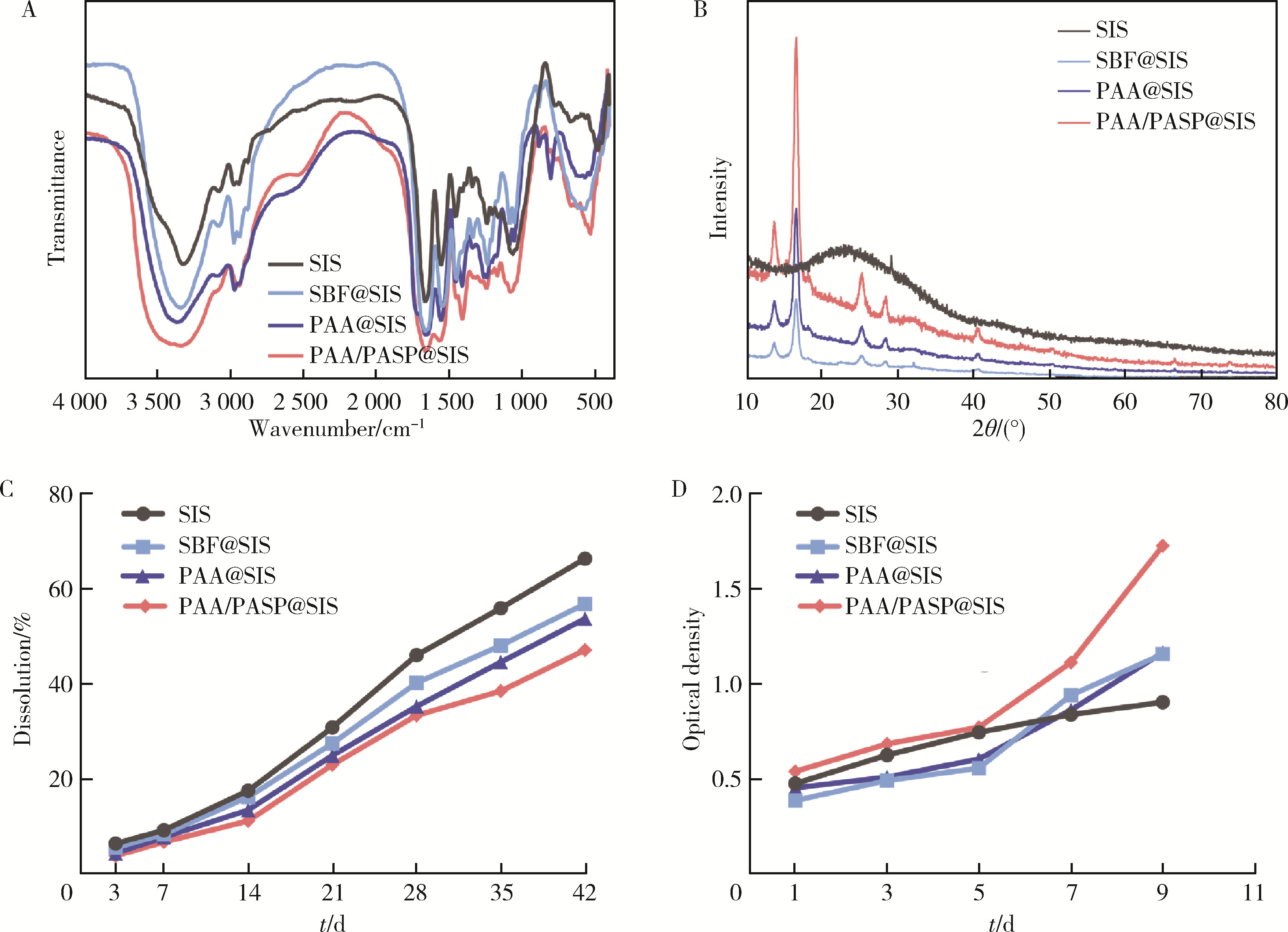
目的: 探究不同种类的聚合物对脱细胞猪小肠黏膜下层(small intestinal submucosa,SIS)支架体外仿生矿化的影响,并基于理化性能和生物相容性指标评价各组SIS矿化支架。方法: 将冷冻干燥法制备而成的SIS支架分别浸泡在模拟体液(simulated body fluid,SBF)、含聚丙烯酸(polyacrylic acid,PAA)的矿化液和同时含PAA和聚天冬氨酸(polyaspartic acid,PASP)的矿化液中持续2周,隔天换液,依次得到SBF@SIS、PAA@SIS、PAA/PASP@SIS支架,以未矿化的SIS支架为对照组,评价上述支架的理化性能及生物相容性。结果: 环境扫描电子显微镜(environment scanning electron microscopy,ESEM)下各组支架均呈适宜孔径的三维多孔结构,各组矿化支架均可见晶体附着,其中以PAA/PASP@SIS支架晶体沉积更为规则,同时可见胶原纤维增粗。能谱分析显示,3组矿化支架均可见钙、磷元素的特征峰,以PAA/PASP@SIS支架峰值最高;傅里叶变换红外光谱分析证实,3组矿化支架均实现了羟基磷灰石与SIS结合;各组支架均具有良好的亲水性;3组矿化支架压缩强度均高于对照组,以PAA/PASP@SIS支架压缩强度最优;各组支架均能有效吸附蛋白,以PAA/PASP@SIS组吸附能力最佳。CCK-8细胞增殖实验(周期为1、3、5、7、9 d)中,PAA/PASP@SIS组展现出最佳的促细胞增殖能力。结论: 经同时含PAA和PASP的矿化液制备的PAA/PASP@SIS支架与其他矿化支架相比具有更优的理化性能和生物相容性,具有骨组织工程应用的潜能。
中图分类号:
- R318
| 1 |
Qu H , Fu H , Han Z , et al. Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering scaffolds: A review[J]. RSC Adv, 2019, 9 (45): 26252- 26262.
