北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 843-850. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.05.011
近红外荧光靶向探针用于前列腺神经血管束术中成像
张展奕1,张帆1,颜野1,曹财广2,李长剑3,邓绍晖1,孙悦皓1,黄天亮1,管允鹤1,李楠4,陆敏5,胡振华2,*( ),张树栋1,*(
),张树栋1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科, 北京 100191
2. 中国科学院自动化研究所, 北京市分子影像重点实验室, 中国科学院分子影像重点实验室, 北京 100190
3. 北京航空航天大学医工交叉创新研究院, 北京大数据精准医疗高精尖创新中心, 北京 100191
4. 北京大学第三医院临床流行病学研究中心, 北京 100191
5. 北京大学第三医院病理科, 北京 100191
Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles
Zhan-yi ZHANG1,Fan ZHANG1,Ye YAN1,Cai-guang CAO2,Chang-jian LI3,Shao-hui DENG1,Yue-hao SUN1,Tian-liang HUANG1,Yun-he GUAN1,Nan LI4,Min LU5,Zhen-hua HU2,*( ),Shu-dong ZHANG1,*(
),Shu-dong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
3. Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Big Data-Based Precision Medicine, School of Medicine and Engineering, Bei hang University, Beijing 100191, China
4. Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
5. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
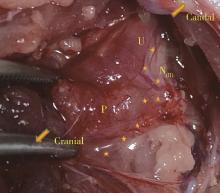
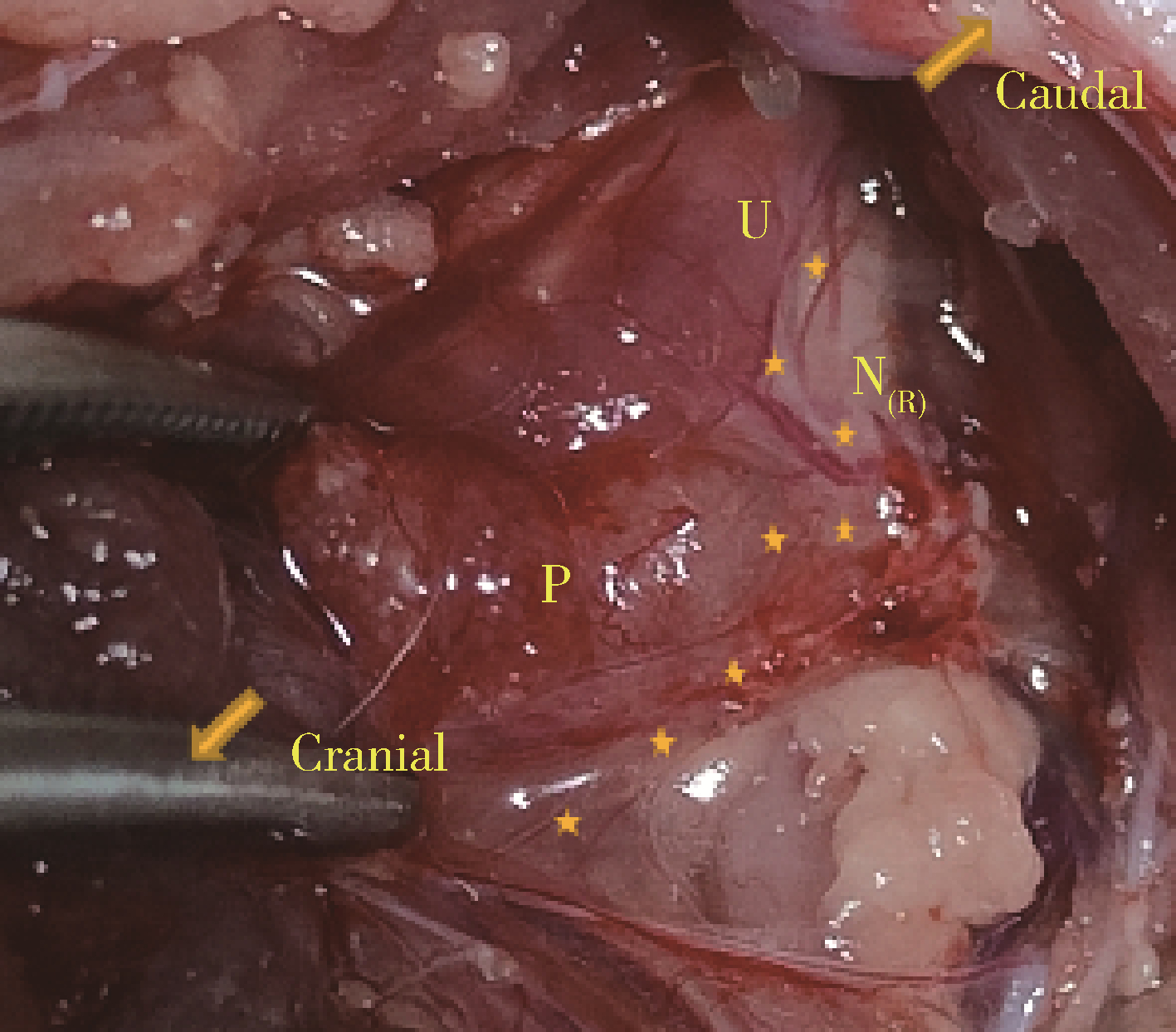
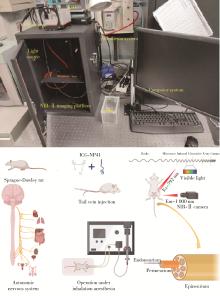
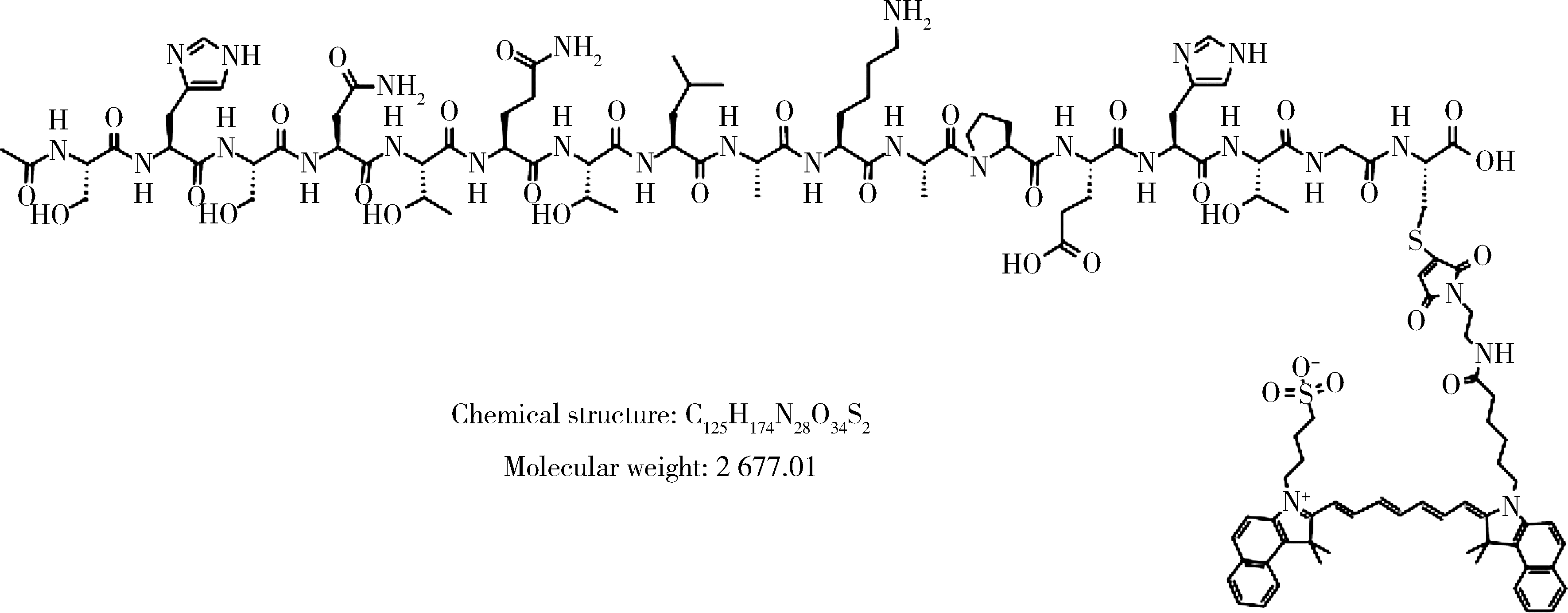
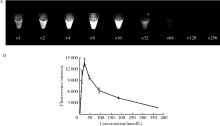
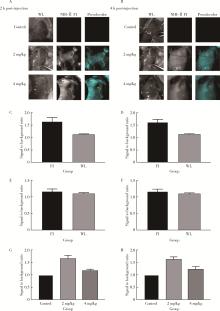
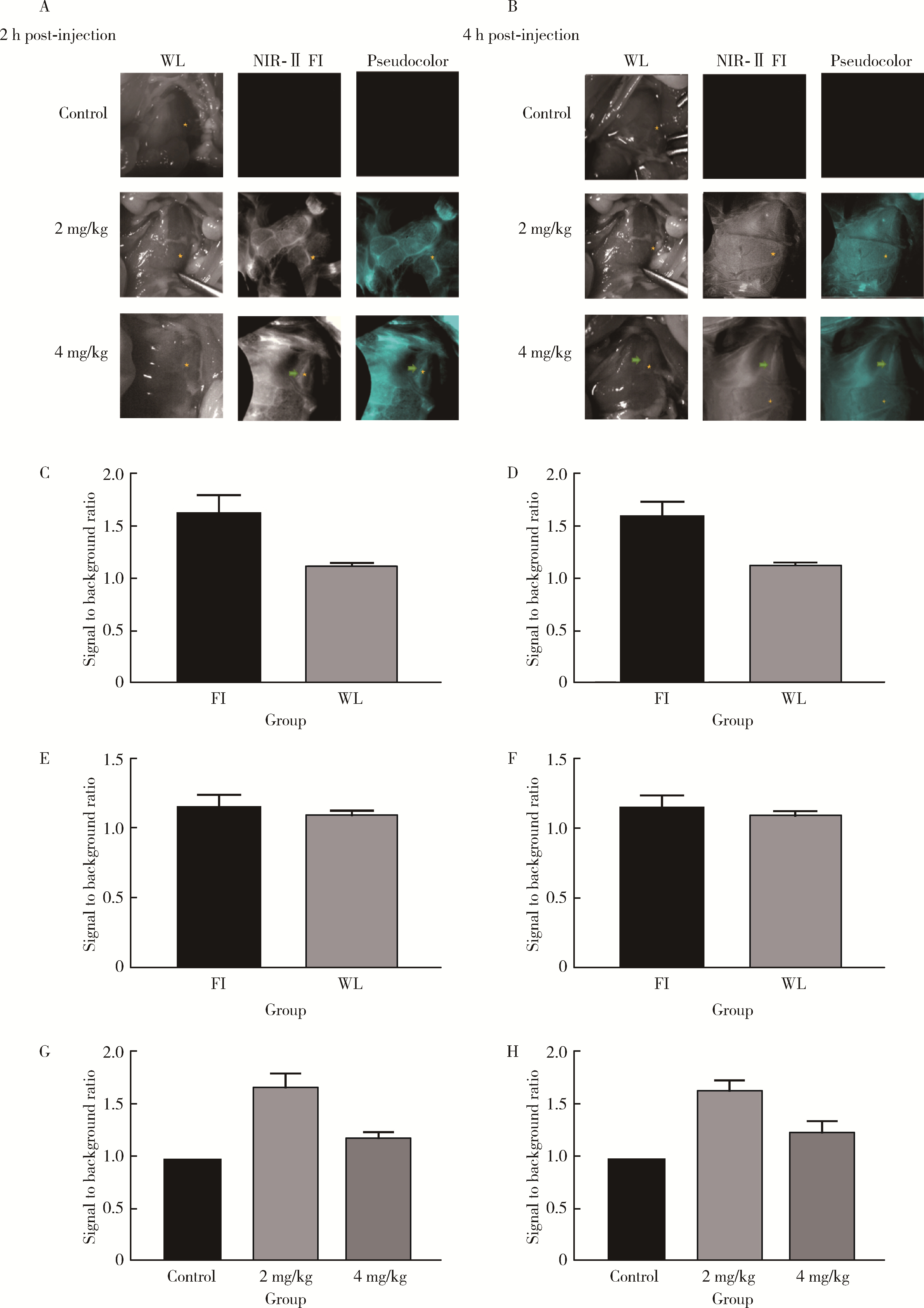
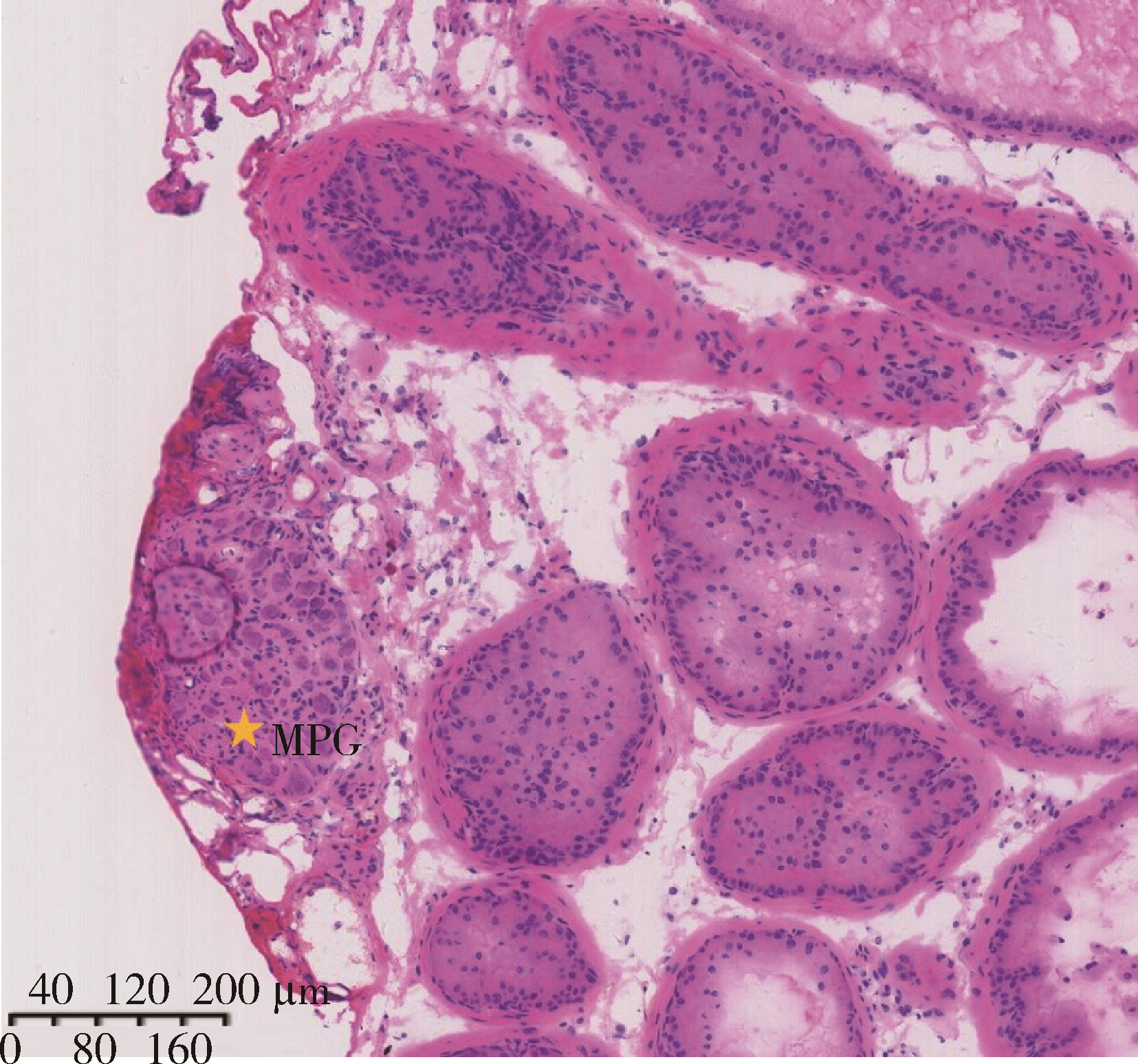
目的: 研究近红外荧光靶向探针ICG-NP41在大鼠体内实验中对前列腺周围神经血管束(neurovascular bundles,NVB)的成像效果。方法: 构建近红外荧光靶向探针ICG-NP41,建立Sprague-Dawley大鼠(250~400 g)NVB体内成像的动物模型,利用本团队自主研发的近红外二区小动物活体成像系统进行大鼠体内试验,采用ImageJ及Origin对采集的图像进行处理,利用GraphPad Prism对荧光信号数据进行统计分析,定量计算探针用于NVB成像的信背比(signal to background ratio, SBR),探索有效的给药剂量及成像时间,并对成像结构进行石蜡病理切片及HE染色。结果: 除对照组大鼠(n=2)外,两组尾静脉注射ICG-NP41的大鼠(n=2)均在给药后2 h、4 h后于NIR-Ⅱ荧光模式下拍摄到右侧NVB中的海绵体神经。给药后2 h和4 h,2 mg/kg组大鼠的海绵体神经在荧光模式下的平均SBR分别为1.651±0.142和1.619±0.110,均高于白光模式(1.111±0.036),但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);4 mg/kg组大鼠的海绵体神经在荧光模式下的平均SBR分别为1.168±0.066和1.219±0.118,均高于白光模式(1.081±0.040),但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。