北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 126-132. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.016
基于多视图立体视觉的无牙颌种植固定修复软组织数字印模的方法
杨咏涛1,2, 田淯文2, 单珅瑶2, 李文博2, 商相宜2, 王艺蓁2, 郭殊玮1, 高梓翔1, 温奥楠1, 赵一姣1,2,*( ), 王勇1,2,*(
), 王勇1,2,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔医学数字化研究中心, 口腔修复教研室, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 国家卫生健康委员会口腔数字医学重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院, 北京 100191
A multi-view stereo vision methodology for digital soft-tissue impressions in fixed implant rehabilitation of edentulous patients
Yongtao YANG1,2, Yuwen TIAN2, Shenyao SHAN2, Wenbo LI2, Xiangyi SHANG2, Yizhen WANG2, Shuwei GUO1, Zixiang GAO1, Aonan WEN1, Yijiao ZHAO1,2,*( ), Yong WANG1,2,*(
), Yong WANG1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Center of Digital Dentistry, Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
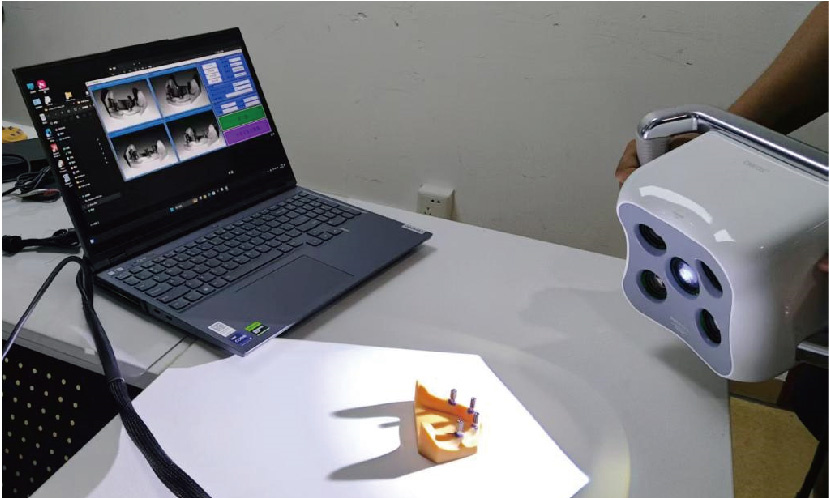
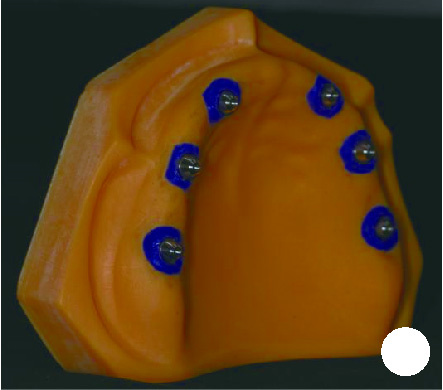
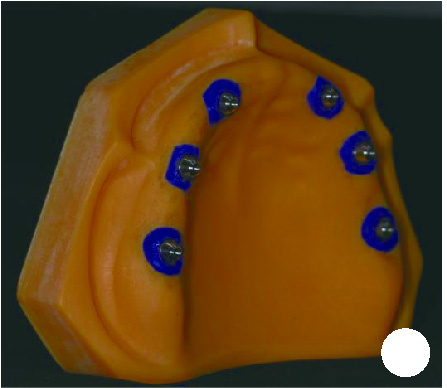
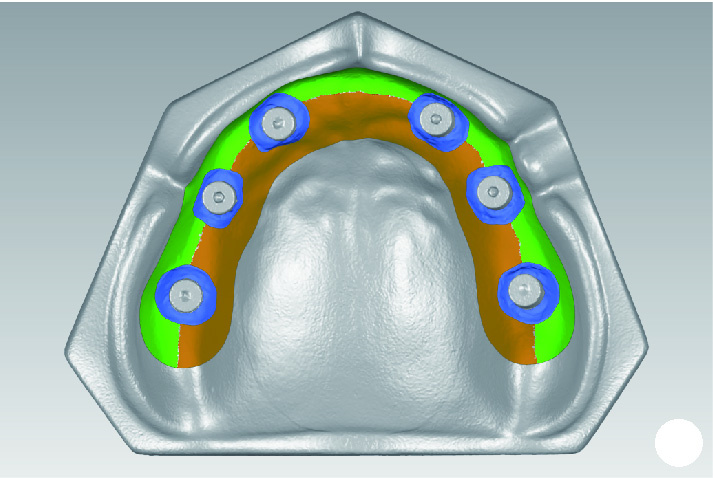
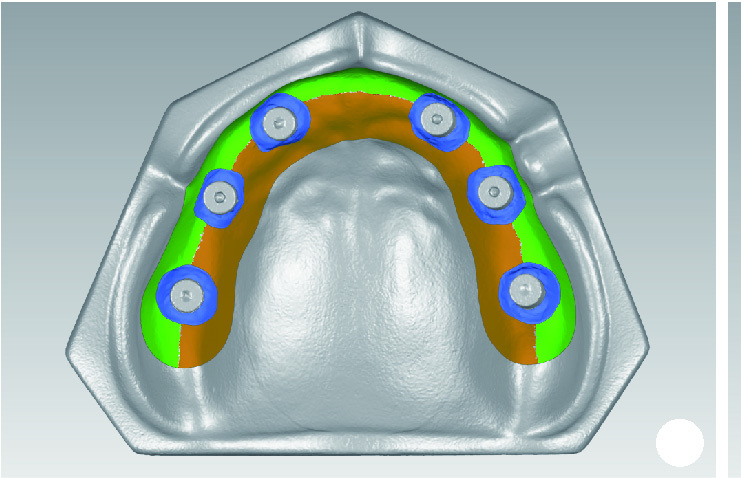
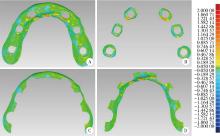
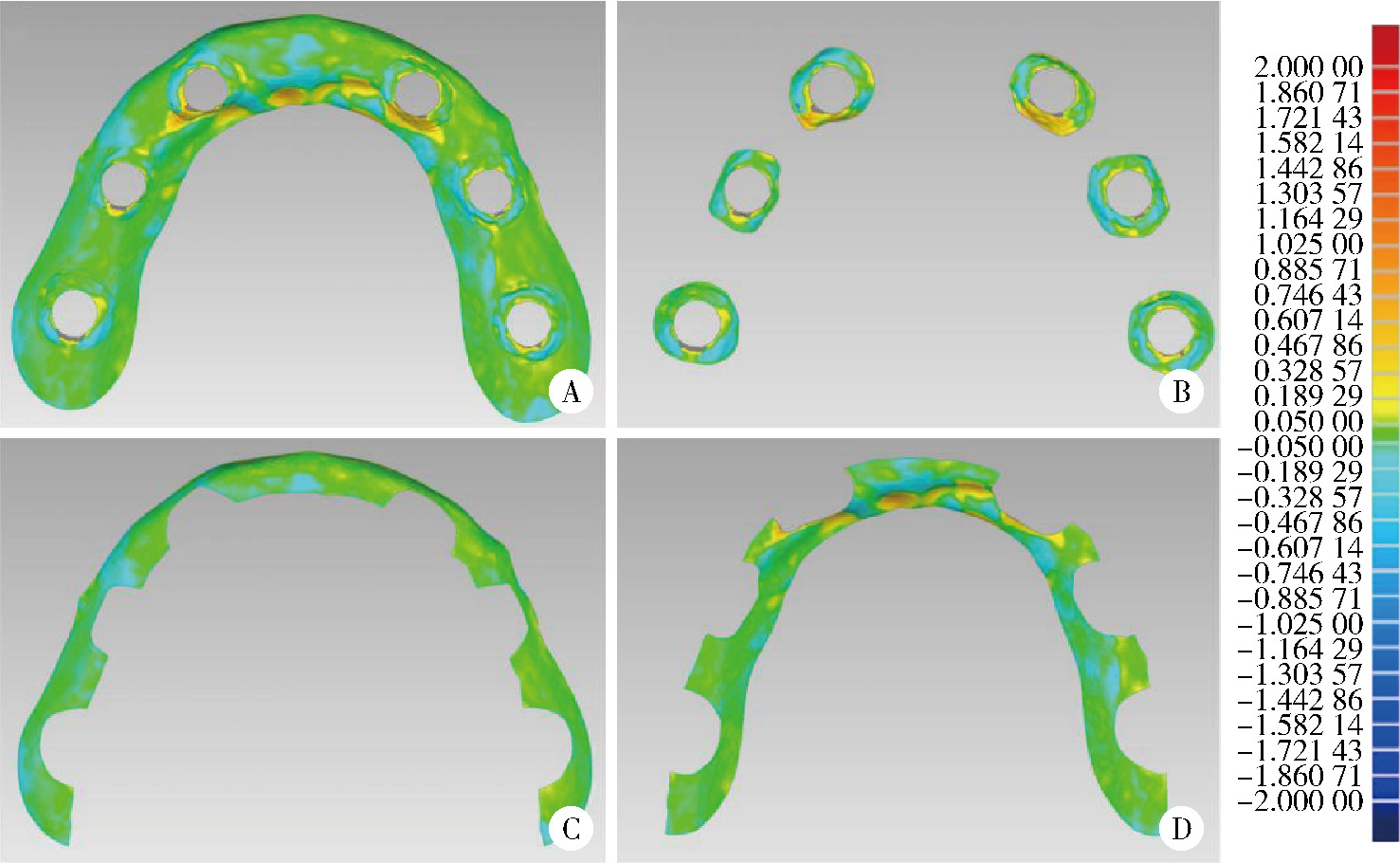
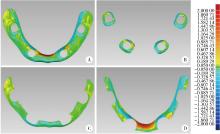
