北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 384-389. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.025
儿童和青少年牙外伤急诊患者临床分析
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,急诊科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Clinical analysis of children and adolescents emergency dental trauma cases
YANG Xue,SUN Wei,WANG Zhe,JI Ai-ping,BAI Jie( )
)
- Department of Oral Emergency, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
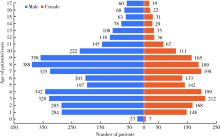
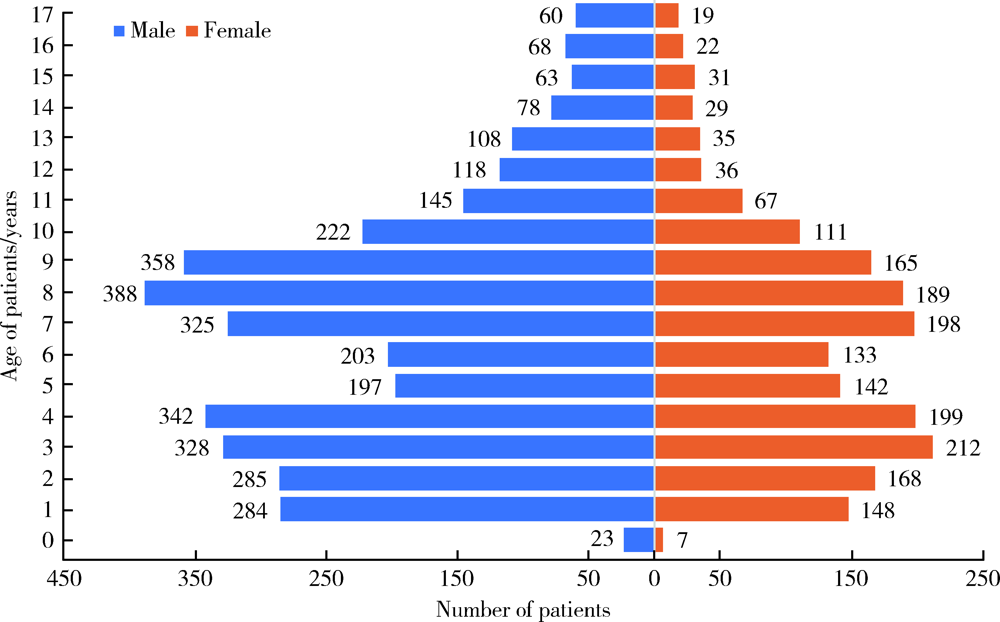
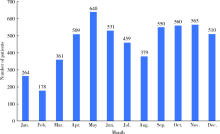
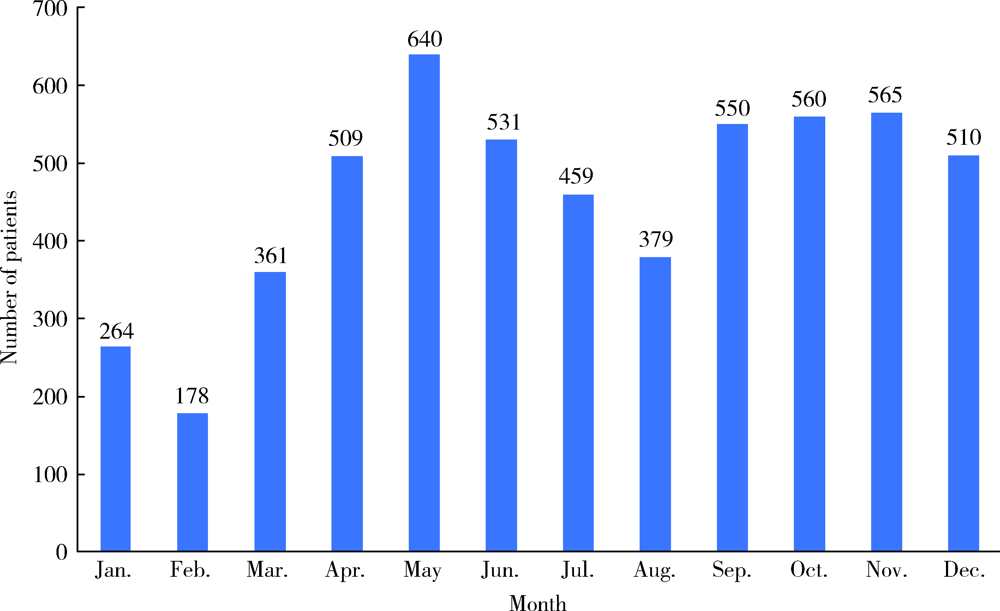
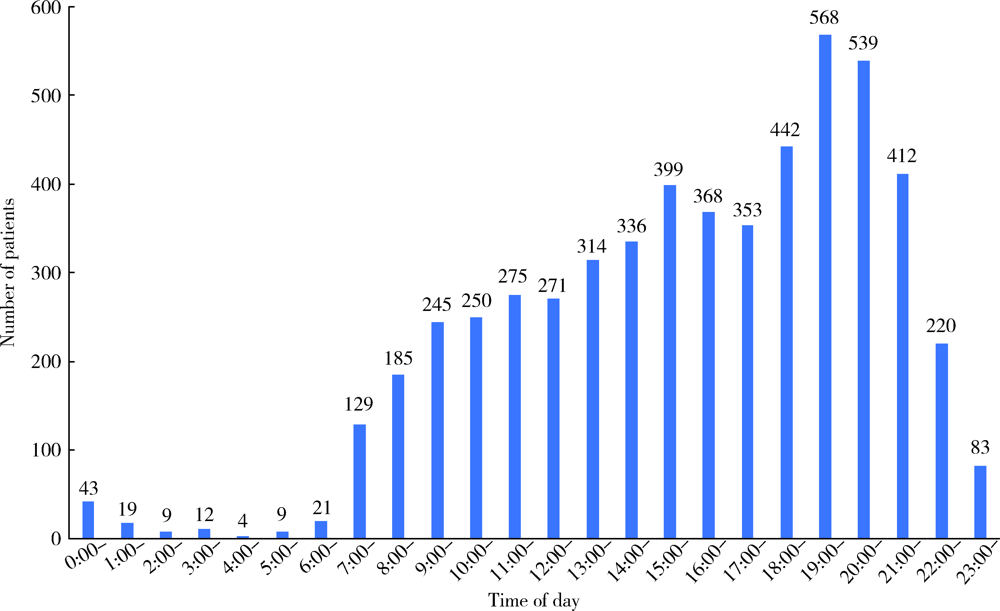
目的: 分析口腔急诊18岁以下牙外伤患者的发病情况和临床特点,指导儿童和青少年的牙外伤防护和治疗。方法: 回顾性分析2016年1月至2018年12月就诊于北京大学口腔医院急诊科有完整电子病历信息的18岁以下儿童和青少年牙外伤患者的临床资料,总结急诊儿童和青少年牙外伤的性别、年龄、时间分布,外伤牙的数目、牙位、牙外伤类型及合并伤等情况。