北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 615-620. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.04.006
乳头状肾细胞癌的临床病理特征和预后分析
博尔术1,洪鹏1,张宇1,邓绍晖1,葛力源1,陆敏2,李楠3,马潞林1,张树栋1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院病理科,北京 100191
3. 北京大学第三医院临床流行病学研究中心,北京 100191
Clinicopathological features and prognostic analysis of papillary renal cell carcinoma
Er-shu BO1,Peng HONG1,Yu ZHANG1,Shao-hui DENG1,Li-yuan GE1,Min LU2,Nan LI3,Lu-lin MA1,Shu-dong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Research Centre of Clinical Epidemiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
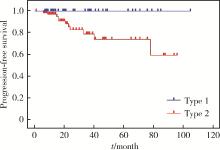
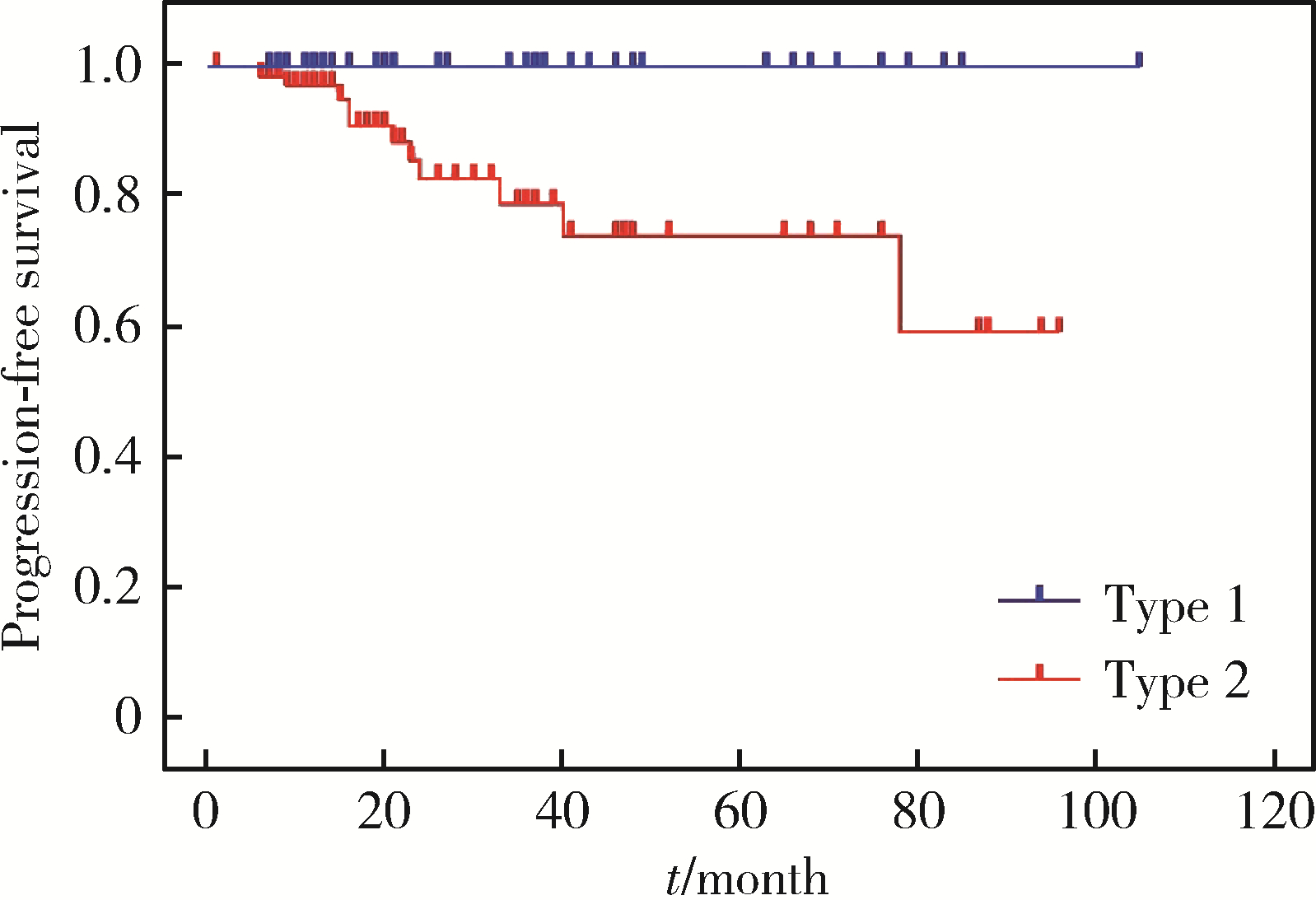
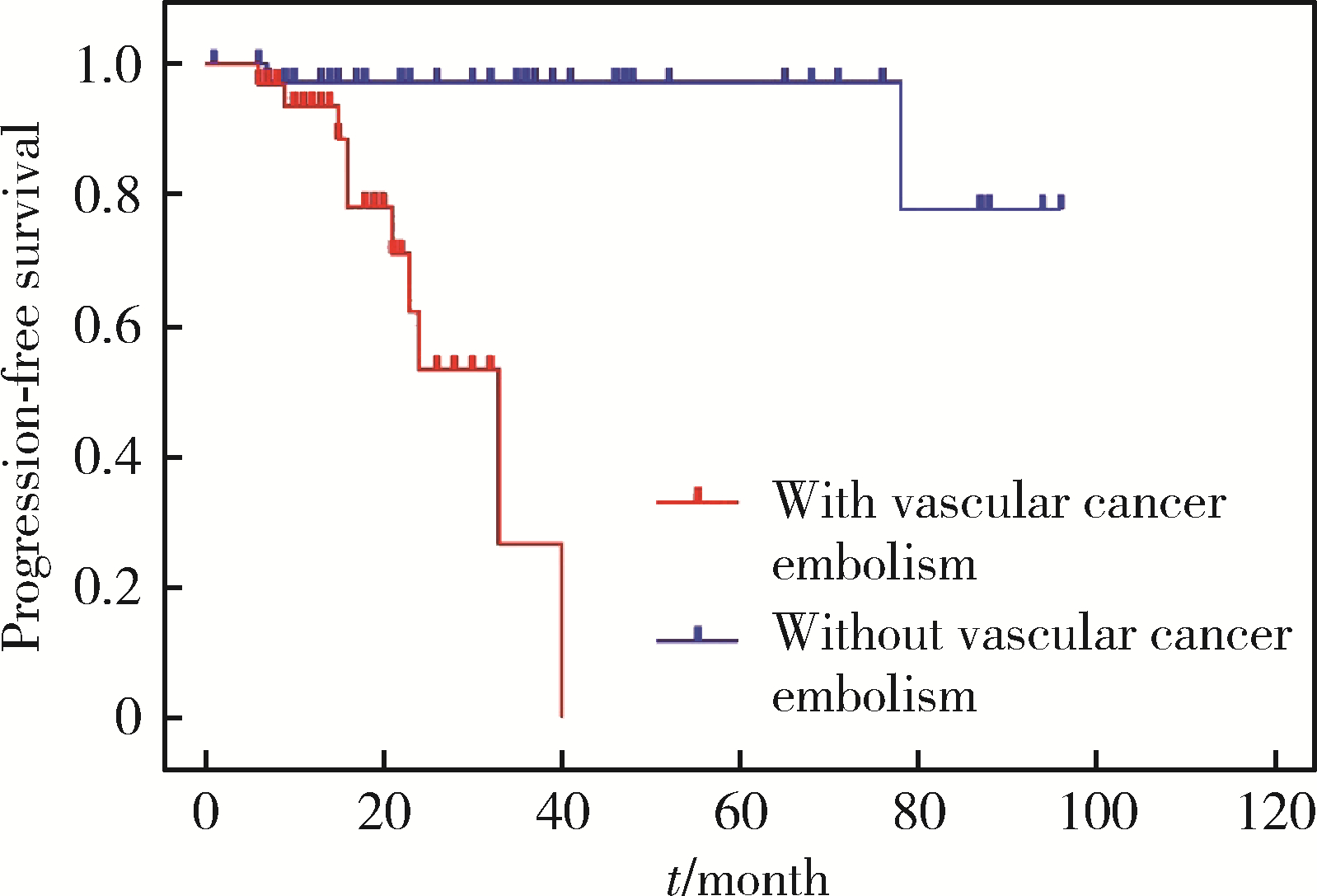
目的: 探讨乳头状肾细胞癌(papillary renal cell carcinoma,pRCC)的临床病理特征和预后特点。方法: 回顾性分析2012年5月至2021年5月北京大学第三医院泌尿外科收治的114例pRCC患者的临床资料,包括91例男性和23例女性。所有病例均为手术患者,病理诊断明确,随访数据完整。