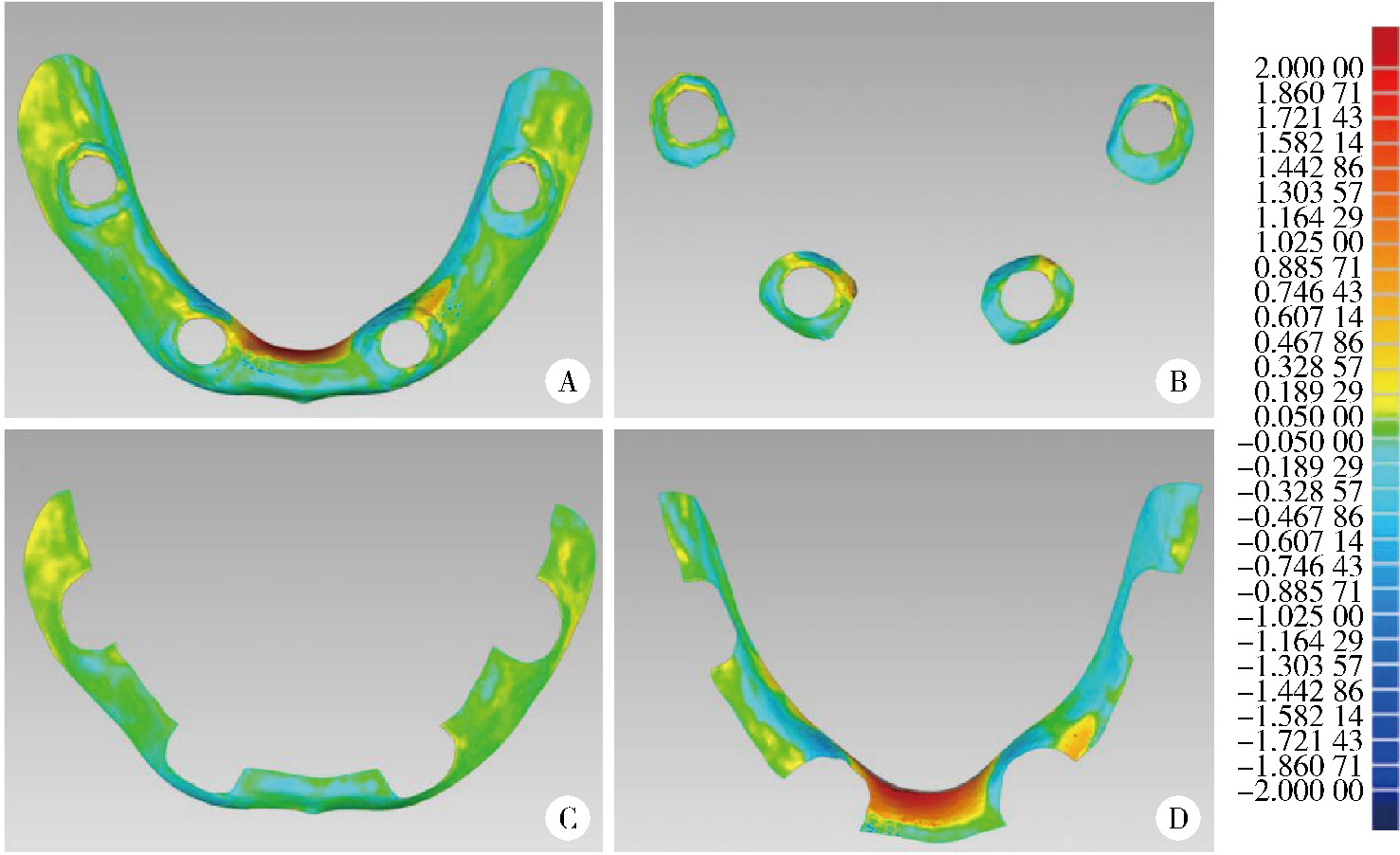
目的: 探索基于多视图立体视觉技术的无牙颌种植固定修复软组织形态重建的方法及其可行性, 初步评价该方法在体外重建软组织形态的正确度。方法: 设计并打印一对无牙颌种植树脂模型, 上颌放置6枚替代体, 下颌放置4枚替代体。以自主研发(简称自研)的摄影测量四目相机组加自动化重建软件RealityScan 2.0.1作为实验组, 将自研扫描杆安装于替代体, 手持自研相机组在体外拍摄模型图像, 每次拍摄数量4×12张, 导入软件重建三维模型, 导出".stl"数据(n=10);以口内扫描仪作为对照组, 将扫描帽安装于替代体, 使用口内扫描仪扫描模型的三维形态, 输出".stl"数据(n=10);使用模型扫描仪EX-PRO获取上、下颌树脂模型的".stl"数据各1例, 作为参考数据。将以上数据导入Geomagic Wrap 2021软件, 分别计算实验组、对照组数据与参考数据三维形态的均方根(root mean squre, RMS), 代表实验组、对照组的三维形态偏差大小, 并评价正确度, 评价范围为牙槽嵴区域、种植体周围软组织区域、颊侧区域和舌侧区域。