北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 692-698. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.04.018
基于多中心数据库的10年上尿路修复手术术式及术型变化趋势
左炜1,高菲1,袁昌巍1,熊盛炜1,李志华1,张雷1,杨昆霖1,李新飞1,刘靓2,魏来2,张鹏3,王冰4,谷亚明4,朱宏建2,赵峥1,*( ),李学松1,*(
),李学松1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科,北京大学泌尿外科研究所,国家泌尿、男性生殖系肿瘤研究中心,北京 100034
2. 北京市健宫医院泌尿外科,北京 100054
3. 应急总医院泌尿外科,北京 100028
4. 北京市密云区医院(北京大学第一医院密云院区),北京 101599
Trends in upper urinary tract reconstruction surgery over a decade based on a multi-center database
Wei ZUO1,Fei GAO1,Chang-wei YUAN1,Sheng-wei XIONG1,Zhi-hua LI1,Lei ZHANG1,Kun-lin YANG1,Xin-fei LI1,Liang LIU2,Lai WEI2,Peng ZHANG3,Bing WANG4,Ya-ming GU4,Hong-jian ZHU2,Zheng ZHAO1,*( ),Xue-song LI1,*(
),Xue-song LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Urology, Beijing Jiangong Hospital, Beijing 100054, China
3. Department of Urology, Emergency General Hospital, Beijing 100028, China
4. Department of Urology, Miyun District Hospital (Miyun Hospital, Peking University First Hospital), Beijing 101599, China
