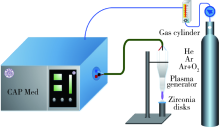
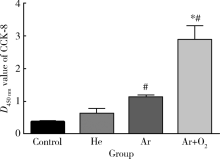
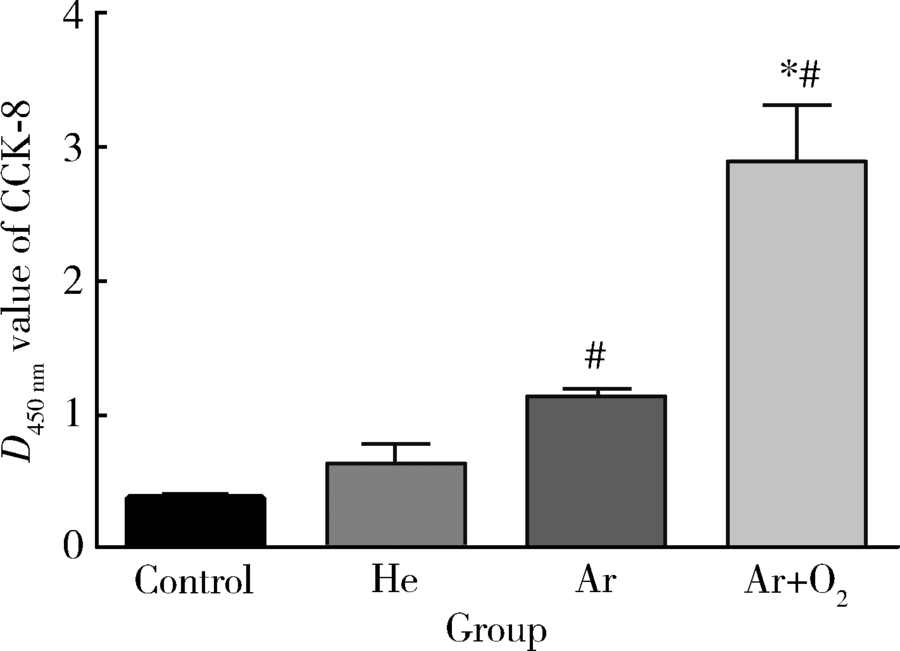
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 315-320. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
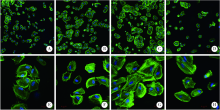
Effect of different plasma treated zirconia on the adhensive behaviour of human gingival fibroblasts
Miao ZHENG1,Ling-lu ZHAN2,Zhi-qiang LIU3,4,He-ping LI3,∆( ),Jian-guo TAN2,∆(
),Jian-guo TAN2,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Stomatology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Engineering Phy-sics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4. College of Mechanical Engineering, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei, China
CLC Number:
- R783.3
| [1] | Kawahara H, Kawahara D, Hashimoto K , et al. Morphologic stu-dies on the biologic seal of titanium dental implants. Report Ⅰ. In vitro study on the epithelialization mechanism around the dental implant[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1998,13(4):457-464. |
| [2] |
Schwarz F, Derks J, Monje A , et al. Peri-implantitis[J]. J Periodontol, 2018,89(Suppl 1):S267-S290.
doi: 10.1002/JPER.16-0350 |
| [3] |
Kim YS, Shin SY, Moon SK , et al. Surface properties correlated with the human gingival fibroblasts attachment on various materials for implant abutments: a multiple regression analysis[J]. Acta Odontol Scand, 2015,73(1):38-47.
doi: 10.3109/00016357.2014.949845 |
| [4] |
Kim JH, Lee MA, Han GJ , et al. Plasma in dentistry: a review of basic concepts and applications in dentistry[J]. Acta Odontol Scand, 2014,72(1):1-12.
doi: 10.3109/00016357.2013.795660 |
| [5] |
Zheng M, Yang Y, Liu XQ , et al. Enhanced biological behavior of in vitro human gingival fibroblasts on cold plasma-treated zirconia[J]. PLoS One, 2015,10:e0140278.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140278 |
| [6] |
Yin L, Nakanishi Y, Alao AR , et al. A review of engineered zirconia surfaces in biomedical applications[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2017,65:284-290.
doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.04.057 |
| [7] |
Rigolin MSM, de Avila ED, Basso FG , et al. Effect of different implant abutment surfaces on OBA-09 epithelial cell adhesion[J]. Microsc Res Tech, 2017,80(12):1304-1309.
doi: 10.1002/jemt.22941 |
| [8] |
Abrahamsson I, Zitzmann NU, Berglundh T , et al. The mucosal attachment to titanium implants with different surface characteristics: an experimental study in dogs[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2002,29(5):448-455.