结果: 在上颌中, 实验组在牙槽嵴区域、种植体周围软组织区域和舌侧区域的RMS均显著高于对照组[(124.89±21.30) μm vs. (53.90±8.93) μm、(157.74±19.13) μm vs. (67.03±3.94) μm、(146.01±33.87) μm vs. (46.20±11.19) μm, 均P < 0.001], 实验组在颊侧区域的RMS略低于对照组[(50.56±8.34) μm vs. (53.83±12.66) μm, P=0.571];在下颌中, 实验组在牙槽嵴区域、种植体周围软组织区域和舌侧区域的RMS均显著高于对照组[(254.04±88.42) μm vs. (58.28±38.96) μm、(165.18±21.30) μm vs. (70.48±28.20) μm、(421.75±59.51) μm vs. (54.59±36.77) μm, 均P < 0.001];颊舌侧两组相比较, 实验组上颌、下颌的舌侧RMS均显著高于颊侧(均P < 0.001), 对照组上颌舌侧RMS显著低于颊侧(P < 0.05), 下颌舌侧RMS高于颊侧(P=0.378)。结论: 自研相机组配合多视图立体视觉重建软件可实现软组织三维形态记录, 为无牙颌种植口外摄影测量设备同步定位多单位种植体空间的位置和获取软组织形态提供了一定的研究基础。
中图分类号:
- R783.6
| 1 |
周永胜. 口腔修复学[M]. 3版 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2020.
