北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 343-350. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.021
5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价
温奥楠1,2,刘微3,柳大为4,朱玉佳2,萧宁2,王勇1,2,*( ),赵一姣1,2,*(
),赵一姣1,2,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院数字化研究中心, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心, 国家药品监督管理局口腔材料重点实验室, 北京 100081
3. 银川市口腔医院, 银川 750004
4. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院正畸科, 北京 100081
Preliminary evaluation of the trueness of 5 chairside 3D facial scanning techniques
Ao-nan WEN1,2,Wei LIU3,Da-wei LIU4,Yu-jia ZHU2,Ning XIAO2,Yong WANG1,2,*( ),Yi-jiao ZHAO1,2,*(
),Yi-jiao ZHAO1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
3. Yinchuan Stomatology Hospital, Yinchuan 750004, China
4. Department of Orthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
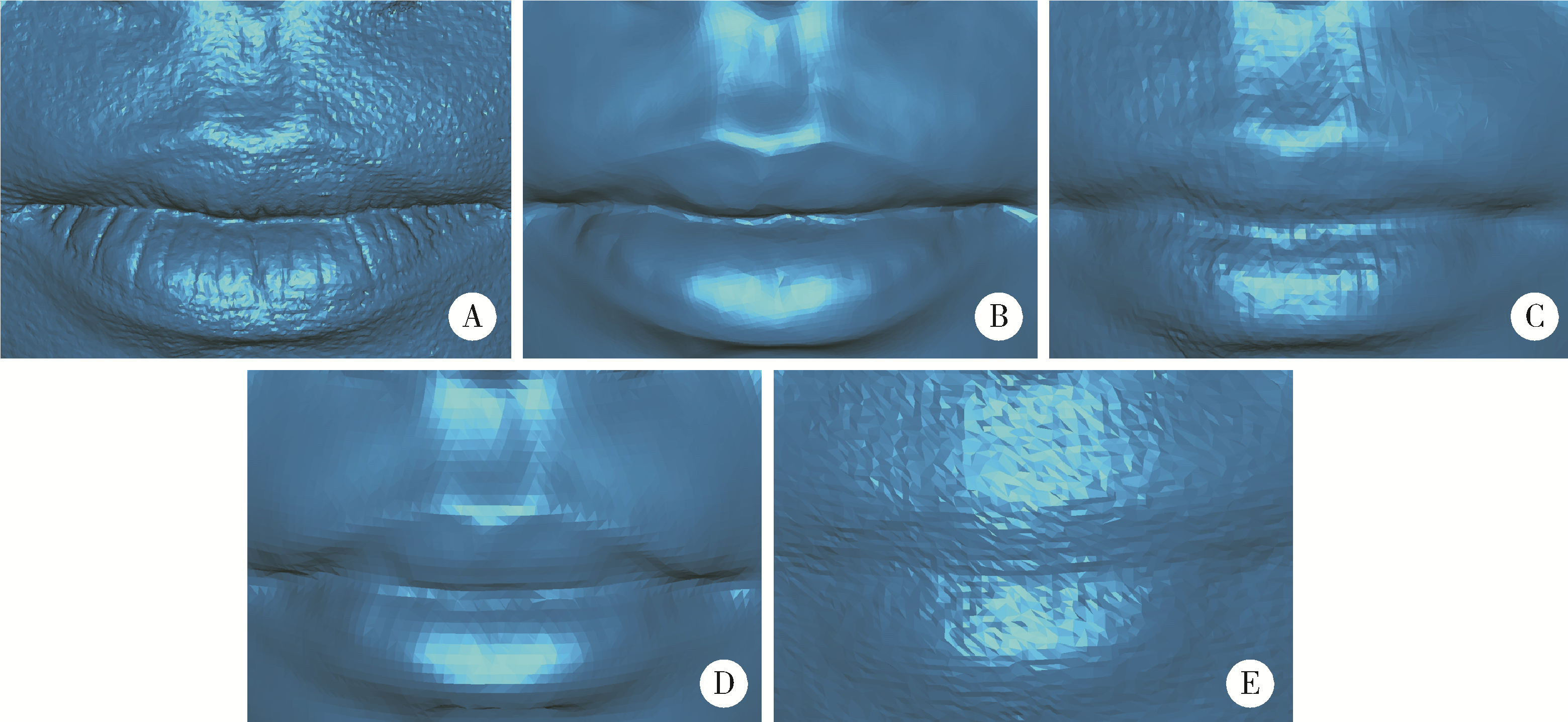
目的: 量化评价5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术的正确度,为口腔临床诊疗应用提供参考。方法: 使用传统专业型三维颜面扫描仪Face Scan采集受试者三维颜面数据,作为本研究的参考数据。分别使用4种便携式三维颜面扫描仪(Space Spider、LEO、EVA和DS-FScan)及iPhone Ⅹ手机(Bellus3D颜面扫描APP),采集受试者三维颜面数据。在Geomagic Studio 2013中通过数据配准、偏差分析等功能计算上述5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术的整体三维偏差和面部分区三维偏差,评价其正确度的表现。扫描过程中同时记录扫描时间,并对受试者舒适度采用视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale,VAS)进行评分,评价5种三维颜面扫描技术的扫描效率和患者接受度。结果: 测试数据与参考数据间平均整体和平均分区三维偏差最小者均为DS-FScan(分别为0.334 mm和0.329 mm),最大者均为iPhone Ⅹ手机(分别为0.483 mm和0.497 mm)。Space Spider获取的三维颜面数据的细节特征表现力最好。扫描效率最高和受试者接受度最高者均为iPhone Ⅹ手机,平均扫描时间为14 s,受试者扫描舒适度的VAS评分为9分。结论: 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术中,4种便携式设备的扫描数据正确度没有显著差异,均优于iPhone Ⅹ手机的扫描数据,iPhone Ⅹ扫描技术的受试者体验最好。
中图分类号:
- R780.4
| 1 |