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.2002.290510.x |
| [9] |
Schwarz F, Herten M, Sager M , et al. Histological and immunohistochemical analysis of initial and early subepithelial connective tissue attachment at chemically modified and conventional SLA titanium implants. A pilot study in dogs[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2007,11(3):245-255.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-007-0110-7 |
| [10] |
Schwarz F, Mihatovic I, Becker J , et al. Histological evaluation of different abutments in the posterior maxilla and mandible: an experimental study in humans[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2013,40(8):807-815.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.2013.40.issue-8 |
| [11] |
Canullo L, Genova T, Wang HL , et al. Plasma of argon increases cell attachment and bacterial decontamination on different implant surfaces[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2017,32(6):1315-1323.
doi: 10.11607/jomi.5777 |
| [12] |
Yang Y, Zhou J, Liu X , et al. Ultraviolet light-treated zirconia with different roughness affects function of human gingival fibroblasts in vitro: the potential surface modification developed from implant to abutment[J]. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2015,103(1):116-124.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.v103.1 |
| [13] |
Hoshi N, Negishi H, Okada S , et al. Response of human fibroblasts to implant surface coated with titanium dioxide photocatalytic films[J]. J Prosthodont Res, 2010,54(4):185-191.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpor.2010.04.005 |
| [14] |
An N, Rausch-fan X, Wieland M , et al. Initial attachment, subsequent cell proliferation/viability and gene expression of epithelial cells related to attachment and wound healing in response to dif-ferent titanium surfaces[J]. Dent Mater, 2012,28(12):1207-1214.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2012.08.007 |
| [15] |
Canullo L, Genova T, Tallarico M , et al. Plasma of argon affects the earliest biological response of different implant surfaces: an in vitro comparative study[J]. J Dent Res, 2016,95(5):566-573.
doi: 10.1177/0022034516629119 |
| [1] | Shan HE,Xin CHEN,Qi CHENG,Lingjiang ZHU,Peiyu ZHANG,Shuting TONG,Jing XUE,Yan DU. Tofacitinib inhibits the transformation of lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts through JAK/STAT3 pathway [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 505-511. |
| [2] | Yuru HU,Juan LIU,Wenjing LI,Yibing ZHAO,Qiqiang LI,Ruifang LU,Huanxin MENG. Relationship between short-chain fatty acids in the gingival crevicular fluid and periodontitis of stage Ⅲ or Ⅳ [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 332-337. |
| [3] | Jiayun DONG,Xuefen LI,Ruifang LU,Wenjie HU,Huanxin MENG. Histopathological characteristics of peri-implant soft tissue in reconstructed jaws with vascularized bone flaps [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 25-31. |
| [4] | Yuan PAN,Hang GU,Han XIAO,Lijun ZHAO,Yiman TANG,Wenshu GE. Ubiquitin-specific protease 42 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 9-16. |
| [5] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [6] | Qian DING,Wen-jin LI,Feng-bo SUN,Jing-hua GU,Yuan-hua LIN,Lei ZHANG. Effects of surface treatment on the phase and fracture strength of yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia implants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [7] | Xiao-juan ZHU,Hong ZHANG,Shuang ZHANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ling XU,Ting LI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [8] | Fei SUN,Jian LIU,Si-qi LI,Yi-ping WEI,Wen-jie HU,Cui WANG. Profiles and differences of submucosal microbial in peri-implantitis and health implants: A cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [9] | Wei-wei LI,Hu CHEN,Yong WANG,Yu-chun SUN. Research on friction and wear behaviors of silicon-lithium spray coating on zirconia ceramics [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 94-100. |
| [10] | Yue WANG,Shuang ZHANG,Hong ZHANG,Li LIANG,Ling XU,Yuan-jia CHENG,Xue-ning DUAN,Yin-hua LIU,Ting LI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 853-862. |
| [11] | Jin-feng JIA,Fei LIANG,Jian-wei HUANG,Hao WANG,Pu-qing HAN. Effect of artificial liver with double plasma molecular absorb system model on patients' platelets and corresponding treatment strategy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 548-551. |
| [12] | LI Jia,XU Yu,WANG You-ya,GAO Zhan-cheng. Clinical characteristics of influenza pneumonia in the elderly and relationship between D-dimer and disease severity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 153-160. |
| [13] | YUAN Lin-tian,MA Li-sha,LIU Run-yuan,QI wei,ZHANG Lu-dan,WANG Gui-yan,WANG Yu-guang. Computer simulation of molecular docking between methylene blue and some proteins of Porphyromonas gingivalis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 23-30. |
| [14] | WANG Zheng,DING Qian,GAO Yuan,MA Quan-quan,ZHANG Lei,GE Xi-yuan,SUN Yu-chun,XIE Qiu-fei. Effect of porous zirconia ceramics on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 31-39. |
| [15] | ZHOU Chuan-xiang,ZHOU Zheng,ZHANG Ye,LIU Xiao-xiao,GAO Yan. Clinicopathological study in 28 cases of oral basaloid squamous cell carcinomas [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 62-67. |
|
||