北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 856-862. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.010
CMTM5基因与冠心病患者支架内再狭窄发生风险
- 首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院心血管内科,北京 100034
Association of CMTM5 gene expression with the risk of in-stent restenosis in patients with coronary artery disease after drug-eluting stent implantation and the effects and mechanisms of CMTM5 on human vascular endothelial cells
Teng-fei LIU,Tao LIN,Li-hui REN,Guang-ping LI,Jian-jun PENG( )
)
- Department of Cardiology, Shijitan Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
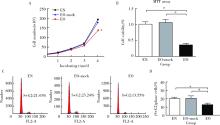
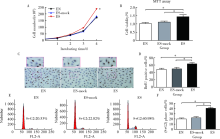
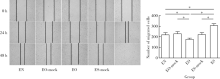
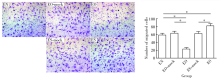
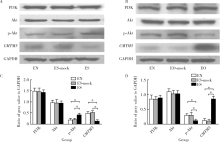
目的:探讨趋化素样因子超家族成员5 (CKLF-like marvel transmembrane domain containing member, CMTM5)基因与冠心病患者支架内再狭窄(in-stent restenosis, ISR)发生风险及该基因对人血管内皮细胞(endothelial cells, ECs)增殖和迁移作用及其机制。方法: 选择2015年1月至2016年12月在首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院心血管内科接受住院治疗并行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗手术的冠心病患者,共计124例,采用光学比浊法测定血小板聚集率并进行血小板高反应性分组;冠脉造影术明确患者支架内再狭窄发生;RT-PCR法测定CMTM5基因表达;构建CMTM5基因过表达、敲减及对照组内皮细胞系,采用细胞计数法、MTT法、Brdu掺入实验和流式细胞术检测ECs增殖能力,刮伤和Transwell实验检测ECs迁移能力,Western-blot检测信号通路表达。结果: CMTM5基因在血小板高反应性(high on aspirin platelet reactivity,HAPR)组表达量为非血小板高反应性(no-high on aspirin platelet reactivity,No-HAPR)组表达量的1.72倍(P<0.05)。HAPR组ISR发生率为25.8%(8例), No-HAPR组ISR发生率为 9.7%(9例), HAPR组患者ISR的发生率高于No-HAPR组的发生率(P=0.04,OR=2.95,95%CI:1.16~7.52),表明该基因与冠心病患者支架术后支架内再狭窄发生风险显著相关(P<0.05)。CMTM5基因过表达抑制ECs增殖和迁移能力(P<0.05), PI3K/Akt信号通路参与该基因对内皮细胞增殖和迁移调控作用。结论:CMTM5基因与冠心病患者支架内再狭窄事件发生风险可能存在相关性,CMTM5基因通过PI3K/Akt信号通路参与调控ECs增殖和迁移。
中图分类号:
- R543.3
| [1] |
Kokkinidis DG, Waldo SW, Armstrong EJ. Treatment of coronary artery in-stent restenosis[J]. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther, 2017,15(3):191-202.
doi: 10.1080/14779072.2017.1284588 pmid: 28116914 |
| [2] |
Kuchulakanti PK, Chu WW, Torguson R, et al. Correlates and long-term outcomes of angiographically proven stent thrombosis with sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents[J]. Circulation, 2006,113(8):1108-1113.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.600155 pmid: 16490815 |
| [3] |
Philip F. Duration of triple therapy in patients requiring oral anticoagulation after drug-eluting stent implantation[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015,66(9):1088-1089.
pmid: 26314542 |
| [4] |
Byrne RA, Joner M, Kastrati A. Stent thrombosis and restenosis: what have we learned and where are we going? The andreas gruntzig lecture ESC 2014[J]. Eur Heart J, 2015,36(47):3320-3331.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv511 pmid: 26417060 |
| [5] |
Moliterno DJ. Healing achilles: sirolimus versus paclitaxel[J]. N Engl J Med, 2005,353(7):724-727.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMe058140 pmid: 16105991 |
| [6] |
Virmani R, Farb A. Pathology of in-stent restenosis[J]. Curr Opin Lipidol, 1999,10(6):499-506.
doi: 10.1097/00041433-199912000-00004 pmid: 10680043 |
| [7] |
Ma X, Hibbert B, McNulty M, et al. Heat shock protein 27 attenuates neointima formation and accelerates reendothelialization after arterial injury and stent implantation: importance of vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation[J]. FASEB J, 2014,28(2):594-602.