给药后2 h和4 h,2 mg/kg和4 mg/kg组大鼠的海绵体神经在荧光模式下的平均SBR均高于对照组(SBR=1),2 mg/kg组的平均SBR均高于4 mg/kg组,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。通过半高宽法测量神经的平均直径约为(178±15) μm。石蜡切片HE染色可见右侧盆腔大神经节。结论: 近红外荧光靶向探针ICG-NP41能够用于大鼠前列腺周围NVB的术中实时成像,为根治性前列腺切除术中实时定位NVB提供了一种可供转化的有效手段。
中图分类号:
- R699.8
| 1 | Mazariego CG , Egger S , King MT , et al. Fifteen year quality of life outcomes in men with localised prostate cancer: Population based Australian prospective study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 371, 3503. |
| 2 |
Schatloff O , Chauhan S , Sivaraman A , et al. Anatomic grading of nerve sparing during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 61 (4): 796- 802.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.12.048 |
| 3 |
Song WH , Park JH , Tae BS , et al. Establishment of novel intraoperative monitoring and mapping method for the cavernous nerve during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Results of the phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ, first-in-human, feasibility study[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 78 (2): 221- 228.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.04.042 |
| 4 |
Yoon Y , Jeon SH , Park YH , et al. Visualization of prostatic nerves by polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography[J]. Biomed Opt Express, 2016, 7 (9): 3170- 3183.
doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.003170 |
| 5 | 陈欣然, 王保军, 高宇, 等. 全息影像技术在机器人根治性前列腺切除术中的应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42 (7): 497- 501. |
| 6 |
Mieog JSD , Achterberg FB , Zlitni A , et al. Fundamentals and developments in fluorescence-guided cancer surgery[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2022, 19 (1): 9- 22.
doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00548-3 |
| 7 |
Walsh EM , Cole D , Tipirneni KE , et al. Fluorescence imaging of nerves during surgery[J]. Ann Surg, 2019, 270 (1): 69- 76.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003130 |
| 8 |
Whitney MA , Crisp JL , Nguyen LT , et al. Fluorescent peptides highlight peripheral nerves during surgery in mice[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2011, 29 (4): 352- 356.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1764 |
| 9 |
Hingorani DV , Whitney MA , Friedman B , et al. Nerve-targeted probes for fluorescence-guided intraoperative imaging[J]. Theranostics, 2018, 8 (15): 4226- 4237.
doi: 10.7150/thno.23084 |
| 10 | Liu X, Lovell P, Cruz DR, et al. Novel intra-operative peripheral nerve agent for fluorescence guided imaging. Symposium on Clinical and Translational Neurophotonics 2020 held at SPIE BiO Conference, February 01, 2020[C]. San Francisco, CA: Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering, 2020. |
| 11 |
Chen Y , Zhang H , Lei Z , et al. Recent advances in intraoperative nerve bioimaging: Fluorescence-guided surgery for nerve preservation[J]. Small Struct, 2020, 1 (1): 2000036.