结果: 纳入儿童和青少年牙外伤初诊患者共5 506例,占所有牙外伤患者(10 164例)的54.2%。牙外伤的高峰年龄段为3~4岁和7~9岁,各年龄组男童发病率均高于女童。5—6月份及9—11月份牙外伤的发病率较高,牙外伤患者的日就诊高峰时段为19:00~20:00。受伤牙位左右基本对称,上中切牙最易受累,52.3%的患者累及两颗及两颗以上牙。各类型恒牙外伤中,釉质-牙本质折断最为多见。各类型乳牙外伤中,亚脱位最为多见。19.7%的患者合并较严重的颌面部软硬组织损伤。结论: 儿童和青少年牙外伤具有明显的年龄双峰特点,常累及发育中的乳牙和年轻恒牙,临床诊疗应考虑儿童生长发育特点,同时应加强家庭、学校和幼托机构中针对儿童和青少年牙外伤的宣教,提高防护意识。
中图分类号:
- R782.4
| [1] | Ghadimi S, Seraj B, Keshavarz H, et al. The effect of using an educational poster on elementary school health teachers’ know-ledge of emergency management of traumatic dental injuries[J]. J Dent (Tehran), 2014,11(6):620-628. |
| [2] |
Lee JY, Divaris K. Hidden consequences of dental trauma: the social and psychological effects[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2009,31(2):96-101.
