北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 105-110. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.019
全程数字化夜磨牙保护牙合垫的制作和初步应用
王时敏1,李峥1,王冠博1,叶红强1,刘云松1,△( ),佟岱1,2,高文慧2,周永胜1
),佟岱1,2,高文慧2,周永胜1
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 修复科,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 义齿加工中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Preliminary clinical application of complete digital workflow of design and manufacturing occlusal splint for sleep bruxism
Shi-min WANG1,Zheng LI1,Guan-bo WANG1,Hong-qiang YE1,Yun-song LIU1,△( ),Dai TONG1,2,Wen-hui GAO2,Yong-sheng ZHOU1
),Dai TONG1,2,Wen-hui GAO2,Yong-sheng ZHOU1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing 100081, China
2. Dental Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
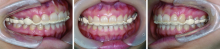
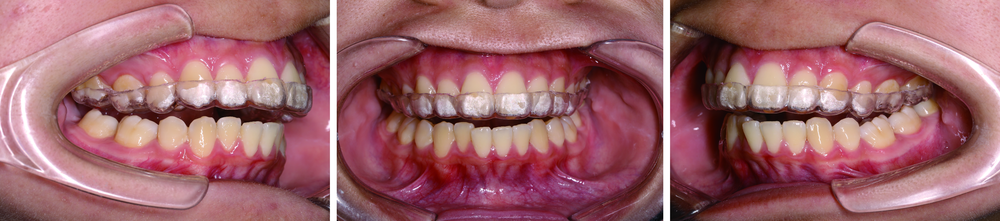
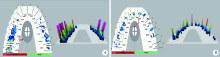
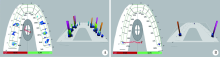
目的:建立一套夜磨牙保护牙合垫的全程数字化设计制作流程,并将其初步应用于临床,观察其临床效果。方法:选取需要通过佩戴牙合垫缓解夜磨牙症的患者24名,使用随机数表法分为两组,实验组使用口内扫描仪获取患者的上下牙列数字印模和抬高后的咬合关系,采用计算机辅助设计软件(computer aided design, CAD)进行数字化设计,将设计数据导入计算机辅助制作软件(computer aided manufacturing, CAM)进行切削;对照组通过真空压膜法制作传统软牙合垫。将两种方法制作的牙合垫分别让两组患者进行口内试戴,应用T-scan Ⅲ咬合分析系统分析佩戴两种牙合垫后的牙合接触特征,并由患者对牙合垫的固位、美观与咬合舒适度进行评分,采用IBM SPSS 20.0软件进行Mann-Whitney双侧检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。结果:成功建立了夜磨牙保护牙合垫的全程数字化设计制作流程。临床应用发现,两组患者对两种牙合垫的固位评价差异无统计学意义(Z=-0.538,P=0.590), 实验组的美观评分(Z=2.038,P=0.042)与咬合舒适度评分(Z=-2.579,P=0.010)均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义。T-scan结果显示,正中咬合时,对照组仅有双侧第二磨牙区存在牙合接触,而实验组可与下颌全牙列接触,前后牙合力均匀。结论:全程数字化设计制作的夜磨牙保护牙合垫改良了咬合设计,极大地简化和优化了牙合垫的制作流程,节约了医疗资源,有益环保,能够更加便捷、高效地为患者服务。
中图分类号:
- R783.2
| [1] | American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International classification of sleep disorder: Diagnostic and coding manual[M]. Chicago, Illinois: American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 2005: 189-192. |
| [2] |
Karakis D, Dogan A, Bek B . Evaluation of the effect of two diffe-rent occlusal splints on maximum occlusal force in patients with sleep bruxism: A pilot study[J]. J Adv Prosthodont, 2014,6(2):103-108.
doi: 10.4047/jap.2014.6.2.103 pmid: 4024553 |
| [3] |
Guaita M, Hogl B . Current treatments of bruxism[J]. Curr Treat Options Neurol, 2016,18(2):10.
doi: 10.1007/s11940-016-0396-3 |
| [4] | Bumann A, Lotzmann U . TMJ disorders and orofacial pain: The role of dentistry in a multidisciplinary diagnostic approach[M]. Stuttgart, New York: Thieme, 2002. |
| [5] | Ye H, Li X, Wang G , et al. A novel computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacture method for one-piece removable partial denture and evaluation of fit[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2018, doi: 10.11607/ijp.5508. |
| [6] | 李欣欣, 柳玉树, 孙玉春 , 等. 计算机辅助设计与制作一体化聚醚醚酮可摘局部义齿不同形态组件的适合性评价 [J/OL]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, [ 2018- 12- 07]. . |
| [7] | 金智文, 韩建民, 刘云松 , 等. 聚醚醚酮制作可摘义齿人工牙耐磨性及硬度的研究[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2018,19(4):236-240. |
| [8] |
Lavigne GJ, Khoury S, Abe S , et al. Bruxism physiology and pathology: An overview for clinicians[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2008,35(7):476-494.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2008.01881.x pmid: 18557915 |
| [9] |
Manfredini D, Winocur E, Guarda-Nardini L , et al. Epidemiology of bruxism in adults: A systematic review of the literature[J]. J Orofac Pain, 2013,27(2):99-110.