采用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线并通过log-rank检验分析患者临床病理特征与生存时间的关系,使用Cox比例风险回归模型分析影响患者无进展生存率的因素。结果: 114例患者平均年龄(57.3±12.6)岁。肿瘤位于左肾49例,右肾65例。48例行根治性肾切除术,66例行肾部分切除术。1型pRCC 42例,2型72例,肿瘤平均最大径为(5.5±3.6) cm。肿瘤分期pT1a期52例,pT1b期22例,pT2期4例,pT3期33例,pT4期3例。2016年世界卫生组织/国际泌尿病理学会(World Health Organization / International Society of Urological Pathology,WHO/ISUP)分级Ⅰ级13例,Ⅱ级44例,Ⅲ级51例,Ⅳ级6例。114例患者中34例伴有脉管癌栓,30例伴淋巴结转移,3例伴肾上腺转移。患者术后中位随访时间为22个月,3年无进展生存率为95.6%。1型和2型pRCC患者在年龄(P=0.046)、体重指数(P=0.008)、手术方式(P=0.001)、肿瘤最大径(P < 0.001)、脉管癌栓(P < 0.001)、淋巴结转移(P < 0.001)、pT分期(P < 0.001)和核分级(P < 0.001)方面差异均有统计学意义。1型和2型pRCC的3年无进展生存率分别为100%和69.4%,1型预后明显优于2型(P=0.003)。2型pRCC患者的单因素分析结果显示,pT分期(P < 0.001)、脉管癌栓(P < 0.001)和淋巴结转移(P < 0.001)与其预后紧密相关;多因素分析显示,脉管癌栓为2型pRCC无进展生存率的独立预后因素(P=0.001)。行根治性肾切除术的pRCC患者的单因素分析结果显示,pT分期(P=0.006)、脉管癌栓(P=0.001)和淋巴结转移(P=0.008)是影响其预后的显著因素,进一步多因素分析显示只有脉管癌栓是其无进展生存率的独立预后因素(P=0.006)。结论: 2型pRCC比1型pRCC发病率更高,淋巴结转移更易出现,pT分期更晚,核分级更高。在2型pRCC和根治性切除术后的pRCC患者中,脉管癌栓是其独立预后因素。
中图分类号:
- R737.11
| 1 |
Siegel RL , Miller KD , Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69 (1): 7- 34.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21551 |
| 2 |
Qu Y , Chen H , Gu W , et al. Age-dependent association between sex and renal cell carcinoma mortality: A population-based analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5 (1): 9160.
doi: 10.1038/srep09160 |
| 3 |
Znaor A , Lortet-Tieulent J , Laversanne M , et al. International variations and trends in renal cell carcinoma incidence and mortality[J]. Eur Urol, 2015, 67 (3): 519- 530.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.10.002 |
| 4 |
Akhtar M , Al-Bozom IA , Al Hussain T . Papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC): An update[J]. Adv Anat Pathol, 2019, 26 (2): 124- 132.
doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000220 |
| 5 |
Mir MC , Derweesh I , Porpiglia F , et al. Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for clinical T1b and T2 renal tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71 (4): 606- 617.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.060 |
| 6 |
Mancilla-Jimenez R , Stanley RJ , Blath RA , et al. Papillary renal cell carcinoma a clinical, radiologic, and pathologic study of 34 cases[J]. Cancer, 1976, 38 (6): 2469- 2480.
doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197612)38:6<2469::AID-CNCR2820380636>3.0.CO;2-R |
| 7 |
Thoenes W , Störkel S , Rumpelt HJ . Histopathology and classification of renal cell tumors (adenomas, oncocytomas and carcinomas): The basic cytological and histopathological elements and their use for diagnostics[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 1986, 181 (2): 125- 143.
doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(86)80001-2 |
| 8 | Delahunt B , Eble JN . Papillary renal cell carcinoma: A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 105 tumors[J]. Mod Pathol, 1997, 10 (6): 537- 544. |
| 9 |
Aron M , Nguyen MM , Stein RJ , et al. Impact of gender in renal cell carcinoma: An analysis of the SEER database[J]. Eur Urol, 2008, 54 (1): 133- 140.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.12.001 |
| 10 |
Hong B , Hou H , Chen L , et al. The clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma: A multicenter retrospective study in Chinese population[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11, 753690.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.753690 |
| 11 |
Bigot P , Bernhard JC , Gill IS , et al. The subclassification of papillary renal cell carcinoma does not affect oncological outcomes after nephron sparing surgery[J]. World J Urol, 2016, 34 (3): 347- 352.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-015-1634-0 |
| 12 |
洪保安, 侯惠民, 陈凌霄, 等. 乳头状肾细胞癌的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 41 (12): 896- 900.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200502-00350 |
| 13 | 董樑, 黄吉炜, 奚倩雯, 等. 乳头状肾细胞癌的临床病理特征和预后分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 36 (3): 183- 187. |
| 14 |
Ha YS , Chung JW , Choi SH , et al. Clinical significance of subclassification of papillary renal cell carcinoma: Comparison of cli-nicopathologic parameters and oncologic outcomes between papillary histologic subtypes 1 and 2 using the Korean renal cell carcinoma database[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2017, 15 (2): e181- e186.
doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2016.07.020 |
| 15 |
Pan H , Ye L , Zhu Q , et al. The effect of the papillary renal cell carcinoma subtype on oncological outcomes[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10 (1): 21073.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78174-9 |
| 16 |
Sukov WR , Lohse CM , Leibovich BC , et al. Clinical and pathological features associated with prognosis in patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Urol, 2012, 187 (1): 54- 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.09.053 |
| 17 |
Ku JH , Moon KC , Kwak C , et al. Is there a role of the histologic subtypes of papillary renal cell carcinoma as a prognostic factor?[J]. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2009, 39 (10): 664- 670.
doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyp075 |
| 18 | 黄健. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南(2019版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 6- 8. |
| 19 |
Fernandes DS , Lopes JM . Pathology, therapy and prognosis of papillary renal carcinoma[J]. Future Oncol, 2015, 11 (1): 121- 132.
doi: 10.2217/fon.14.133 |
| 20 |
Begg CB , Cramer LD , Hoskins WJ . Impact of hospital volume on operative mortality for major cancer surgery[J]. JAMA, 1998, 280 (20): 1747- 1751.
doi: 10.1001/jama.280.20.1747 |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [8] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [9] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [10] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [11] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [12] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [13] | 朱晓娟,张虹,张爽,李东,李鑫,徐玲,李挺. 人表皮生长因子受体2低表达乳腺癌的临床病理学特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [14] | 赖玉梅,李忠武,李欢,吴艳,时云飞,周立新,楼雨彤,崔传亮. 68例肛管直肠黏膜黑色素瘤临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
| [15] | 沈棋,刘亿骁,何群. 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌的临床病理特点及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
|
||