北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 448-455. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.011
中国西部5城市中老年人血清25羟基维生素D与握力的相关性
靖婷1,江华2,李婷3,申倩倩1,叶兰1,曾银丹1,梁文欣1,冯罡3,司徒文佑3,张玉梅1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院营养与食品卫生学系,北京 100191
2. 北京大学护理学院,北京 100191
3. 国家乳业技术创新中心,呼和浩特 010110
Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and handgrip strength in middle-aged and elderly people in five cities of Western China
Ting JING1,Hua JIANG2,Ting LI3,Qianqian SHEN1,Lan YE1,Yindan ZENG1,Wenxin LIANG1,Gang FENG3,Man-Yau Szeto Ignatius3,Yumei ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Peking University School of Nursing, Beijing 100191, China
3. National Dairy Technology Innovation Center, Hohhot 010110, China
摘要:
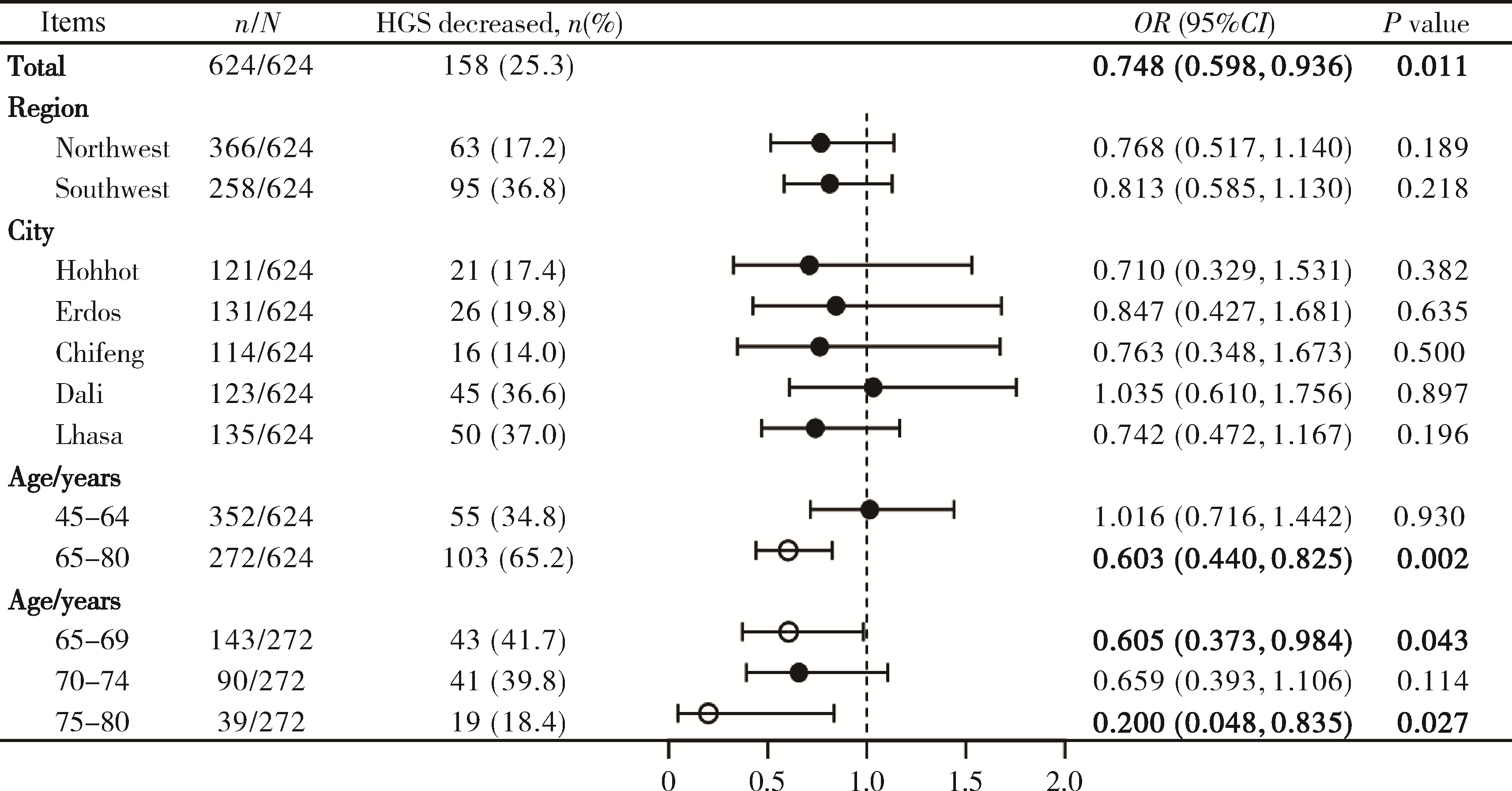
目的: 探究中国西部5城市中老年人血清25羟基维生素D [25-hydroxyvitamin D, 25(OH)D]与握力的相关性。方法: 基于2023年2—7月在中国西部5个城市开展的横断面调查数据,通过问卷收集中老年人的相关人口学特征,通过体格检查记录握力,采集空腹血液样本分离血清并使用高效液相色谱串联质谱法测定血清25(OH)D浓度,使用卡方检验进行组间比较,使用Logistic回归分析西部5城市中老年人血清25(OH)D与握力的相关性。结果: 我国西部5城市中老年人维生素D的缺乏率和不足率分别为52.9%和34.5% [维生素D缺乏定义为血清25(OH)D总浓度 < 20 μg/L,维生素D不足定义为血清25(OH)D总浓度为20~30 μg/L],高龄、女性、采样季节在冬季的中老年人血清25(OH)D水平更低(P < 0.05)。25.3%的中老年人发生了握力减退,65~80岁25(OH)D缺乏的老年人握力减退的发生率高于25(OH)D不足的老年人(45.0% vs. 32.6%)和25(OH)D充足的老年人(45.0% vs. 20.6%);25(OH)D缺乏的75~80岁老年人握力减退的发生率最高(62.1%),25(OH)D不足组次之(11.1%,P < 0.05)。