摘要:
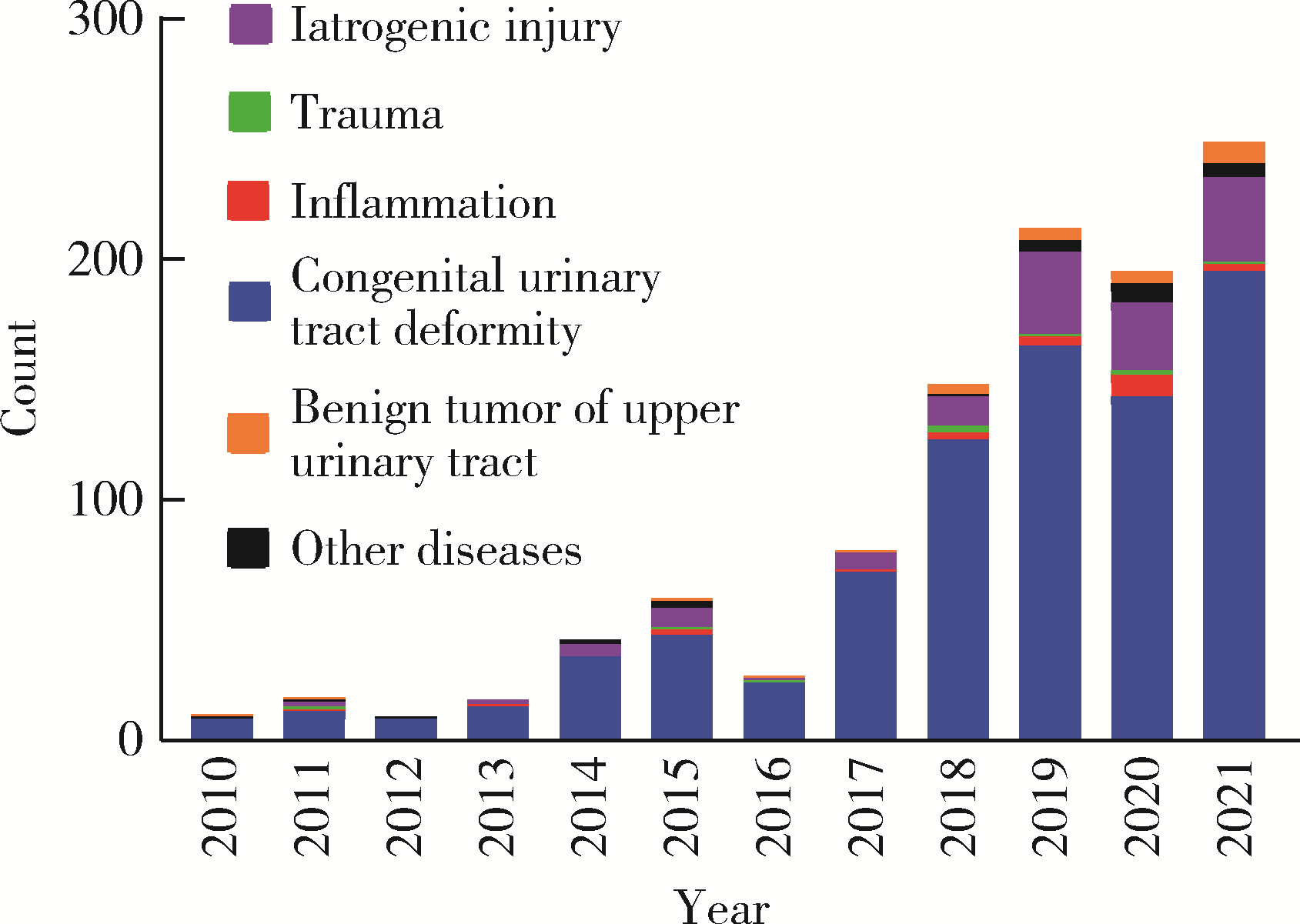
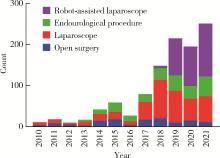
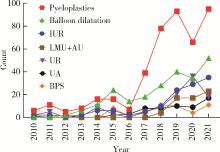
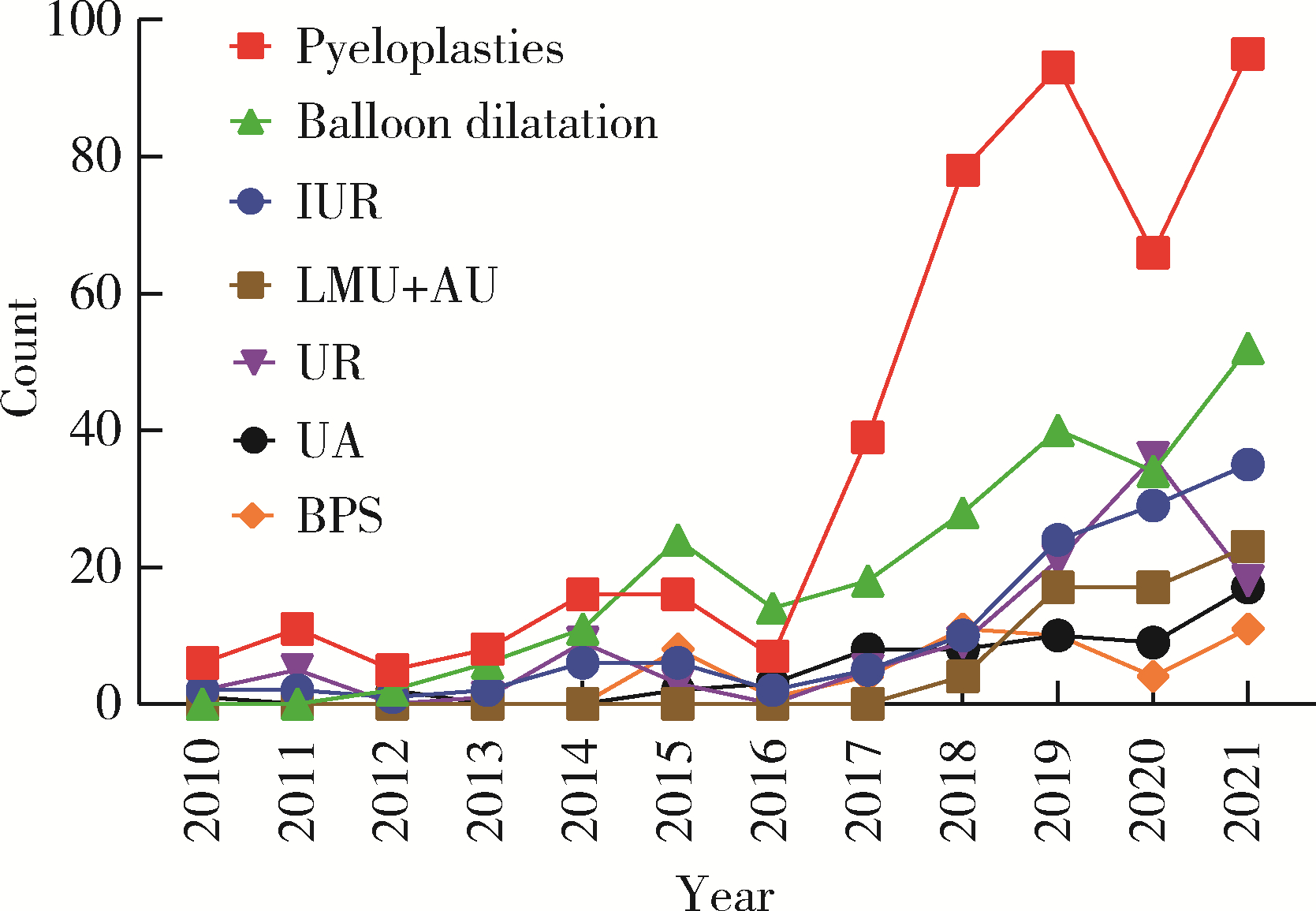
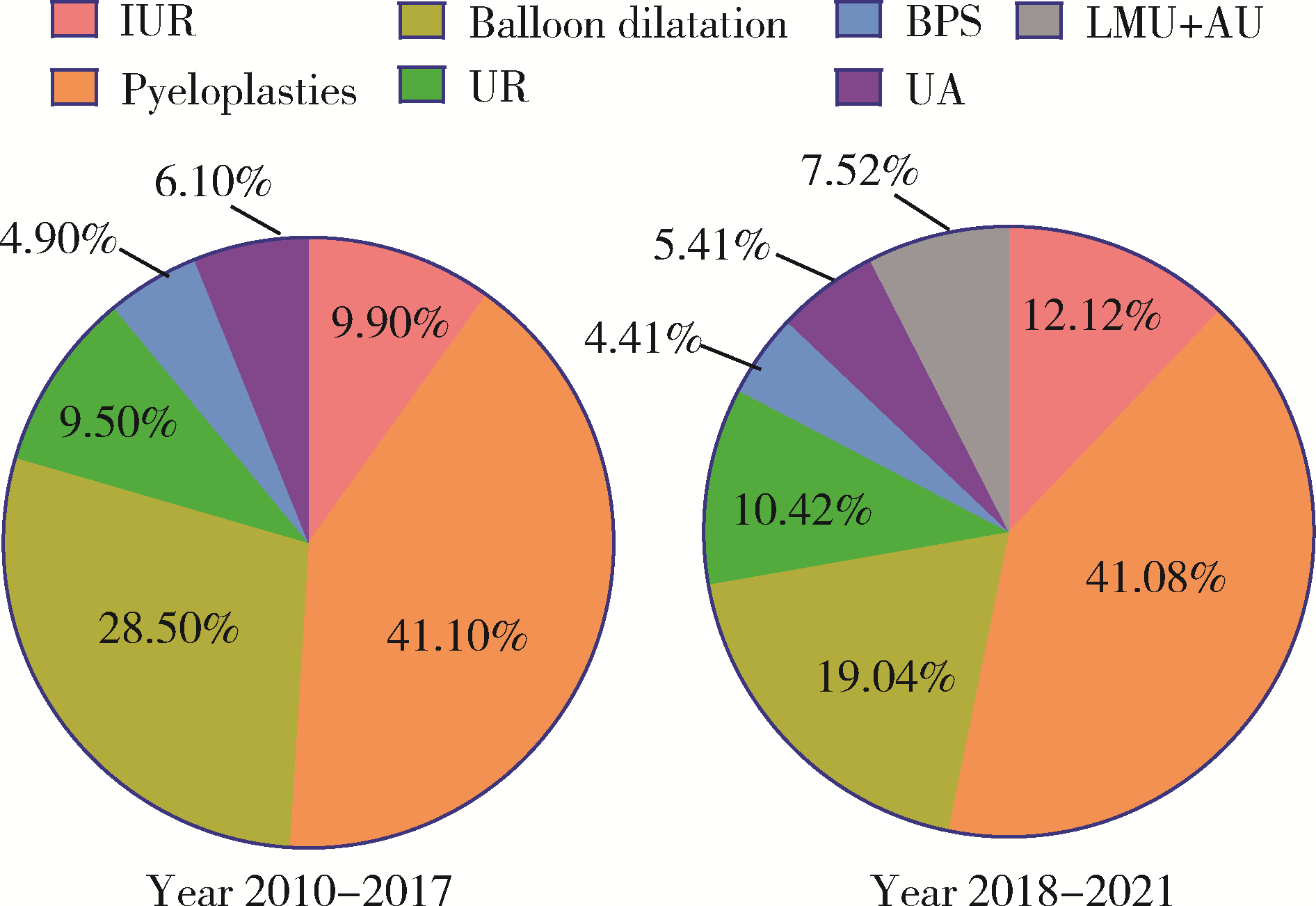
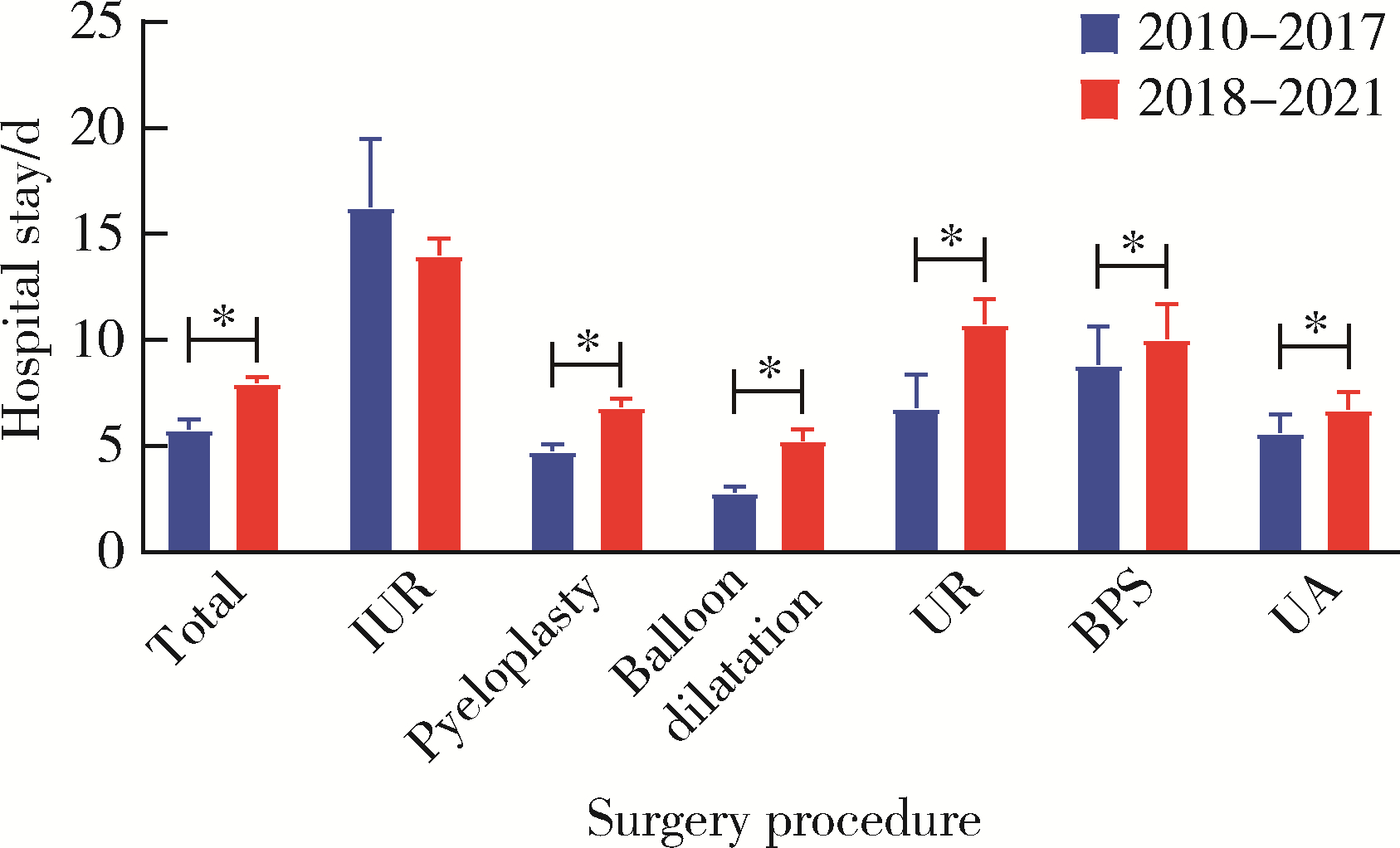
目的: 探究近10年上尿路修复手术的病因以及上尿路修复手术术式、术型变化趋势。方法: 基于北京大学泌尿外科研究所牵头创建的多中心RECUTTER(Reconstruction of Urinary Tract:Technology,Epidemiology and Result)数据库资料,分析2010—2021年行上尿路修复手术患者的术前基本信息、围手术期临床资料及随访结果。比较2010—2017和2018—2021两年段间上尿路修复手术术式、术型、住院时间与手术时长、短期并发症发生率以及再次进行修复手术的患者比例。结果: RECUTTER数据库中共纳入1 072例患者,先天因素和医源性损伤是患者进行上尿路修复手术的主要病因,其中开放手术129例(12.0%)、腹腔镜手术403例(37.6%)、机器人手术322例(30.0%)、内镜手术218例(20.3%),近10年手术量呈现逐年增高趋势,2018—2021年间机器人手术占比显著高于2010—2017年(P < 0.001)。1 072例上尿路修复手术患者的术型包括回肠代输尿管术124例(11.6%)、肾盂成形术440例(41.1%)、球囊扩张术229例(21.4%)、输尿管膀胱再植术109例(10.2%)、膀胱悬吊联合膀胱瓣手术49例(4.6%)、输尿管-输尿管吻合术60例(5.6%)、舌黏膜/阑尾补片修补术61例(5.7%)。肾盂成形术和球囊扩张术虽仍是主要术型,但补片修补术的占比显著增加(P < 0.05)。此外,2018年后手术时间明显增长(P < 0.05),考虑与机器人辅助腹腔镜手术占比升高有关。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,微创手术(腔内治疗及机器人手术)是术后短期并发症的独立危险因素(P=0.050,OR=0.472),可减少术后短期并发症的发生率。结论: 多中心RECUTTER数据库在临床科研工作中有重要的数据支持价值,为国内外更大范围多中心数据库建设提供了基础。近10年来,上尿路修复手术术式呈“微创化”、术型呈“复杂化”趋势,提示了机器人辅助手术在上尿路重建手术中的优越性。