Fink M , Hirschfelder U , Hirschinger V , et al. Assessment of facial soft-tissue profiles based on lateral photographs versus three-dimensional face scans[J]. J Orofac Orthop, 2017, 78 (1): 70- 76.
doi: 10.1007/s00056-016-0055-z |
| 2 |
Topsakal O , Akbas MI , Smith BS , et al. Evaluating the agreement and reliability of a web-based facial analysis tool for rhinoplasty[J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2021, 16 (8): 1381- 1391.
doi: 10.1007/s11548-021-02423-z |
| 3 | Anas IY , Bamgbose BO , Nuhu S . A comparison between 2D and 3D methods of quantifying facial morphology[J]. Heliyon, 2019, 5 (6): e1880. |
| 4 |
Stebel A , Desmedt D , Bronkhorst E , et al. Rating nasolabial appearance on three-dimensional images in cleft lip and palate: A comparison with standard photographs[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2016, 38 (2): 197- 201.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjv024 |
| 5 |
Krneta B , Primo IJ , Zhurov A , et al. Three-dimensional evaluation of facial morphology in children aged 5-6 years with a class Ⅲ malocclusion[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2014, 36 (2): 133- 139.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs018 |
| 6 |
Bockey S , Berssenbrügge P , Dirksen D , et al. Computer-aided design of facial prostheses by means of 3D-data acquisition and following symmetry analysis[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2018, 46 (8): 1320- 1328.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.05.020 |
| 7 |
Farook TH , Jamayet NB , Abdullah JY , et al. Designing 3D prosthetic templates for maxillofacial defect rehabilitation: A comparative analysis of different virtual workflows[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2020, 118, 103646.
doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103646 |
| 8 |
Duppe K , Becker M , Schonmeyr B . Evaluation of facial anthropometry using three-dimensional photogrammetry and direct mea-suring techniques[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2018, 29 (5): 1245- 1251.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004580 |
| 9 |
van der Meer WJ , Dijkstra PU , Visser A , et al. Reliability and validity of measurements of facial swelling with a stereophotogrammetry optical three-dimensional scanner[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 52 (10): 922- 927.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.08.019 |
| 10 |
Andrade LM , Rodrigues da Silva AMB , Magri LV , et al. Repeatability study of angular and linear measurements on facial morpho-logy analysis by means of stereophotogrammetry[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2017, 28 (4): 1107- 1111.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000003554 |
| 11 | Zhao Y , Xiong Y , Wang Y . Three-dimensional accuracy of facial scan for facial deformities in clinics: A new evaluation method for facial scanner accuracy[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (1): e169402. |
| 12 | Gaber A, Faher MF, Waned MA. Automated grading of facial paralysis using the Kinect v2: A proof of concept study: International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation (ICVR)[C]. Valencia, Spain: IEEE, 2015: 258-264. |
| 13 |
Sidequersky FV , Verze L , Mapelli A , et al. Quantification of facial movements by optical instruments: Surface laser scanning and optoelectronic three-dimensional motion analyzer[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2014, 25 (1): e65- e70.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000379 |
| 14 | Gaber A , Taher MF , Wahed MA . Quantifying facial paralysis using the Kinect v2[J]. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, 2015, 2015, 2497- 2501. |
| 15 |
Knoops PG , Beaumont CA , Borghi A , et al. Comparison of three-dimensional scanner systems for craniomaxillofacial imaging[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2017, 70 (4): 441- 449.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2016.12.015 |
| 16 |
Modabber A , Peters F , Kniha K , et al. Evaluation of the accuracy of a mobile and a stationary system for three-dimensional facial scanning[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2016, 44 (10): 1719- 1724.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.08.008 |
| 17 |
Ahn H , Chang Y , Kim K , et al. Measurement of three-dimensional perioral soft tissue changes in dentoalveolar protrusion patients after orthodontic treatment using a structured light scanner[J]. Angle Orthod, 2014, 84 (5): 795- 802.
doi: 10.2319/112913-877.1 |
| 18 |
Dindaroǧlu F , Kutlu P , Duran GS , et al. Accuracy and reliability of 3D stereophotogrammetry: A comparison to direct anthropometry and 2D photogrammetry[J]. Angle Orthod, 2016, 86 (3): 487- 494.
doi: 10.2319/041415-244.1 |
| 19 | 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 等. 两种评价面部三维表面数据不对称度方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47 (2): 340- 343. |
| 20 |
Zeng W , Chen G , Ju R , et al. The combined application of database and three-dimensional image registration technology in the restoration of total nose defect[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2018, 29 (5): e484- e487.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004500 |
| 21 | 赵一姣, 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 等. 2种三维颜面部扫描仪测量精度的定量评价[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2016, 32 (1): 37- 42. |
| 22 |
Artopoulos A , Buytaert JA , Dirckx JJ , et al. Comparison of the accuracy of digital stereophotogrammetry and projection moiré profilometry for three-dimensional imaging of the face[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 43 (5): 654- 662.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.10.005 |
| 23 |
Winder RJ , Darvann TA , McKnight W , et al. Technical validation of the Di3D stereophotogrammetry surface imaging system[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008, 46 (1): 33- 37.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2007.09.005 |
| 24 |
Lo Russo L , Di Gioia C , Salamini A , et al. Integrating intraoral, perioral, and facial scans into the design of digital dentures[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2020, 123 (4): 584- 588.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.05.030 |
| 25 |
Swennen G , Pottel L , Haers PE . Custom-made 3D-printed face masks in case of pandemic crisis situations with a lack of commercially available FFP2/3 masks[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2020, 49 (5): 673- 677.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2020.03.015 |
| 26 | Mai H , Lee D . The effect of perioral scan and artificial skin markers on the accuracy of virtual dentofacial integration: stereophotogrammetry versus smartphone three-dimensional face-scanning[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18 (1): 229. |
| 27 |
Duran GS , Dindaroglu F , Kutlu P . Hard- and soft-tissue symmetry comparison in patients with Class Ⅲ malocclusion[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2019, 155 (4): 509- 522.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2018.05.021 |
| 28 |
史雨林, 商洪涛, 田磊, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类错 畸形患者双颌手术前后面部软组织变化的三维研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32 (5): 612- 616. 畸形患者双颌手术前后面部软组织变化的三维研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32 (5): 612- 616.
