北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 348-354. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.020
熔融沉积成型3D打印盐酸维拉帕米胃漂浮制剂的制备与体外评价
陈迪1,徐翔宇2,汪明睿1,李芮1,臧根奥2,张悦1,钱浩楠1,闫光荣2,Δ( ),范田园1,Δ(
),范田园1,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学药学院药剂学系,北京大学药学院分子药剂学与新释药系统北京市重点实验室, 北京 100191
2.北京航空航天大学机械工程及自动化学院, 北京 100191
Preparation and in vitro evaluation of fused deposition modeling 3D printed verapa-mil hydrochloride gastric floating formulations
CHEN Di1,XU Xiang-yu2,WANG Ming-rui1,LI Rui1,ZANG Gen-ao2,ZHANG Yue1,QIAN Hao-nan1,YAN Guang-rong2,Δ( ),FAN Tian-yuan1,Δ(
),FAN Tian-yuan1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Pharmaceutics, Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Pharmaceutics and New Drug Delivery Systems, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
2. School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
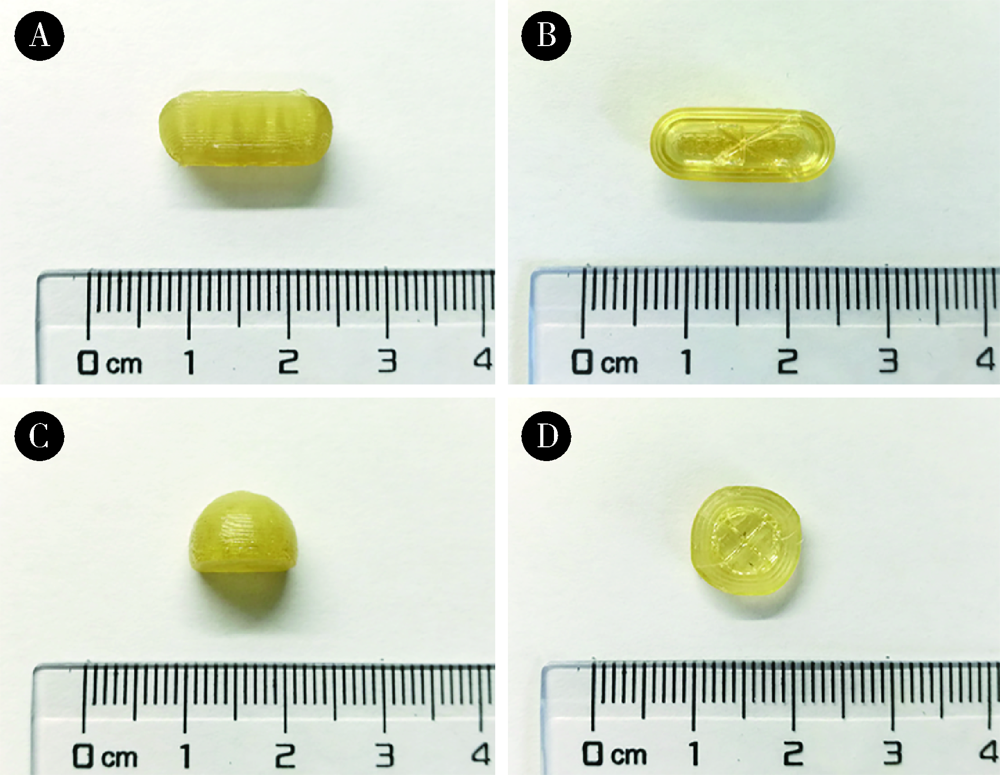
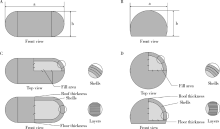
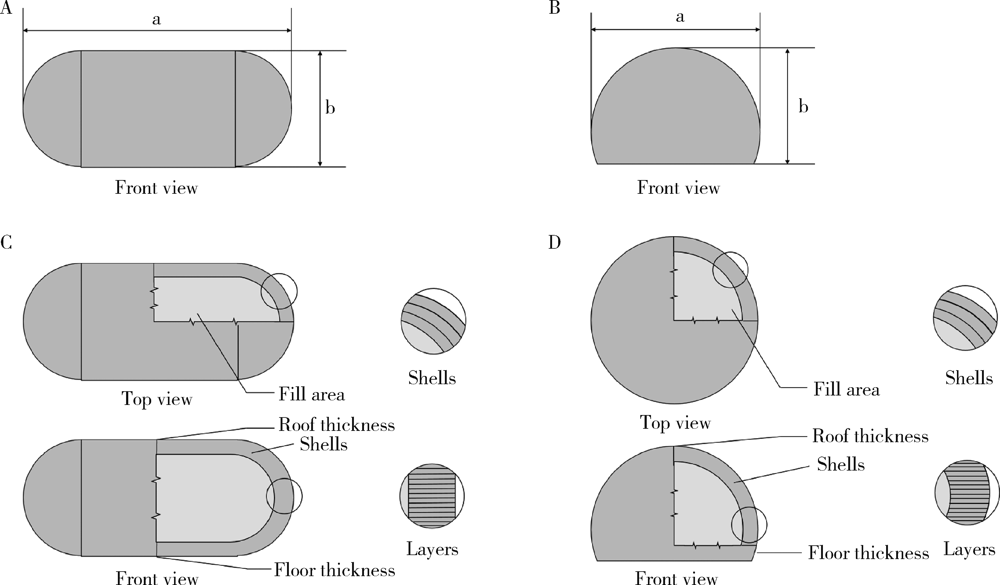
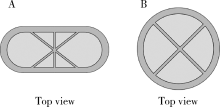
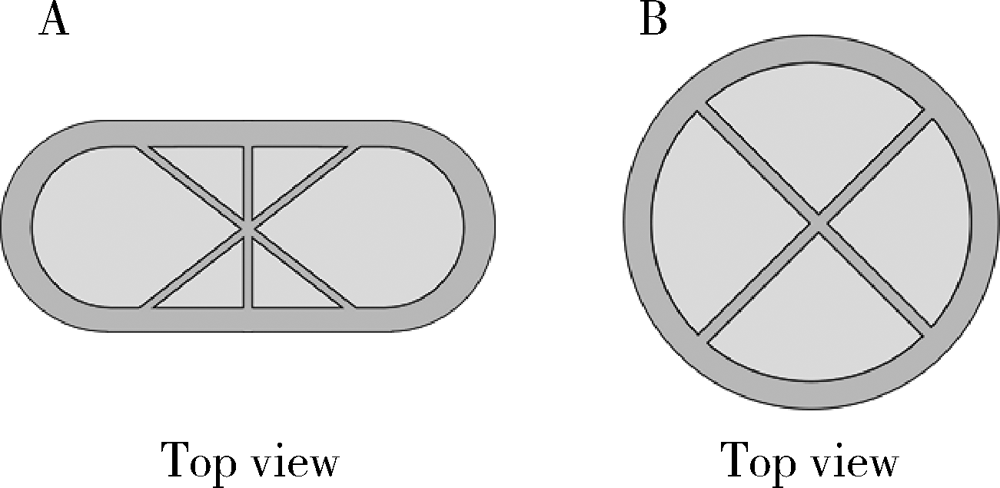
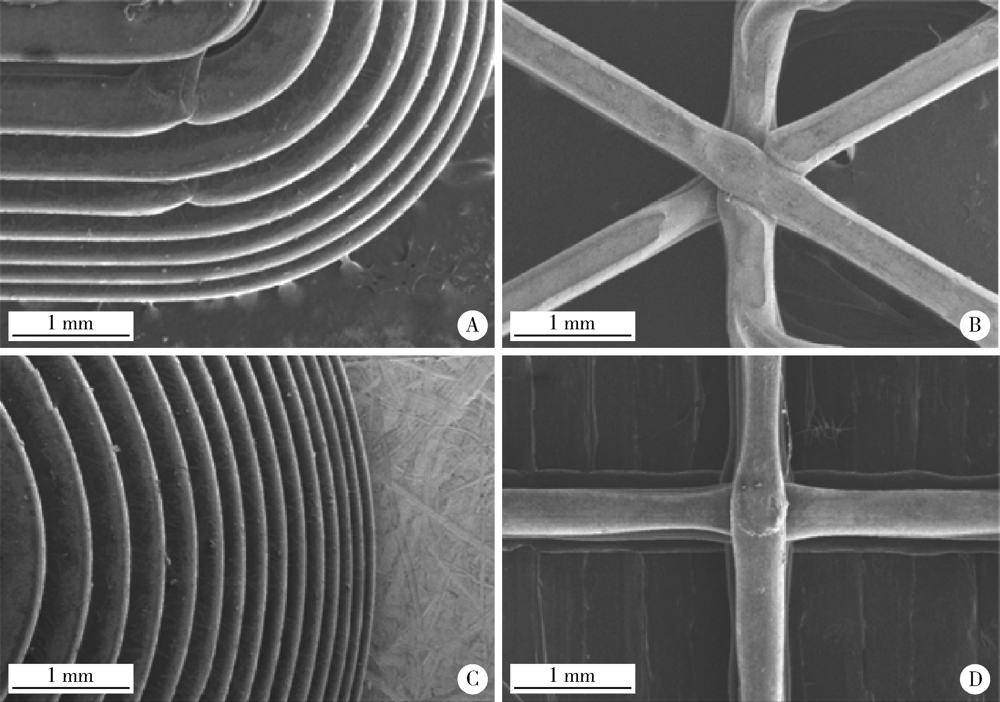
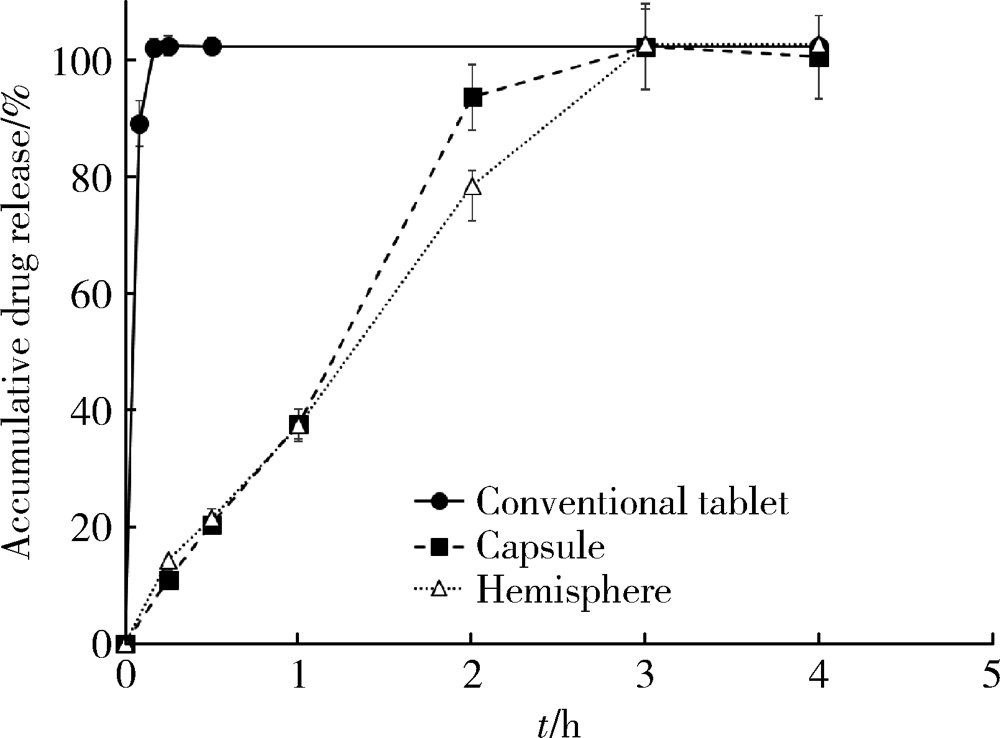
目的: 探究以熔融沉积成型(fused deposition modeling,FDM)3D打印技术研制胃漂浮制剂的可行性,并对所研制的FDM 3D打印胃漂浮制剂进行相关的体外质量评价。方法: 以盐酸维拉帕米为模型药物,聚乙烯醇(polyvinyl alcohol,PVA)为辅料,利用FDM 3D打印技术制备胶囊型和半球型的两种胃漂浮制剂,其填充率均为15%,层高均为0.2 mm,顶底厚均为0.8 mm,壳数分别为3和4。