pmid: 19455926 |
| [3] | 白洁, 姬爱平, 于冬梅. 急诊牙外伤患者临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010,42(1):90-93. |
| [4] | 王晓敏, 苏雪龙, 王红, 等. 西安市学龄儿童年轻恒牙外伤的现况调查[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2018,36(2):194-198. |
| [5] |
Kirzioglu Z, Oz E. Changes in the etiological factors of dental trauma in children over time: An 18-year retrospective study[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2019,35(4-5):259-267.
pmid: 31054189 |
| [6] | 夏斌, 葛立宏, 王忠桂, 等. 北京大学口腔医学院256例急诊就诊儿童情况分析[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2006,20(2):214-215. |
| [7] |
Ivancic Jokic N, Bakarcic D, Fugosic V, et al. Dental trauma in children and young adults visiting a University Dental Clinic[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2009,25(1):84-87.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2008.00711.x pmid: 19208016 |
| [8] | Llarena del Rosario ME, Acosta Alfaro VM, Garcia-Godoy F. Traumatic injuries to primary teeth in Mexico City children[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2010,8(5):213-214. |
| [9] |
Levin L, Day PF, Hicks L, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: General introduction[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2020,36(4):309-313.
pmid: 32472740 |
| [10] | 葛立宏. 儿童口腔医学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012. |
| [11] | 樊明文. 牙体牙髓病学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016. |
| [12] | 王晓敏, 苏雪龙, 王红, 等. 西安市学龄儿童年轻恒牙外伤就诊及预后的现况调查[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2018,36(3):308-313. |
| [13] |
Kim C, Choi E, Park KM, et al. Characteristics of patients who visit the dental emergency room in a dental college hospital[J]. J Dent Anesth Pain Med, 2019,19(1):21-27.
pmid: 30859130 |
| [14] | Blagojevic D, Petrovic B, Markovic D, et al. Pulp vitality preservation after traumatic dental injuries to permanent teeth[J]. Med Pregl, 2013,66(3/4):149-152. |
| [15] | 迟丹丹, 徐海峰, 马卫东. 202例急诊牙外伤临床分析[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2012,28(5):443-446. |
| [16] |
Francisco SS, Filho FJ, Pinheiro ET, et al. Prevalence of traumatic dental injuries and associated factors among Brazilian schoolchildren[J]. Oral Health Prev Dent, 2013,11(1):31-38.
doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a29373 pmid: 23507679 |
| [17] | 白洁, 姬爱平, 于冬梅. 175例急诊儿童牙外伤情况分析[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2010,18(4):231-233. |
| [18] | Suhasini SJ, Gheena S. Dental trauma in children and young adults[J]. J Pharm Sci Res, 2015,7(6):344-346. |
| [19] |
Fouad AF, Abbott PV, Tsilingaridis G, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2020,36(4):331-342.
doi: 10.1111/edt.12573 pmid: 32460393 |
| [20] |
Day PF, Flores MT, O’Connell AC, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 3. Injuries in the primary dentition[J]. Dent Traumatol, 2020,36(4):343-359.
pmid: 32458553 |
| [1] | 王敏, 李倩. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性影响因素的路径分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 809-814. |
| [2] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [3] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [4] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [5] | 费秀文,刘斯,汪波,董爱梅. 成人及儿童组织坏死性淋巴结炎临床特征及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [6] | 沈鹤军,侍崇艳,郑清,黄玉,景涛. 我国高中生静坐时长与健康素养现状及其影响因素调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 239-246. |
| [7] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [8] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [9] | 弭小艺,侯杉杉,付子苑,周末,李昕璇,孟召学,蒋华芳,周虹. 中文版童年不良经历问卷在学龄前儿童父母中应用的信效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [10] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [11] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [12] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [13] | 郑丹枫,李君禹,李佳曦,张英爽,钟延丰,于淼. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸椎旁肌的病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 283-291. |
| [14] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [15] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
|
||