|
| 29 | 刘文静, 史雨林, 许方方, 等. 偏突颌畸形患者手术前后面部软组织的三维测量研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2018, 18 (14): 2669- 2673. |
| 30 | Yamamoto S , Miyachi H , Fujii H , et al. Intuitive facial imaging method for evaluation of postoperative swelling: A combination of 3-dimensional computed tomography and laser surface scanning in orthognathic surgery[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 74 (12): 2501- 2506. |
| 31 |
Özsoy U , Uysal H , Hizay A , et al. Three-dimensional objective evaluation of facial palsy and follow-up of recovery with a handheld scanner[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2021, 74 (12): 3404- 3414.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2021.05.003 |
| 32 | 王勇, 赵一姣, 司燕. 与三维测量有关的名词浅析[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2009, 16 (2): 111- 113. |
| 33 | 陈俊锴, 孙玉春, 陈虎, 等. 口内三维扫描仪扫描精度的定量评价方法研究[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2021, 56 (9): 920- 925. |
| 34 | 曹悦, 陈俊锴, 邓珂慧, 等. 三款口内三维扫描仪获取无牙颌红膏初印模精度的对比评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (1): 129- 137. |
| 35 | Rudy HL , Wake N , Yee J , et al. Three-dimensional facial scanning at the fingertips of patients and surgeons: accuracy and precision testing of iphone Ⅹ three-dimensional scanner[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2020, 146 (6): 1407- 1417. |
| 36 | 赵一姣, 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 等. 3种不同原理颜面部扫描仪测量精度的评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46 (1): 76- 80. |
| 37 | Amornvit P , Sanohkan S . The accuracy of digital face scans obtained from 3d scanners: An in vitro study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019, 16 (24): 5061. |
| 38 | Petrides G , Clark JR , Low H , et al. Three-dimensional scanners for soft-tissue facial assessment in clinical practice[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2021, 74 (3): 605- 614. |
| [1] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [2] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [3] | 王哲,孙伟,杨雪,宋颖,姬爱平,白洁. 口腔急诊颌面部感染患者临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 543-547. |
| [4] | 宿骞,彭歆,周传香,俞光岩. 369例口腔颌面部非霍奇金淋巴瘤的临床病理特点及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 13-21. |
| [5] | 马芮,宣岩,段瑶,帅婷. 口腔颌面部恶性肿瘤患者术后正念水平调查及影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 727-734. |
| [6] | 邱淑婷,朱玉佳,王时敏,王飞龙,叶红强,赵一姣,刘云松,王勇,周永胜. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [7] | 朱玉佳,赵一姣,郑盛文,温奥楠,傅湘玲,王勇. 基于赋权形态学分析的三维面部对称参考平面构建方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 220-226. |
| [8] | 国丹妮,潘韶霞,衡墨笛,屈健,魏秀霞,周永胜. 应用于无牙颌种植修复设计的三维面部扫描配准方法的对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 83-87. |
| [9] | 唐祖南,Hui Yuh Soh,胡耒豪,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 混合现实技术在口腔颌面部肿瘤手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1124-1129. |
| [10] | 邱天成,刘筱菁,薛竹林,李自力. 基于三维动态照相机的正常人面部表情可重复性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1107-1111. |
| [11] | 白珊珊,莫思怡,徐啸翔,刘云,谢秋菲,曹烨. 大鼠咬合干扰致口颌面痛敏的自我赏罚实验行为学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 51-57. |
| [12] | 王顺吉,章文博,于尧,谢晓艳,杨宏宇,彭歆. 术前虚拟设计在股前外侧皮瓣修复口腔颌面部缺损中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 119-123. |
| [13] | 刘存瑞, 徐啸翔, 曹烨, 谢秋菲. 咬合干扰时间因素对大鼠咀嚼肌机械痛觉敏感的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 51-56. |
| [14] | 何颖, 郭传瑸, 邓旭亮, 王兴, 王晓霞. 北方正常人群颅颌面三维比例测量及面部对称性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 708-713. |
| [15] | 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 王勇. 两种评价面部三维表面数据不对称度方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(2): 340-343. |
|
||