北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1043-1048. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.006
IgG4相关性疾病中枢神经系统受累的临床特点分析
孟广艳1,2,张筠肖1,3,张渝昕1,刘燕鹰1,4,△
- 1.北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科,北京 100044
2.北京大学人民医院检验科,北京 100044
3.北京市监狱管理局清河分局医院内科,天津 300481
4.首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院风湿免疫科,北京 100050
Clinical characteristics of central nervous system involvement in IgG4 related diseases
MENG Guang-yan1,2,ZHANG Yun-xiao1,3,ZHANG Yu-xin1,LIU Yan-ying1,4,△
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
3. Department of Internal Medicine, Hospital of Qinghe Branch of Beijing Prison Administration, Tianjin 300481, China
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
摘要:
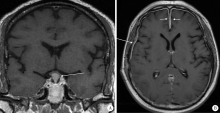
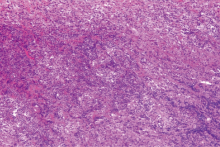
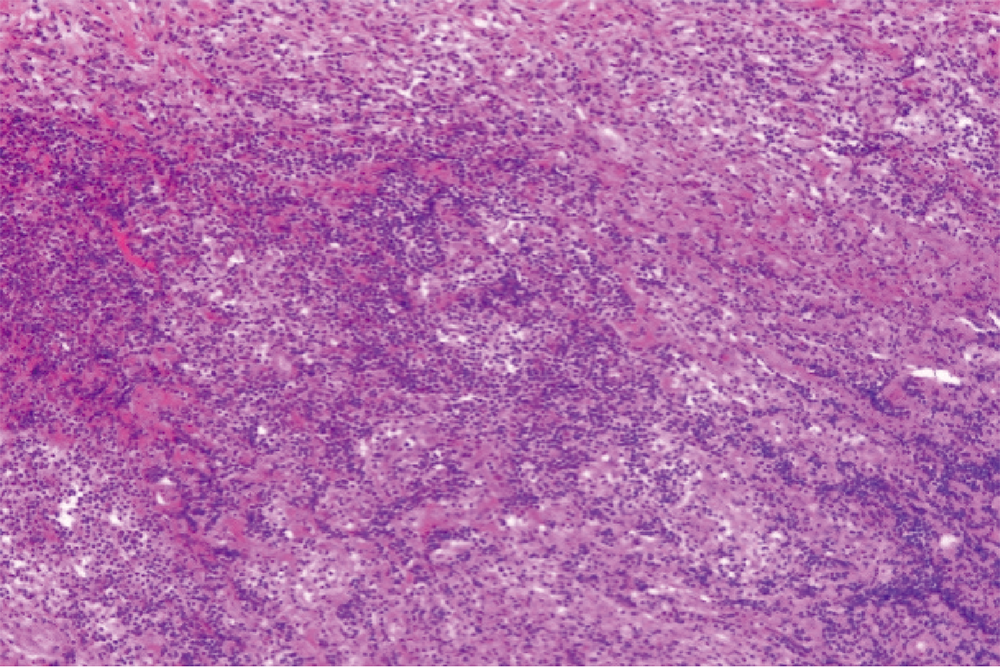
目的:提高对IgG4相关性疾病伴有中枢神经系统病变的认识,以早期诊断、早期治疗。方法:回顾性分析10例IgG4相关性疾病伴有中枢神经系统病变患者的临床资料,总结其临床表现、实验室检查、影像学检查、组织病理学及治疗方面的特点。结果:10例IgG4相关性疾病合并中枢神经系统受累的患者中,垂体受累者6例,硬脑膜受累者4例;单纯神经系统受累者仅2例,其余8例患者均合并其他脏器受累;一半患者以神经系统受累为首发表现,神经系统症状多表现为多饮、多尿、头痛、视力下降等。实验室检查中,9例(90.0%)血清IgG4水平升高,血清总IgE升高者7例(87.5%),部分患者血清IgG、血红细胞沉降率、C反应蛋白升高,补体C3、C4下降。8例患者接受了不同部位的组织病理活检,病理检查均可见大量淋巴细胞、浆细胞浸润,部分可见纤维组织增生。所有患者均接受了糖皮质激素治疗,8例(80%)联合了免疫抑制剂治疗,3例因病情反复给予利妥昔单抗治疗。所有患者中,2例(20%)达到完全缓解,8例(80%)部分缓解,中位随访时间13.5个月,复发4例。结论:IgG4相关性疾病的中枢神经系统病变中,垂体、硬脑膜为常见受累部位,大多合并其他脏器受累,但半数患者以神经系统症状为首发表现,因症状不典型,应结合实验室、影像学检查,必要时行组织病理活检明确诊断。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| [1] |
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopatholo-gical entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2003, 38(10):982-984.
