北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 190-195. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.025
肌萎缩侧索硬化患者经皮内镜下胃造瘘术后早期并发症及相关危险因素分析
- 1. 北京大学第三医院消化科, 北京 100191
2. 清华大学附属北京清华长庚医院消化内科, 北京 102218
Analysis of early complications and risk factors in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Xueli TIAN1, Zhiqiang SONG1, Yonghui HUANG2,*( ), Wei YAO1
), Wei YAO1
- 1. Department of Gastroenterology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital, Beijing 102218, China
摘要:
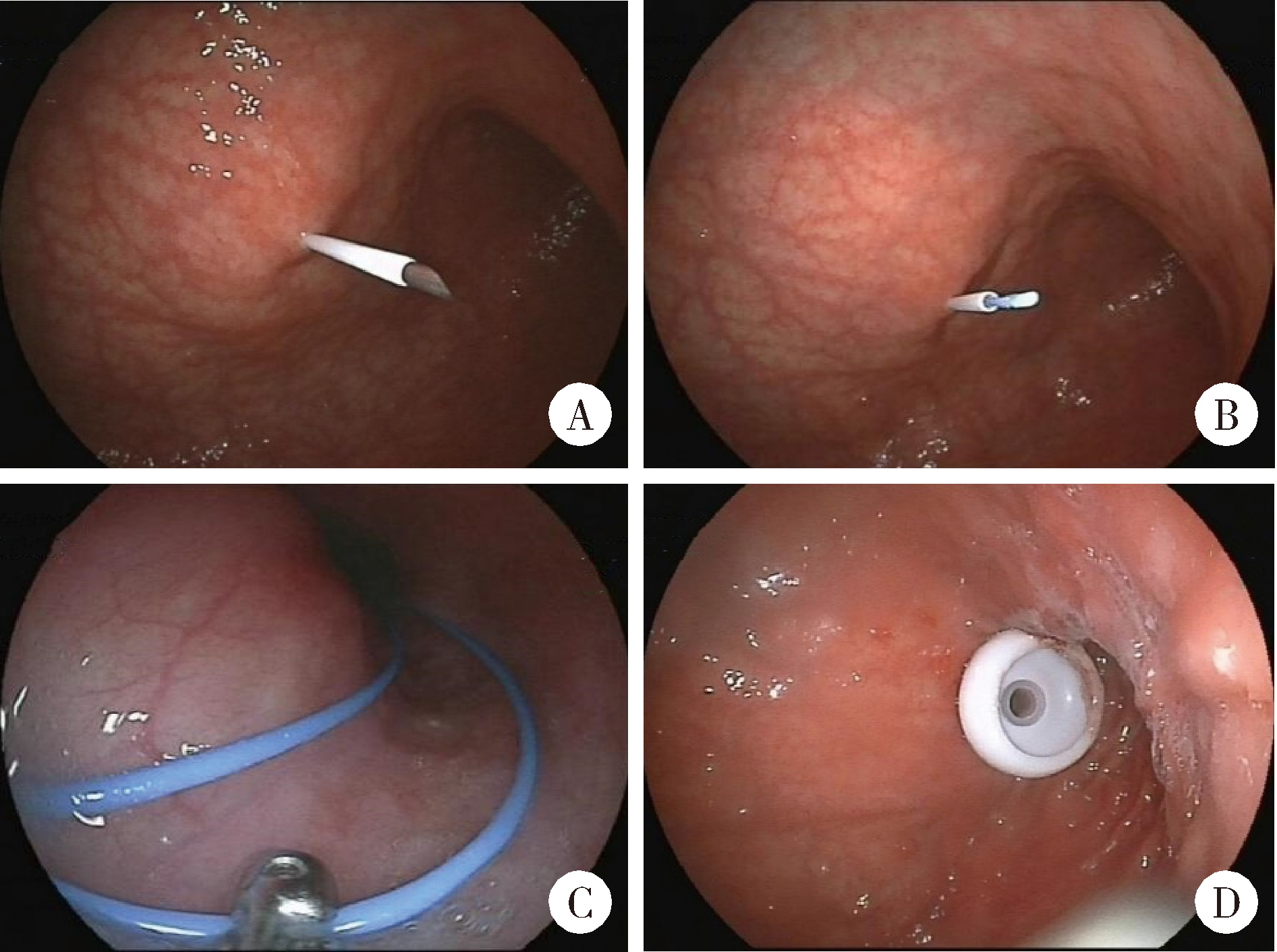
目的: 探讨肌萎缩侧索硬化(amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,ALS)患者经皮内镜下胃造瘘术(percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy,PEG)后发生早期并发症(≤14 d)的临床特征及危险因素。方法: 连续纳入2011年1月至2020年12月在北京大学第三医院首次行PEG的ALS患者,回顾性分析患者的临床资料,明确早期(≤14 d)并发症的发生情况,根据有无并发症以及并发症严重程度进行分组,采用SPSS 27.0统计软件进行数据分析,最终应用多变量Logistic回归模型系统评估早期并发症发生的独立危险因素。结果: 192例PEG均成功完成。97例(51%)男性,ALS发病的平均年龄为(55±11)岁,93例(48%)为延髓起病型。PEG后14 d内40例(21%)发生并发症,均出现发热,16例无明确感染灶,18例呼吸道感染,6例造瘘口感染。13例患者(7%)被判定为严重并发症(11例呼吸道感染,2例造瘘口感染),其中2例呼吸道感染并发呼吸衰竭死亡,余11例经升级抗生素抗感染后好转。未观察到营养管脱落、良性气腹、出血或包埋综合征等并发症。并发症组的手术时间和术后住院时间显著长于无并发症组[(16±5) min vs. (13±5) min,P<0.001; 6 (5, 9) d vs. 5 (3, 7) d,P=0.009]。严重并发症亚组与轻度并发症亚组相比,肌酐和甘油三酯显著降低[(46.5±16.2) μmol/L vs.(66.8±16.4) μmol/L,P<0.001;(1.1±0.5) mmol/L vs.(1.6±0.7) mmol/L,P=0.038],手术时间显著延长[(20±5) min vs. (15±5) min,P=0.002]。Logistic回归模型分析显示,手术时间延长是并发症发生的独立危险因素(OR=1.132,95%CI: 1.051~1.220,P=0.001)。结论: PEG是ALS患者放置营养管的可靠方法,术后发热是最常见的早期并发症,手术时间延长是早期并发症(≤14 d)发生的独立危险因素。
中图分类号:
- R744.8
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| [1] | 王晓林, 郭邵逸, 陈大召, 温锡杰, 华勇, 张亮, 张秦. 全髋关节置换术治疗系统性红斑狼疮继发股骨头缺血性坏死的随访研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1081-1088. |