doi: 10.1096/fj.13-230417 |
| [8] |
Li H, Guo X, Shao L, et al. CMTM5-v1, a four-transmembrane protein, presents a secreted form released via a vesicle-mediated secretory pathway[J]. BMB Rep, 2010,43(3):182-187.
doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2010.43.3.182 pmid: 20356458 |
| [9] |
Voora D, Cyr D, Lucas J, et al. Aspirin exposure reveals novel genes associated with platelet function and cardiovascular events[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013,62(14):1267-1276.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.073 pmid: 23831034 |
| [10] |
Liu TF, Zhang JW, Chen XH, et al. Comparison between urinary 11-dehydrothromboxane B2 detection and platelet light transmission aggregometry (LTA) assays for evaluating aspirin response in elderly patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Gene, 2015,571(1):23-27.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.06.045 pmid: 26095809 |
| [11] |
刘滕飞, 张婧薇, 陈夏欢, 等. CMTM5基因rs723840单核苷酸多态性与阿司匹林治疗下血小板高反应性的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(6):905-909.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671167X.2015.06.003 |
| [12] |
Teirstein P, Reilly JP. Late stent thrombosis in brachytherapy: the role of long-term antiplatelet therapy[J]. J Invasive Cardiol, 2002,14(3):109-114.
pmid: 11870263 |
| [13] | Schmieder RE. Endothelial dysfunction: how can one intervene at the beginning of the cardiovascular continuum[J]. J Hypertens Suppl, 2006,24(Suppl 2):S31-35. |
| [14] |
Xiao Y, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, et al. CMTM5 is reduced in prostate cancer and inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2015,17(6):431-437.
doi: 10.1007/s12094-014-1253-z pmid: 25387568 |
| [1] | 罗靓,李云,王红彦,相晓红,赵静,孙峰,张晓盈,贾汝琳,李春. 抗内皮细胞抗体检测在早期流产中的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1039-1044. |
| [2] | 顾阳阳,谭晓辉,宋文鹏,方冬,宋卫东,袁亦铭,冯宁翰,关瑞礼. 4′-甲基醚金连木黄酮对棕榈酸诱导的大鼠阴茎海绵体内皮细胞功能障碍的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 599-604. |
| [3] | 申杰, 杨迪, 陈梦圆, 郭新彪. 长度和化学修饰在多壁碳纳米管诱导内皮细胞活化中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 439-446. |
| [4] | 黄丽东,宫玮玉,董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖及成血管的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 371-377. |
| [5] | 刘滕飞,林涛,任利辉,李广平,彭建军. CMTM5基因与冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病的关联研究及机制探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1082-1087. |
| [6] | 谢静,赵玉鸣,饶南荃,汪晓彤,方滕姣子,李晓霞,翟越,李静芝,葛立宏,王媛媛. 3种口腔颌面部来源的间充质干细胞成血管内皮分化潜能的比较研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 900-906. |
| [7] | 张静,李素芳,陈红,宋俊贤. miR-106b-5p在调节内皮细胞基因表达谱中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 221-227. |
| [8] | 刘颖君,欧阳翔英,王宇光,吕培军,安娜. 生长停滞特异性蛋白6在牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖诱导内皮细胞黏附因子及趋化因子表达中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 20-25. |
| [9] | 梁乃文,石磊,黄颖,邓旭亮. 不同形貌纯钛表面对人脐静脉内皮细胞生物学行为的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 43-048. |
| [10] | 李蓬1,万蒙2,刘健如2,李良忠1,张大鹍3△. 过氧化物酶体增生物激活受体γ在牙龈卟啉单胞菌刺激血管内皮细胞氧化应激中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 977-982. |
| [11] | 高倩,彭清,陈靖,张巍,王朝霞,袁云,左越焕,刘靖. 法布里病的在体血管功能评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 796-799. |
| [12] | 吴迪, 欧阳翔英, 万蒙. 牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染内皮细胞导致白介素-8表达升高的胞内机制初探[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 278-283. |
| [13] | 陈鑫磊, 边曦, 秦泽莲. Periostin在酸性环境下对人脐静脉内皮细胞功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(6): 855-860. |
| [14] | 杨玲玲, 邵珲, 原鹏波, 郭晓玥, 张小为, 赵扬玉. 缺氧诱导因子-1α及其靶基因在双胎输血综合征胎盘组织中的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(6): 792-797. |
| [15] | 刘涛, 覃新程, 李维仁, 周峰, 李广永, 辛华, 巩艳青, 辛钟成. 淫羊藿苷和淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ对内皮细胞eNOS表达和NOS活性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(4): 500-504. |
|
||