doi: 10.1039/C9RA05214C |
| 2 |
Langer R , Vacanti JP . Tissue engineering[J]. Science, 1993, 260 (5110): 920- 926.
doi: 10.1126/science.8493529 |
| 3 |
Asti A , Gioglio L . Natural and synthetic biodegradable polymers: Different scaffolds for cell expansion and tissue formation[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2014, 37 (3): 187- 205.
doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000307 |
| 4 | Turnbull G , Clarke J , Picard F , et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Bioact Mater, 2018, 3 (3): 278- 314. |
| 5 | Saravanan S , Leena RS , Selvamurugan N . Chitosan based biocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2016, 93 (Pt B): 1354- 1365. |
| 6 |
Zhao J , Lu X , Duan K , et al. Improving mechanical and biological properties of macroporous HA scaffolds through composite coatings[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2009, 74 (1): 159- 166.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.07.012 |
| 7 |
Bian T , Zhao K , Meng Q , et al. The construction and perfor-mance of multi-level hierarchical hydroxyapatite (HA)/collagen composite implant based on biomimetic bone Haversian motif[J]. Mater Des, 2019, 162, 60- 69.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.11.040 |
| 8 |
Ye Z , Qi Y , Zhang A , et al. Biomimetic mineralization of fibrillar collagen with strontium-doped hydroxyapatite[J]. ACS Macro Lett, 2023, 12 (3): 408- 414.
doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.3c00039 |
| 9 | Kato T , Suzuki T , Amamiya T , et al. Effects of macromolecules on the crystallization of CaCO3 the formation of organic/inorganic composites[J]. Supramol Sci, 1998, 5 (3): 411- 415. |
| 10 |
Aizenberg J , Addadi L , Weiner S , et al. Stabilization of amorphous calcium carbonate by specialized macromolecules in biological and synthetic precipitates[J]. Adv Mater, 1996, 8 (3): 222- 226.
doi: 10.1002/adma.19960080307 |
| 11 |
Nudelman F , Lausch A , Sommerdijk N , et al. In vitro models of collagen biominerallization[J]. J Struct Biol, 2013, 183 (2): 258- 269.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2013.04.003 |
| 12 | Gower LA , Tirrell DA . Calcium carbonate films and helices grown in solutions of poly(aspartate)[J]. J Cryst Growth, 1998, 191 (1): 153- 160. |
| 13 |
Dai L , Qi Y , Niu L , et al. Inorganic-organic nanocomposite assembly using collagen as a template and sodium tripolyphosphate as a biomimetic analog of matrix phosphoprotein[J]. Cryst Growth Des, 2011, 11 (8): 3504- 3511.
doi: 10.1021/cg200663v |
| 14 | 龚春玲, 陈飞扬, 卜寿山, 等. 仿生矿化前后静电纺复合支架的性能对比[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 40 (5): 748- 753. |
| 15 |
Öfkeli F , Demir D , Bölgen N . Biomimetic mineralization of chitosan/gelatin cryogels and in vivo biocompatibility assessments for bone tissue engineering[J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2021, 138 (14): e50337.