doi: 10.1002/sstr.202000036 |
| 12 |
Uetani H , Nakaura T , Kitajima M , et al. A preliminary study of deep learning-based reconstruction specialized for denoising in high-frequency domain: Usefulness in high-resolution three-dimensional magnetic resonance cisternography of the cerebellopontine angle[J]. Neuroradiology, 2021, 63 (1): 63- 71.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02513-w |
| 13 |
Antaris AL , Chen H , Diao S , et al. A high quantum yield molecule-protein complex fluorophore for near-infrared Ⅱ imaging[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8, 15269.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms15269 |
| 14 | Hu Z , Fang C , Li B , et al. First-in-human liver-tumour surgery guided by multispectral fluorescence imaging in the visible and near-infrared-Ⅰ/Ⅱ windows[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2020, 4 (3): 259- 271. |
| 15 |
Qu Q , Nie H , Hou S , et al. Visualisation of pelvic autonomic nerves using NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence imaging[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49 (13): 4752- 4754.
doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05895-6 |
| 16 |
Glasgow HL , Whitney MA , Gross LA , et al. Laminin targeting of a peripheral nerve-highlighting peptide enables degenerated nerve visualization[J]. PNAS, 2016, 113 (45): 12774- 12779.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611642113 |
| 17 |
Hussain T , Nguyen LT , Whitney M , et al. Improved facial nerve identification during parotidectomy with fluorescently labeled peptide[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126 (12): 2711- 2717.
doi: 10.1002/lary.26057 |
| 18 | Jiang YF , Ngyen Q , Whitney M , et al. Vagal innervation of the esophagus and stomach: Visualized using a novel nerve peptide (NP41)[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152 (5): S932. |
| 19 |
You H , Shang W , Min X , et al. Sight and switch off: Nerve density visualization for interventions targeting nerves in prostate cancer[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6 (6): eaax6040.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6040 |
| 20 |
Haney NM , Nguyen HMT , Honda M , et al. Bilateral cavernous nerve crush injury in the rat model: A comparative review of pharmacologic interventions[J]. Sex Med Rev, 2018, 6 (2): 234- 241.
doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.07.007 |
| 21 |
Barth CW , Gibbs SL . Direct administration of nerve-specific contrast to improve nerve sparing radical prostatectomy[J]. Theranostics, 2017, 7 (3): 573- 593.
doi: 10.7150/thno.17433 |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [3] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [4] | 许素环,王蓓蓓,庞秋颖,钟丽君,丁炎明,黄燕波,车新艳. 等体温膀胱冲洗对经尿道前列腺电切术患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [5] | 张帆,陈曲,郝一昌,颜野,刘承,黄毅,马潞林. 术前及术后膜性尿道长度与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [6] | 张帆,黄晓娟,杨斌,颜野,刘承,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺尖部深度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后早期控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [7] | 郝瀚,刘越,陈宇珂,司龙妹,张萌,范宇,张中元,唐琦,张雷,吴士良,宋毅,林健,赵峥,谌诚,虞巍,韩文科. 机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术后患者的控尿恢复时间[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 697-703. |
| [8] | 黄炳伟,王杰,张鹏,李喆,毕泗成,王强,岳才博,杨昆霖,李学松,周利群. 吲哚菁绿在复杂上尿路修复手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [9] | 张树栋,洪鹏,王滨帅,邓绍晖,张帆,陶立元,曹财广,胡振华,马潞林. 吲哚菁绿标记的荧光实时显影技术在腹腔镜肾部分切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 657-662. |
| [10] | 张帆,张树栋,肖春雷,黄毅,马潞林. 80岁及以上前列腺癌患者行腹腔镜前列腺根治性切除术围手术期参数及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 822-827. |
| [11] | 张帆,肖春雷,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺体积及前列腺突入膀胱长度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 621-625. |
| [12] | 左强,张帆,黄毅,马潞林,陆敏,卢剑. 前列腺癌根治术后病理升级的临床危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 603-606. |
| [13] | 杨竣, 王涛, 张岩, 徐华, 王少刚, 刘继红, 叶章群. 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在老龄大鼠血清及阴茎海绵体中的含量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 582-585. |
| [14] | 刘磊, 侯小飞, 马潞林, 赵磊, 张洪宪. 晚期前列腺癌膀胱出口梗阻患者姑息性经尿道前列腺切除术疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 597-600. |
| [15] | 廖晓星, 邢念增, 乔鹏, 康宁, 张军晖, 牛亦农. “三明治”法尿道重建技术改善腹腔镜下根治性前列腺切除术后早期尿控的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 601-604. |
|
||