与25(OH)D充足的中老年人相比,25(OH)D缺乏的中老年人发生握力减退的风险增加1.4倍(OR=2.403,95%CI:1.202~4.804,P=0.013),未发现25(OH)D不足与中老年人握力状况存在显著相关关系;血清总25(OH)D每增加5 μg/L,其发生握力减退的风险降低13.1%(OR=0.869,95%CI:0.768~0.982,P=0.025);血清25(OH)D2每增加5 μg/L,其发生握力减退的风险降低24.1%(OR=0.759,95%CI:0.582~0.990,P=0.042);未发现血清25(OH)D3含量与握力减退风险存在显著相关关系。血清25(OH)D水平每增加一个等级(缺乏、不足和充足),中老年人发生握力减退的风险降低25.2%(OR=0.748,95%CI:0.598~0.936,P=0.011)。在65~80岁和65~69岁的两组调查对象中,血清25(OH)D水平每增加一个等级,发生握力减退的风险降低40.0%,而在75~80岁的调查对象中,25(OH)D水平每增加一个等级,发生握力减退的风险降低80.0%。结论: 中国西部5城市中老年人血清总25(OH)D和25(OH)D2含量与握力状况存在一定关联。
中图分类号:
- R153.3
| 1 | Zhang W , Stoecklin E , Eggersdorfer M .A glimpse of vitamin D status in Mainland China[J].Nutrition,2013,29(7/8):953-957. |
| 2 |
van Schoor N , Lips P .Global overview of vitamin D status[J].Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am,2017,46(4):845-870.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.002 |
| 3 | 杨文婕, 葛淼, 王晶, 等. 健康老年人血清25-羟基维生素D参考值的地理差异与地理影响因素——以中国为例[C]//中国环境科学学会2021年科学技术年会论文集(三). 西安: 陕西师范大学地理科学与旅游学院健康地理研究所, 2021: 8. |
| 4 |
Charoenngam N , Holick MF .Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease[J].Nutrients,2020,12(7):2097.
doi: 10.3390/nu12072097 |
| 5 |
Chen LK , Woo J , Assantachai P , et al.Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J].J Am Med Dir Assoc,2020,21(3):300-307.
doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012 |
| 6 |
Haslam A , Johnson MA , Hausman DB , et al.Vitamin D status is associated with grip strength in centenarians[J].J Nutr Gerontol Geriatr,2014,33(1):35-46.