| [2] | 左超, 王国立, 杨昆霖, 车新艳, 孟一森, 张凯. 前列腺体积不同的患者经尿道光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术的有效性及安全性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 711-716. |
| [3] | 赵兆, 张维宇, 杨文博, 张勇杰, 张晓鹏, 赵慧颖, 周刚, 王强. 低龄、低体重儿童肾移植2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 803-807. |
| [4] | 王菲, 张馨月, 刘木清, 王恩博, 段登辉. 顺牙长轴拔牙法在下颌近中与水平智齿拔除术中的应用及三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 106-112. |
| [5] | 王丽薇, 刘冰川, 曲音音, 吴长毅, 田耘. 多学科诊疗模式在慢性难愈合创面诊疗中的临床应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 185-191. |
| [6] | 谢芳菲, 乔虹, 李博雅, 袁翠, 王芳, 孙瑜, 李双玲. 妊娠期重度营养不良合并急性肾盂肾炎致脓毒症、难治性感染性休克、多器官功能衰竭1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 202-207. |
| [7] | 万利, 张周沧, 丁嘉祥, 王梅. 中心静脉导管拔除后静脉空气栓塞1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 938-941. |
| [8] | 许素环,王蓓蓓,庞秋颖,钟丽君,丁炎明,黄燕波,车新艳. 等体温膀胱冲洗对经尿道前列腺电切术患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [9] | 叶珊,金萍萍,张楠,邬海博,石林,赵强,杨坤,袁慧书,樊东升. 肌萎缩侧索硬化患者认知功能改变与脑皮层厚度分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [10] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [11] | 姜保国,张培训. 老年髋部骨折的围手术期风险评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 803-809. |
| [12] | 于博,赵扬玉,张喆,王永清. 妊娠合并感染性心内膜炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [13] | 吴俊慧,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,秦雪英,王梦莹,王小文,王伽婷,胡永华. 北京城镇职工2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病率及主要危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 249-254. |
| [14] | 李伟浩,李伟,张学民,李清乐,焦洋,张韬,蒋京军,张小明. 去分支杂交手术和传统手术治疗胸腹主动脉瘤的结果比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [15] | 王成,孟令宇,陈拿云,李玳,王健全,敖英芳. 前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节感染的诊断和治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 850-856. |
|
||