|
| 2 |
Rutkūnas V, Gedrimiene A, Mischitz I, et al. EPA consensus project paper: Accuracy of photogrammetry devices, intraoral scanners, and conventional techniques for the full-arch implant impressions: A systematic review [J/OL]. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent, 2023 [2023-6-13]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37314199/.
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2022.09.010 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2021.09.015 |
| 5 |
杨咏涛, 温奥楠, 商相宜, 等. 基于摄影测量技术的无牙颌种植口外扫描系统的研发和精度评价[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2025, 60 (8): 863- 870.
|
| 6 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2025.105654 |
| 7 |
张力, 刘玉轩, 孙洋杰, 等. 数字航空摄影三维重建理论与技术发展综述[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51 (7): 1437- 1457.
|
| 8 |
龚健雅, 季顺平. 从摄影测量到计算机视觉[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2017, 42 (11): 1518-1522, 1615.
|
| 9 |
Revilla-León M, Cascos R, Barmak AB, et al. Registration accuracy of soft tissue information scan captured using an intraoral scanner and implant position scan recorded using extraoral and intraoral photogrammetry systems [J/OL]. J Prosthet Dent, 2025: S0022-S3913(25)00392-0 [2025-05-30]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40450447/.
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2025.06.015 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.14208 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109780 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2024.105081 |
| 14 |
樊铭瑞, 申冰可, 牛文龙, 等. 基于深度学习的多视图立体视觉综述[J]. 软件学报, 2025, 36 (4): 1692- 1714.
|
| 15 |
Li J, Chen Z, Liu F, et al. Obtaining full-arch implant scan with smartphone video and deep learning: An in vitro investigation on trueness and precision [J/OL]. J Prosthodont, 2025 [2025-03-08]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40055947/.
|
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2025.105559 |
| [1] | 王宇蓝, 曾浩, 张玉峰. 口腔种植中血浆基质的临床转化现状与前沿探索[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 836-840. |
| [2] | 于子杨, 郭厚佐, 蒋析, 韩玮华, 林野. 穿颧种植体上颌窦段成骨的影像学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 967-974. |
| [3] | 王鹃, 邱立新, 尉华杰. 下颌磨牙穿龈形态设计对种植体周围软组织影响的随机对照临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 65-72. |
| [4] | 李虹, 马斐斐, 翁金龙, 杜阳, 吴彬彰, 孙凤. 口腔即刻种植时动态导航系统的种植精度分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 85-90. |
| [5] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [6] | 李穗,马雯洁,王时敏,丁茜,孙瑶,张磊. 上前牙种植单冠修复体切导的数字化设计正确度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [7] | 刘晓强,周寅. 牙种植同期植骨术围术期高血压的相关危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [8] | 丁茜,李文锦,孙丰博,谷景华,林元华,张磊. 表面处理对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体晶相及断裂强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [9] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [10] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [11] | 王鹃,尉华杰,孙井德,邱立新. 预成刚性连接杆用于无牙颌种植即刻印模制取的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 187-192. |
| [12] | 梁峰,吴敏节,邹立东. 后牙区单牙种植修复5年后的临床修复疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 970-976. |
| [13] | 刘晓强,杨洋,周建锋,刘建彰,谭建国. 640例单牙种植术对血压和心率影响的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 390-395. |
| [14] | 周培茹, 蒋析, 华红. 口腔黏膜病患者口腔种植的时机及注意事项[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 5-8. |
| [15] | 李蓬,朴牧子,胡洪成,王勇,赵一姣,申晓婧. 经嵴顶上颌窦底提升术后不植骨同期种植的影像研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 95-101. |
|
||