以扫描电镜观察制剂的形态,以称重法考察制剂的平均质量,采用物性测定仪测定制剂互相垂直的两个方向的硬度,高效液相色谱法测定制剂中的药物含量,并对制剂的体外漂浮和释药行为进行表征。结果: 所制备的FDM 3D打印胶囊型和半球型制剂均形态良好,无打印缺陷;胶囊型和半球型制剂的平均质量分别为(584±13) mg和(550±12) mg;胶囊型和半球型制剂的硬度均大于800.0 N;胶囊型和半球型制剂均实现了体外漂浮且无漂浮滞后时间,体外漂浮时间分别为(3.97±0.41) h和(4.48±0.21) h;胶囊型和半球型制剂在体外释药完全的时间均为3 h。结论: 采用FDM 3D打印技术成功制备了胶囊型和半球型的盐酸维拉帕米胃漂浮制剂。
中图分类号:
- R944.9
| [1] | Kaushik AY, Tiwari AK, Gaur A. Role of excipients and polyme-ric advancements in preparation of floating drug delivery systems[J]. Int J Pharm Investig, 2015,5(1):1-12. |
| [2] |
Pawar VK, Kansal S, Garg G, et al. Gastroretentive dosage forms: A review with special emphasis on floating drug delivery systems[J]. Drug Deliv, 2011,18(2):97-110.