doi: 10.1080/21551197.2013.867825 |
| 7 |
Mendoza-Garcés L , Velázquez-Alva MC , Cabrer-Rosales MF , et al.Vitamin D deficiency is associated with handgrip strength, nutritional status and T2DM in community-dwelling older Mexican women: A cross-sectional study[J].Nutrients,2021,13(3):736.
doi: 10.3390/nu13030736 |
| 8 |
Kocak MZ , Aktas G , Atak B , et al.The association between vitamin D levels and handgrip strength in elderly men[J].Acta Endocrinol (Buchar),2020,16(2):263-266.
doi: 10.4183/aeb.2020.263 |
| 9 |
Zeng J , Li T , Sun B , et al.Change of vitamin D status and all-cause mortality among Chinese older adults: A population-based cohort study[J].BMC Geriatr,2022,22(1):245.
doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-02956-1 |
| 10 |
Kitsu T , Kabasawa K , Ito Y , et al.Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with low grip strength in an older Japanese population[J].J Bone Miner Metab,2020,38(2):198-204.
doi: 10.1007/s00774-019-01040-w |
| 11 | 方瑞, 古雪, 李傅冬, 等.老年人饮食行为对握力减退的影响研究[J].预防医学,2022,34(11):1161-1166. |
| 12 |
Müller MJ , Volmer DA .Mass spectrometric profiling of vitamin D metabolites beyond 25-hydroxyvitamin D[J].Clin Chem,2015,61(8):1033-1048.
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2015.241430 |
| 13 |
Holick MF , Binkley NC , Bischoff-Ferrari HA , et al.Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2011,96(7):1911-1930.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385 |
| 14 |
黄馨懿, 章轶立, 孙凯, 等.社区老年人维生素D水平调查及其与健康相关生命质量的相关性研究[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(36):4515-4521.
doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0445 |
| 15 |
Chan Y , Cai D , Guo R , et al.Evaluation of the deficiency status of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and associated factors in Southwest China: A hospital-based retrospective cross-sectional analysis of a low-latitude, high-altitude, multiracial region[J].Nutr Bull,2023,48(4):535-545.
doi: 10.1111/nbu.12645 |
| 16 |
Gouni-Berthold I , Berthold HK .Vitamin D and vascular disease[J].Curr Vasc Pharmacol,2021,19(3):250-268.
doi: 10.2174/18756212MTA1fMzIz1 |
| 17 |
Cui A , Xiao P , Ma Y , et al.Prevalence, trend, and predictor analyses of vitamin D deficiency in the US population, 2001-2018[J].Front Nutr,2022,9,965376.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.965376 |
| 18 | 陈敏敏, 姜鑫, 杜艳萍, 等. 上海社区65岁以上老年人血清维生素D水平影响因素的研究[C]// 2015年老年医学学术年会论文汇编. 杭州: 浙江省科学技术协会, 2015. |
| 19 |
You H , Shin HR , Song S , et al.Vitamin D intake and bone mineral density in Korean adults: Analysis of the 2009-2011 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey[J].Nutr Res Pract,2022,16(6):775-788.
doi: 10.4162/nrp.2022.16.6.775 |
| 20 |
Zhang H , Zhu A , Liu L , et al.Assessing the effects of ultraviolet radiation, residential greenness and air pollution on vitamin D levels: A longitudinal cohort study in China[J].Environ Int,2022,169,107523.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107523 |
| 21 | 胥俊越, 陈渲宇, 张莎娜, 等.北京地区人群血清25羟基维生素D水平检测及维生素D营养状态分析[J].临床军医杂志,2022,50(11):1197-1199. |
| 22 |
Aspell N , Laird E , Healy M , et al.Vitamin D deficiency is associated with impaired muscle strength and physical performance in community-dwelling older adults: Findings from the English longitudinal study of ageing[J].Clin Interv Aging,2019,14,1751-1761.
doi: 10.2147/CIA.S222143 |
| 23 |
Shi Z , Shi K , Zhang Z , et al.Mediating effect of physical activity in the association between low 25-hydroxyvitamin D and frailty trajectories: The English longitudinal study of ageing[J].Nutrients,2022,14(11):2292.
doi: 10.3390/nu14112292 |
| 24 |
Luo S , Chen X , Hou L , et al.The relationship between Sarcopenia and vitamin D levels in adults of different ethnicities: Findings from the West China health and aging trend study[J].J Nutr Health Aging,2021,25(7):909-913.