中图分类号:
- R691.6
| 1 |
Stief CG , Jonas U , Petry KU , et al. Ureteric reconstruction[J]. BJU international, 2003, 91 (2): 138- 142.
doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.2003.03060.x |
| 2 |
Zhu W , Xiong S , Xu C , et al. Initial experiences with preoperative three-dimensional image reconstruction technology in laparoscopic pyeloplasty for ureteropelvic junction obstruction[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2021, 10 (11): 4142- 4151.
doi: 10.21037/tau-21-590 |
| 3 |
Yuan C , Wang J , Cheng S , et al. Robotic ureteral reimplantation for the management of ureterovaginal fistula: Four cases at a single center[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2021, 10 (10): 3705- 3713.
doi: 10.21037/tau-21-454 |
| 4 |
Yang K , Fan S , Wang J , et al. Robotic-assisted lingual mucosal graft ureteroplasty for the repair of complex ureteral strictures: Technique description and the medium-term outcome[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 81 (5): 533- 540.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.01.007 |
| 5 |
Wang J , Xiong S , Fan S , et al. Appendiceal onlay flap ureteroplasty for the treatment of complex ureteral strictures: Initial experience of nine patients[J]. J Endourol, 2020, 34 (8): 874- 881.
doi: 10.1089/end.2020.0176 |
| 6 |
Fan S , Yin L , Yang K , et al. Posteriorly augmented anastomotic ureteroplasty with lingual mucosal onlay grafts for long proximal ureteral strictures: 10 cases of experience[J]. J Endourol, 2021, 35 (2): 192- 199.
doi: 10.1089/end.2020.0686 |
| 7 |
Li X , Wang X , Li T , et al. Cine magnetic resonance urography and whitaker test: Dynamic visualized and quantified tools in ileal ureter replacement[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2021, 10 (11): 4110- 4119.
doi: 10.21037/tau-21-507 |
| 8 | Li X , Yang K , Zhu W , et al. The whitaker test in the follow-up of complex upper urinary tract reconstruction: Is it clinical useful or not[J]. Urol J, 2021, 19 (1): 56- 62. |
| 9 | Ding G , Li X , Fang D , et al. Etiology and ureteral reconstruction strategy for iatrogenic ureteral injuries: A retrospective single-center experience[J]. Urol Int, 2021, 105 (5/6): 470- 476. |
| 10 |
de Onis M , Blössner M . The world health organization global database on child growth and malnutrition: Methodology and applications[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2003, 32 (4): 518- 526.
doi: 10.1093/ije/dyg099 |
| 11 |
Jacobs JP , Lacour-Gayet FG , Jacobs ML , et al. Initial application in the sts congenital database of complexity adjustment to evaluate surgical case mix and results[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2005, 79 (5): 1635- 1649.
doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.09.065 |
| 12 |
Kakeji Y , Yamamoto H , Ueno H , et al. Development of gastroenterological surgery over the last decade in japan: Analysis of the national clinical database[J]. Surg Today, 2021, 51 (2): 187- 193.