pmid: 20958237 |
| [3] | Kotreka UK, Adeyeye MC. Gastroretentive floating drug-delivery systems: A critical review[J]. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst, 2011,28(1):47-99. |
| [4] | Sauzet C, Claeys-Bruno M, Nicolas M, et al. An innovative floating gastro retentive dosage system: formulation and in vitro evaluation[J]. Int J Pharm, 2009,378(1/2):23-29. |
| [5] | Sungthongjeen S, Paeratakul O, Limmatvapirat S, et al. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a multiple-unit floating drug delivery system based on gas formation technique[J]. Int J Pharm, 2006,324(2):136-143. |
| [6] |
Alexander S, Juergen S, Roland B. Gastroretentive drug delivery systems[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 2006,3(2):217-233.
pmid: 16506949 |
| [7] | Konta AA, Garcia-Pina M, Serrano DR. Personalised 3D printed medicines: Which techniques and polymers are more successful?[J]. Bioengineering (Basel), 2017,4(4):79-96. |
| [8] | Long J, Gholizadeh H, Lu J, et al. Application of fused deposition modelling (FDM) method of 3D printing in drug delivery[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2017,23(3):433-439. |
| [9] | Palo M, Hollander J, Suominen J, et al. 3D printed drug delivery devices: Perspectives and technical challenges[J]. Expert Rev Med Devices, 2017,14(9):685-696. |
| [10] |
Alhnan MA, Okwuosa TC, Sadia M, et al. Emergence of 3D printed dosage forms: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Pharm Res, 2016,33(8):1817-1832.
pmid: 27194002 |
| [11] | Sawicki W, Glod J. Preparation of floating pellets with verapamil hydrochloride[J]. Acta Pol Pharm, 2004,61(3):185-190. |
| [12] | Patel A, Modasiya M, Shah D, et al. Development and in vivo floating behavior of verapamil HCl intragastric floating tablets[J]. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2009,10(1):310-315. |
| [13] | 范田园, 张悦. 一种3D打印胃漂浮制剂及其制备方法: 中国,CN106692091A[P]. 2017-05-24. |
| [14] | Srikanth MV, Rao NS, Sunil SA, et al. Statistical design and evaluation of a propranolol HCl gastric floating tablet[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2012,2(1):60-69. |
| [15] | Fu J, Yin H, Yu X, et al. Combination of 3D printing technologies and compressed tablets for preparation of riboflavin floating tablet-in-device (TiD) systems[J]. Int J Pharm, 2018,549(1/2):370-379. |
| [16] |
Goyanes A, Buanz AB, Hatton GB, et al. 3D printing of modified-release aminosalicylate (4-ASA and 5-ASA) tablets[J]. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2015,89:157-162.
pmid: 25497178 |
| [17] |
Fuenmayor E, Forde M, Healy AV, et al. Comparison of fused-filament fabrication to direct compression and injection molding in the manufacture of oral tablets[J]. Int J Pharm, 2019,558:328-340.
pmid: 30659922 |
| [18] | Yang Y, Wang H, Li H, et al. 3D printed tablets with internal scaffold structure using ethyl cellulose to achieve sustained ibuprofen release[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2018,115:11-18. |
| [19] | Tagami T, Nagata N, Hayashi N, et al. Defined drug release from 3D-printed composite tablets consisting of drug-loaded polyvinylalcohol and a water-soluble or water-insoluble polymer filler[J]. Int J Pharm, 2018,543(1/2):361-367. |
| [20] | Solanki NG, Tahsin M, Shah AV, et al. Formulation of 3D printed tablet for rapid drug release by fused deposition modeling: Screening polymers for drug release, drug-polymer miscibility and printability[J]. J Pharm Sci, 2018,107(1):390-401. |
| [21] |
Arafat B, Wojsz M, Isreb A, et al. Tablet fragmentation without a disintegrant: A novel design approach for accelerating disintegration and drug release from 3D printed cellulosic tablets[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2018,118:191-199.