doi: 10.1002/app.50337 |
| 16 |
El-Fiqi A , Kim JK , Kim HW . Novel bone-mimetic nanohydroxyapatite/collagen porous scaffolds biomimetically minera-lized from surface silanized mesoporous nanobioglass/collagen hybrid scaffold: Physicochemical, mechanical and in vivo evaluations[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2020, 110, 110660.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110660 |
| 17 |
Li B , Wang M , Liu Y , et al. Independent effects of structural optimization and resveratrol functionalization on extracellular matrix scaffolds for bone regeneration[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2022, 212, 112370.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112370 |
| 18 |
Wang M , Li B , Liu Y , et al. A novel bionic extracellular matrix polymer Scaffold enhanced by calcium silicate for bone tissue engineering[J]. ACS Omega, 2021, 6 (51): 35727- 35737.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05623 |
| 19 | Antoniac IV , Antoniac A , Vasile E , et al. In vitro characterization of novel nanostructured collagen-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds doped with magnesium with improved biodegradation rate for hard tissue regeneration[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6 (10): 3383- 3395. |
| 20 |
Saxena N , Mizels J , Cremer M , et al. Comparison of synthetic vs. biogenic polymeric process-directing agents for intrafibrillar mine-ralization of collagen[J]. Polymers (Basel), 2022, 14 (4): 775.
doi: 10.3390/polym14040775 |
| 21 |
Bharadwaz A , Jayasuriya AC . Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2020, 110, 110698.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110698 |
| 22 |
Chandika P , Ko SC , Oh GW , et al. Fish collagen/alginate/chitooligosaccharides integrated scaffold for skin tissue regeneration application[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2015, 81, 504- 513.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.038 |
| 23 |
Oosterlaken BM , Vena MP , de With G . In vitro mineralization of collagen[J]. Adv Mater, 2021, 33 (16): e2004418.
doi: 10.1002/adma.202004418 |
| 24 |
Du T , Niu Y , Liu Y , et al. Physical and chemical characterization of biomineralized collagen with different microstructures[J]. J Funct Biomater, 2022, 13 (2): 57.
doi: 10.3390/jfb13020057 |
| 25 |
Yuwono LA , Siswanto , Sari M , et al. Fabrication and characte-rization of hydroxyapatite-polycaprolactone-collagen bone scaffold by electrospun nanofiber[J]. Int J Polym Mater, 2023, 72 (16): 1281- 1293.
doi: 10.1080/00914037.2022.2097675 |
| 26 | Guo M , Pegoraro AF , Mao A , et al. Cell volume change through water efflux impacts cell stiffness and stem cell fate[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114 (41): E8618- E8627. |
| 27 | Tang L , Chen X , Wang M , et al. A biomimetic in situ mineralization ECM composite scaffold to promote endogenous bone regeneration[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2023, 232, 113587. |
| [1] | 潘媛,顾航,肖涵,赵笠君,汤祎熳,葛雯姝. 泛素特异性蛋白酶42调节人脂肪干细胞成骨向分化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 9-16. |
| [2] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [3] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [4] | 蓝璘,贺洋,安金刚,张益. 颧骨缺损不同修复重建方法和预后的回顾性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 356-362. |
| [5] | 敖英芳,曹宸喜. 解析与重塑软骨组织修复再生微环境[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 819-822. |
| [6] | 黄丽东,宫玮玉,董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖及成血管的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 371-377. |
| [7] | 王梅, 李博文, 王思雯, 刘玉华. 猪小肠黏膜下层海绵的制备及促成骨作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 952-958. |
| [8] | 吴唯伊,李博文,刘玉华,王新知. 复层猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜的降解性能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 564-569. |
| [9] | 李博文,吴唯伊,唐琳,张一,刘玉华. 改良猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜在兔下颌骨缺损早期愈合中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 887-892. |
| [10] | 梁晨,张维宇,胡浩,王起,方志伟,许克新. 膀胱扩大术两种不同术式的疗效及并发症比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 293-297. |
| [11] | 李榕,陈科龙,王勇,刘云松,周永胜,孙玉春. 骨组织工程支架3D打印系统的建立与支架宏微结构精度的可控性评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 115-119. |
| [12] | 王子成,程立,吕同德,苏黎,林健,周利群. 炎症因子预处理的脂肪干细胞可明显抑制外周血单个核细胞增殖[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 590-594. |
| [13] | 宫玮玉,刘绍清,董艳梅,高学军,陈晓峰. 纳米生物活性玻璃促进兔颅骨临界骨缺损修复[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 42-48. |
| [14] | 隋华欣, 吕培军, 王宇光, 王勇, 孙玉春. 低能量激光照射对人脂肪基质细胞增殖分化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 337-343. |
| [15] | 姜蔚然,张晓,刘云松,吴刚,葛严军,周永胜. 骨形态发生蛋白-2-磷酸钙共沉淀支架与人脂肪间充质干细胞构建新型组织工程化骨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 6-015. |
|
||