doi: 10.1007/s00595-020-02075-7 |
| 13 |
Bowdish ME , D'Agostino RS , Thourani VH , et al. Sts adult car-diac surgery database: 2021 update on outcomes, quality, and research[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2021, 111 (6): 1770- 1780.
doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2021.03.043 |
| 14 |
Kwoh YS , Hou J , Jonckheere EA , et al. A robot with improved absolute positioning accuracy for ct guided stereotactic brain surgery[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 1988, 35 (2): 153- 160.
doi: 10.1109/10.1354 |
| 15 |
Binder J , Kramer W . Robotically-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. BJU Int, 2001, 87 (4): 408- 410.
doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.00115.x |
| 16 |
Rosero EB , Kho KA , Joshi GP , et al. Comparison of robotic and laparoscopic hysterectomy for benign gynecologic disease[J]. Obstet Gynecol, 2013, 122 (4): 778- 786.
doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3182a4ee4d |
| 17 |
Yates DR , Vaessen C , Roupret M . From leonardo to da vinci: The history of robot-assisted surgery in urology[J]. BJU Int, 2011, 108 (11): 1708- 1713.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10576.x |
| 18 |
Autorino R , Porpiglia F , Dasgupta P , et al. Precision surgery and genitourinary cancers[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017, 43 (5): 893- 908.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.02.005 |
| 19 |
Leal Ghezzi T , Campos Corleta O . 30 years of robotic surgery[J]. World J Surg, 2016, 40 (10): 2550- 2557.
doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3543-9 |
| 20 |
Andolfi C , Adamic B , Oommen J , et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty in infants and children: Is it superior to conventional laparoscopy?[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38 (8): 1827- 1833.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02943-z |
| 21 |
Crocerossa F , Carbonara U , Cantiello F , et al. Robot-assisted radical nephrectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 80 (4): 428- 439.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.10.034 |
| 22 |
Deng T , Liu B , Luo L , et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic versus open ureteral reimplantation for pediatric vesicoureteral reflux: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36 (5): 819- 828.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2194-x |
| [1] | 陈思鹭, 王海菊, 吴宇财, 李志华, 黄燕波, 何宇辉, 许洋洋, 李学松, 贯华. 成人肾积水病因分析:一项单中心横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 913-918. |
| [2] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [3] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [4] | 马建勋,夏有辰,李比,赵红梅,雷玉涛,布希. 乳腺癌改良根治术后即刻乳房重建的方式选择[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [5] | 周利群,徐纯如. 机器人时代中央型肾肿瘤的手术治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 587-591. |
| [6] | 张崔建,何志嵩,周利群. 上尿路尿路上皮癌的淋巴清扫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 592-594. |
| [7] | 戴翔,王飞,杜依青,宋宇轩,徐涛. 上尿路尿路上皮癌组织中脂肪因子表达与临床病理特征及预后的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 605-614. |
| [8] | 李志华,徐纯如,刘颖,贯华,张萌,车新艳,唐琦,黄燕波,李学松,周利群. 饮水习惯与上尿路尿路上皮癌病理特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 621-627. |
| [9] | 丁婷婷,曾楚雄,胡丽娜,余明华. 基于癌症基因组图谱数据库结直肠癌免疫细胞浸润预测模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 203-208. |
| [10] | 蓝璘,贺洋,安金刚,张益. 颧骨缺损不同修复重建方法和预后的回顾性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 356-362. |
| [11] | 郝瀚,刘越,陈宇珂,司龙妹,张萌,范宇,张中元,唐琦,张雷,吴士良,宋毅,林健,赵峥,谌诚,虞巍,韩文科. 机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术后患者的控尿恢复时间[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 697-703. |
| [12] | 黄炳伟,王杰,张鹏,李喆,毕泗成,王强,岳才博,杨昆霖,李学松,周利群. 吲哚菁绿在复杂上尿路修复手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [13] | 张军晖,蒋一航,蒋宇光,张际青,康宁. 双侧同步内镜手术治疗双侧上尿路结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 672-677. |
| [14] | 程嗣达,李新飞,熊盛炜,樊书菠,王杰,朱伟杰,李子奡,丁光璞,俞婷,李万强,孙永明,杨昆霖,张雷,郝瀚,李学松,周利群. 机器人辅助腹腔镜上尿路修复手术:单一术者108例经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 771-779. |
| [15] | 关豹,翁迈,凡航,彭鼎,方冬,熊耕砚,李学松,周利群. 术前贫血对上尿路尿路上皮癌预后的影响: 单中心686例患者回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1056-1061. |
|
||