pmid: 29559404 |
| [22] |
Kadry H, Al-Hilal TA, Keshavarz A, et al. Multi-purposable filaments of HPMC for 3D printing of medications with tailored drug release and timed-absorption[J]. Int J Pharm, 2018,544(1):285-296.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.04.010 pmid: 29680281 |
| [23] |
Sadia M, Arafat B, Ahmed W, et al. Channelled tablets: An innovative approach to accelerating drug release from 3D printed tablets[J]. J Control Release, 2018,269:355-363.
pmid: 29146240 |
| [24] | Tagami T, Fukushige K, Ogawa E, et al. 3D Printing factors important for the fabrication of polyvinylalcohol filament-based tablets[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2017,40(3):357-364. |
| [25] |
Goyanes A, Robles Martinez P, Buanz A, et al. Effect of geometry on drug release from 3D printed tablets[J]. Int J Pharm, 2015,494(2):657-663.
pmid: 25934428 |
| [26] |
Zhang J, Yang W, Vo AQ, et al. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based controlled release dosage by melt extrusion and 3D printing: Structure and drug release correlation[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2017,177:49-57.
pmid: 28962795 |
| [27] |
Goyanes A, Wang J, Buanz A, et al. 3D printing of medicines: Engineering novel oral devices with unique design and drug delease characteristics[J]. Mol Pharm, 2015,12(11):4077-4084.
pmid: 26473653 |
| [28] |
Lunio R, Sawicki W. Influence of the components of Kollicoat SR film on mechanical properties of floating pellets from the point of view of tableting[J]. Pharmazie, 2008,63(10):731-735.
pmid: 18972835 |
| [29] |
Yoshida MI, Gomes EC, Soares CD, et al. Thermal analysis applied to verapamil hydrochloride characterization in pharmaceutical formulations[J]. Molecules, 2010,15(4):2439-2452.
pmid: 20428054 |
| [30] |
Soppimath KS, Kulkarni AR, Aminabhavi TM. Development of hollow microspheres as floating controlled-release systems for car-diovascular drugs: Preparation and release characteristics[J]. Drug Dev Ind Pharm, 2001,27(6):507-515.
pmid: 11548857 |
| [31] |
Durig T, Fassihi R. Evaluation of floating and sticking extended release delivery systems: An unconventional dissolution test[J]. J Control Release, 2000,67(1):37-44.
pmid: 10773327 |
| [32] |
Sawicki W, Lunio R, Walentynowicz O, et al. Influence of the type of cellulose on properties of multi-unit target releasing in sto-mach dosage form with verapamil hydrochloride[J]. Acta Pol Pharm, 2007,64(1):81-88.
pmid: 17665855 |
| [1] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [2] | 展新新,曹露露,项东,汤皓,夏丹丹,林红. 成型方向对3D打印口腔义齿基托树脂材料物理性能及力学性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 345-351. |
| [3] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [4] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [5] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [6] | 胡攀攀,李彦,刘啸,唐彦超,李梓赫,刘忠军. 自稳式人工椎体在颈椎前路手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 161-166. |
| [7] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [8] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [9] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [10] | 温奥楠,刘微,柳大为,朱玉佳,萧宁,王勇,赵一姣. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
| [11] | 周华,王仁吉,刘忠军,刘晓光,吴奉梁,党礌,韦峰. 3D打印人工椎体在颈椎脊索瘤全脊椎切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 144-148. |
| [12] | 熊士凯,史尉利,王安鸿,谢兴,郭秦炜. 腓骨远端撕脱骨折的影像学诊断:踝关节X线与CT三维重建的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 156-159. |
| [13] | 高梓翔,王勇,温奥楠,朱玉佳,秦庆钊,张昀,王晶,赵一姣. 基于三维下颌骨平均模型的颌骨标志点自动确定方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 174-180. |
| [14] | 开地尔娅·阿不都热合曼,张荣赓,钱浩楠,邹振洋,丹尼娅·叶斯涛,范田园. 个性化剂量熔融沉积成型3D打印茶碱片剂的制备和体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1202-1207. |
| [15] | 邢海英,陈玉辉,许珂,黄点点,彭清,刘冉,孙葳,黄一宁. 三维超声血管斑块定量分析技术评估颈动脉粥样硬化斑块[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 991-999. |
|
||