doi: 10.1007/s12603-021-1645-z |
| 25 |
Wang J , Wang X , Gu Y , et al.Vitamin D is related to handgrip strength in adult men aged 50 years and over: A population study from the TCLSIH cohort study[J].Clin Endocrinol (Oxf),2019,90(5):753-765.
doi: 10.1111/cen.13952 |
| 26 |
Zhang JL , Poon CC , Wong MS , et al.Vitamin D supplementation improves handgrip strength in postmenopausal women: A systema-tic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J].Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2022,13,863448.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.863448 |
| 27 |
Park S , Ham JO , Lee BK .A positive association of vitamin D deficiency and sarcopenia in 50 year old women, but not men[J].Clin Nutr,2014,33(5):900-905.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2013.09.016 |
| 28 |
Kim BJ , Kwak MK , Lee SH , et al.Lack of association between vitamin D and hand grip strength in Asians: A nationwide population-based study[J].Calcif Tissue Int,2019,104(2):152-159.
doi: 10.1007/s00223-018-0480-7 |
| 29 |
Feng F , Shi G , Chen H , et al.Comprehensive interventions including vitamin D effectively reduce the risk of falls in elderly osteoporotic patients[J].Orthop Surg,2021,13(4):1262-1268.
doi: 10.1111/os.13009 |
| 30 |
Kocaer A , Sarpel T , Gökcen N , et al.Proximal muscle strength as a predictor of vitamin D insufficiency in elderly[J].Turk J Phys Med Rehabil,2021,67(1):84-90.
doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2021.5323 |
| 31 |
Prokopidis K , Giannos P , Katsikas Triantafyllidis K , et al.Effect of vitamin D monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle,2022,13(3):1642-1652.
doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12976 |
| 32 |
Rosendahl-Riise H , Spielau U , Ranhoff AH , et al.Vitamin D supplementation and its influence on muscle strength and mobility in community-dwelling older persons: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Hum Nutr Diet,2017,30(1):3-15.
doi: 10.1111/jhn.12394 |
| 33 |
Aschauer R , Unterberger S , Zöhrer PA , et al.Effects of vitamin D3 supplementation and resistance training on 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and functional performance of older adults: A randomized placebo-controlled trial[J].Nutrients,2021,14(1):86.
doi: 10.3390/nu14010086 |
| [1] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [2] | 张浩宇,石逸雯,潘薇,刘爱萍,孙昕霙,李曼,张旭熙. 基于不同失能水平的老年人照料需求的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 431-440. |
| [3] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [4] | 汤华萌,袁典琪,王明星,杨晗冰,郭超. 数字融入和健康生活方式对社会经济状况与老年人抑郁关系的序列中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [5] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [6] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [7] | 刘光奇,庞元捷,吴疆,吕敏,于孟轲,李雨橦,黄旸木. 2013—2019年流感季北京市住院老年人流感疫苗接种趋势分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 505-510. |
| [8] | 刘杰,郭超. 正/负性情绪对中国老年人死亡风险影响的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 255-260. |
| [9] | 李佳,徐钰,王优雅,高占成. 老年流感肺炎的临床特征及D-二聚体与疾病严重程度的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 153-160. |
| [10] | 敖明昕,李学民,于媛媛,时会娟,黄红拾,敖英芳,王薇. 视觉重建对老年人行走动态足底压力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 907-914. |
| [11] | 彭顺壮, 付茜茜, 冯星淋. 中国中老年居民教育程度与失能发生:社会参与的中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 549-554. |
| [12] | 陈家丽,金月波,王一帆,张晓盈,李静,姚海红,何菁,李春. 老年发病类风湿关节炎的临床特征及其心血管疾病危险因素分析:一项大样本横断面临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1040-1047. |
| [13] | 陈健,左才红,张财义,杨明,张培训. 解剖型髓内钉和股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 283-287. |
| [14] | 徐小凤,陈茜,赵艺璞,胡秀英. 我国西部地区居家老年人生活自理能力调查分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 457-462. |
| [15] | 魏滨,张华,徐懋,李民,王军,张利萍,郭向阳,赵一鸣,周方. 不同麻醉方法对髋部骨折老年患者术后转归的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 1008-1013. |
|
||