doi: 10.11607/jop.921 pmid: 23630682 |
| [10] |
Dubé C, Rompré PH, Manzini C , et al. Quantitative polygraphic controlled study on efficacy and safety of oral splint devices in tooth-grinding subjects[J]. J Dent Res, 2004,83(5):398-403.
doi: 10.1177/154405910408300509 pmid: 15111632 |
| [11] |
王志瑜, 黄虹, 马明 , 等. 青年夜磨牙症患者经弹性牙合垫治疗前后咬合变化特征的研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2016,32(6):857-860.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2016.06.024 |
| [12] |
刘党利 . 硬牙合垫和软牙合垫治疗夜磨牙的效果比较[J]. 临床医学, 2005,25(10):64-65.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3548.2005.10.044 |
| [13] |
Berntsen C, Kleven M, Heian M , et al. Clinical comparison of conventional and additive manufactured stabilization splints[J]. Acta Biomater Odontol Scand, 2018,4(1):81-89.
doi: 10.1080/23337931.2018.1497491 |
| [14] |
Salmi M, Paloheimo KS, Tuomi J , et al. A digital process for additive manufacturing of occlusal splints: A clinical pilot study[J]. J R Soc Interface, 2013,10(84):20130203.
doi: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0203 pmid: 3673156 |
| [15] |
吴忠文 . 聚醚醚酮类树脂的国际、国内发展历程及新进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2010,38(12):1-4.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2010.12.001 |
| [16] |
邓纯博, 刘冬妍, 刘吉泉 , 等. 聚醚醚酮及其复合材料作为骨科植入物的研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2009,13(5):473-477.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7090.2009.09.026 |
| [17] |
Zoidis P, Papathanasiou I, Polyzois G . The use of a modified poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) as an alternative framework material for removable dental prostheses: A clinical report[J]. J Pros-thodont, 2016,25(7):580-584.
doi: 10.1111/jopr.12325 pmid: 26216668 |
| [18] |
贾洪诚, 王璇 . 应用T-scan Ⅲ型系统分析牙周基础治疗前后咬合变化的临床研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2015,31(4):484-487.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2015.05.07 |
| [1] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [2] | 李穗,马雯洁,王时敏,丁茜,孙瑶,张磊. 上前牙种植单冠修复体切导的数字化设计正确度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [3] | 罗昊,田福聪,王晓燕. 不同椅旁可切削修复材料序列抛光时间及表面粗糙度与光泽度的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 565-571. |
| [4] | 冯莎蔚,国慧,王勇,赵一姣,刘鹤. 乳牙数字化参考牙冠模型的初步构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 327-334. |
| [5] | 李怡,王丽瑜,刘晓强,周倜,吕季喆,谭建国. 不同材料及厚度椅旁CAD/CAM瓷贴面的边缘特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 140-145. |
| [6] | 邱淑婷,朱玉佳,王时敏,王飞龙,叶红强,赵一姣,刘云松,王勇,周永胜. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [7] | 徐啸翔,曹烨,赵一姣,贾璐,谢秋菲. 数字化个齿托盘制取下颌全牙列全冠预备体印模的体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 54-61. |
| [8] | 岳兆国,张海东,杨静文,侯建霞. 数字化评估CAD/CAM个性化基台与成品基台影响粘接剂残留的体外研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 69-75. |
| [9] | 李峥,柳玉树,王时敏,张瑞,贾璐,叶红强,胡文杰,赵文艳,刘云松,周永胜. 数字化方法复制暂时修复体牙合面形态在重度磨耗病例中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 62-68. |
| [10] | 房硕博,杨广聚,康艳凤,孙玉春,谢秋菲. 数字化辅助确定再定位牙合垫颌位方法的探索和精度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 76-82. |
| [11] | 罗佳,张宇,崔宏燕,祝宁,沈惠丹,邸萍,林野. 锥度固位结合数字化技术在后牙连续多牙种植即刻修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 964-970. |
| [12] | 魏菱,邹东,陈虎,潘韶霞,孙玉春,周永胜. 一种数字化全口义齿的临床疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 762-770. |
| [13] | 孙玉春,王勇,邓珂慧,陈虎,李伟伟,赵一姣,潘韶霞,叶红强,周永胜. 功能易适数字化全口义齿的自主创新研发[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 390-394. |
| [14] | 游浪,邓珂慧,李伟伟,赵一姣,孙玉春,周永胜. 无牙颌患者鼻唇角变化侧面观的视觉敏感阈值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 107-112. |
| [15] | 陈硕,贺洋,安金刚,张益. 计算机辅助设计虚拟颌位在儿童颞下颌关节强直合并颌骨畸形同期矫治中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 954-958. |
|
||