pmid: 14614606 |
| [2] |
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2021, 31(3):529-533.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2020.1859710 |
| [3] | Peng L, Zhang P, Zhang X, et al. Clinical features of immunoglobulin G4-related disease with central nervous system involvement: An analysis of 15 cases[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2020, 38(4):626-632. |
| [4] |
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, et al. IgG4-related disease[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9976):1460-1471.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0 pmid: 25481618 |
| [5] | 王子乔, 刘燕鹰, 张霞, 等. 17例误诊为IgG4相关疾病患者的临床特点及误诊原因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6):1025-1031. |
| [6] | 朱星昀, 刘燕鹰, 孙学娟, 等. 免疫球蛋白G4相关疾病患者发病形式及就诊行为特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6):1039-1043. |
| [7] |
Iseda I, Hida K, Tone A, et al. Prednisolone markedly reduced serum IgG4 levels along with the improvement of pituitary mass and anterior pituitary function in a patient with IgG4-related infundibulo-hypophysitis[J]. Endocr J, 2014, 61(2):195-203.
doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ13-0407 |
| [8] | 李芊, 段炼, 李伟, 等. IgG4相关性垂体炎5例临床分析[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(9):861-864. |
| [9] |
Ohkubo Y, Sekido T, Takeshige K, et al. Occurrence of IgG4-related hypophysitis lacking IgG4-bearing plasma cell infiltration during steroid therapy[J]. Intern Med, 2014, 53(7):753-757.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.0714 |
| [10] |
Christakis PG, Machado DG, Fattahi P. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis mimicking neurosarcoidosis[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2012, 114(2):176-178.
doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.10.011 |
| [11] | 苏玉莹, 王晨琼, 董凌莉. IgG4相关性疾病的发病机制及进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2014(14):2713-2717. |
| [12] | 纪宗斐. IgG4相关性疾病(IgG4-RD)发病机制的研究进展[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2019, 46(1):114-118. |
| [13] |
Leporati P, Landek-Salgado MA, Lupi I, et al. IgG4-related hypophysitis: A new addition to the hypophysitis spectrum[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2011, 96(7):1971-1980.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-2970 pmid: 21593109 |
| [14] |
Chan SK, Cheuk W, Chan KT, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing pachymeningitis: A previously unrecognized form of central nervous system involvement in IgG4-related sclerosing disease[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33(8):1249-1252.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181abdfc2 |
| [15] |
Lee YS, Lee HW, Park KS, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis with skull involvement[J]. Brain Tumor Res Treat, 2014, 2(2):87-91.
doi: 10.14791/btrt.2014.2.2.87 |
| [16] |
Peng Y, Li JQ, Zhang PP, et al. Clinical outcomes and predictive relapse factors of IgG4-related disease following treatment: A long-term cohort study[J]. J Intern Med, 2019, 286(5):542-552.
doi: 10.1111/joim.12942 pmid: 31121062 |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | 冯璐,翟佳羽,赵金霞. IgG4相关性疾病患者就诊情况及其临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1028-1032. |
| [5] | 冯敏,陈哲,程永静. 以十二指肠溃疡为突出表现的IgG4相关性疾病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1125-1129. |
| [6] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [7] | 熊焰,李鑫,梁丽,李东,鄢丽敏,李雪迎,邸吉廷,李挺. 甲状腺粗针穿刺活检病理诊断的准确性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [8] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [9] | 宁博涵,张青霞,杨慧,董颖. 伴间质细胞增生、玻璃样变性及索状结构的子宫内膜样腺癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [10] | 陈适,刘田. 重视系统性血管炎的早期识别和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1065-1067. |
| [11] | 曹瑞洁,姚中强,焦朋清,崔立刚. 不同分类标准对中国大动脉炎的诊断效能比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [12] | 徐朝焰,林长艺,叶达梅,吴培埕,宋明辉,刘有添,邓琼,黄雪艳,范忠晓,游雪兰. 感染性关节炎诊断分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1234-1237. |
| [13] | 郝哲,岳蜀华,周利群. 拉曼技术在泌尿系统肿瘤检测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 779-784. |
| [14] | 于博,赵扬玉,张喆,王永清. 妊娠合并感染性心内膜炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [15] | 翟莉,邱楠,宋惠. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1183-1187. |
|
||