北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 120-130. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.019
舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院检验科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院病案管理科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,北京 100081
Establishment and verification of a prognostic nomogram for survival of tongue squamous cell carcinoma patients who underwent cervical dissection
Junqi SU1,Xiaoying WANG2,Zhiqiang SUN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Medical Record, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
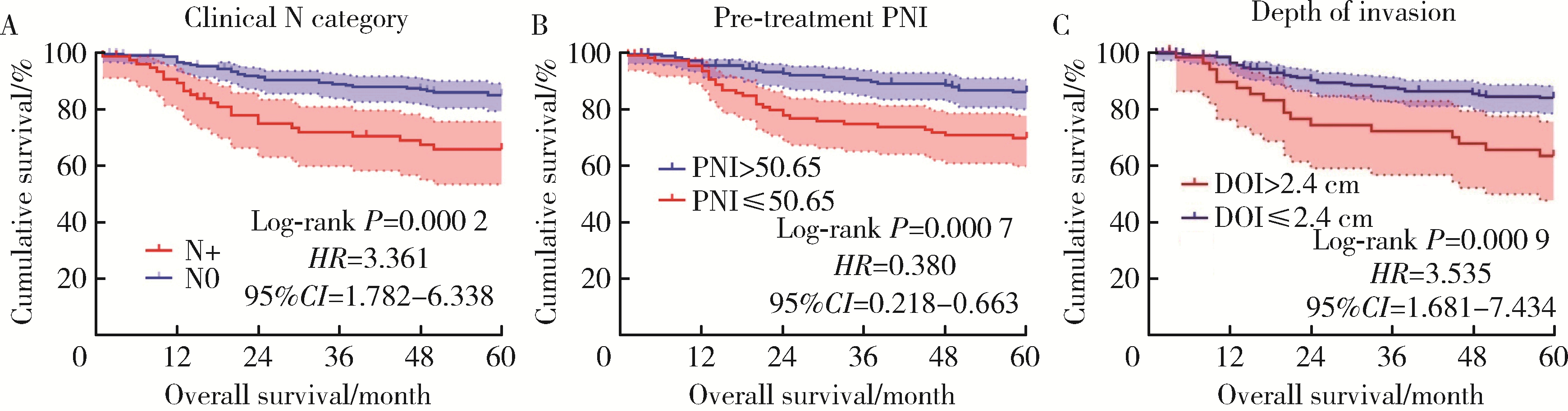
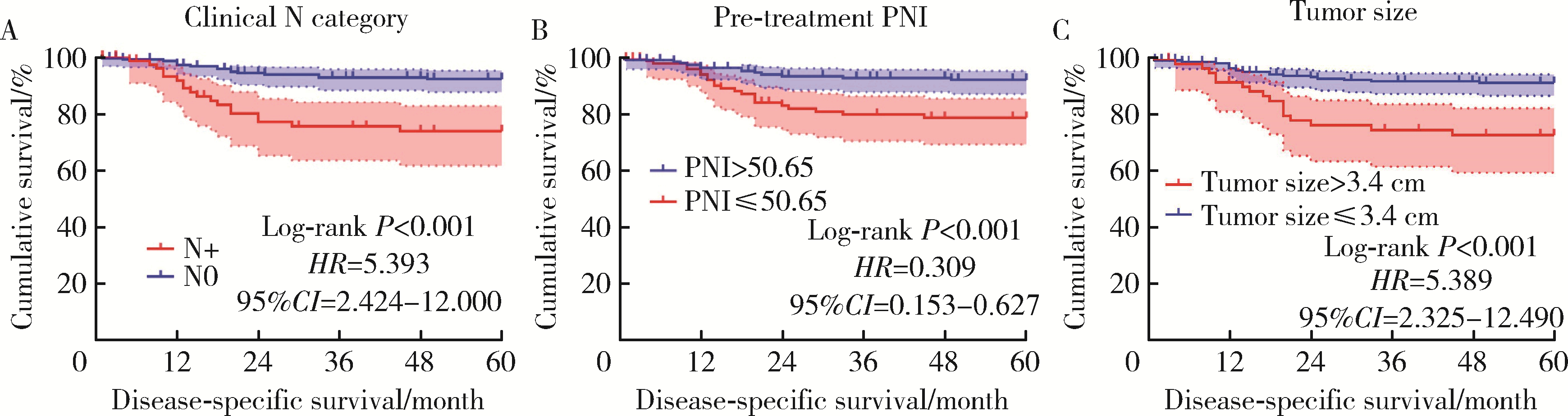
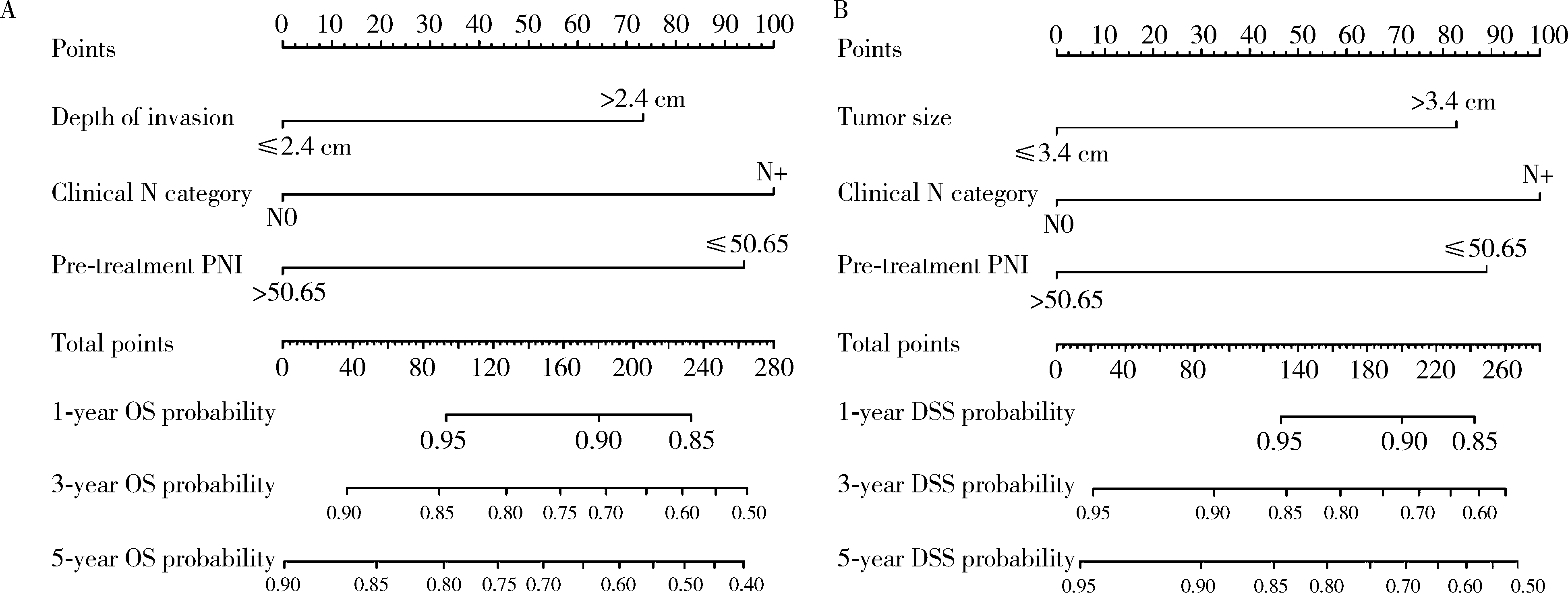
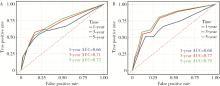
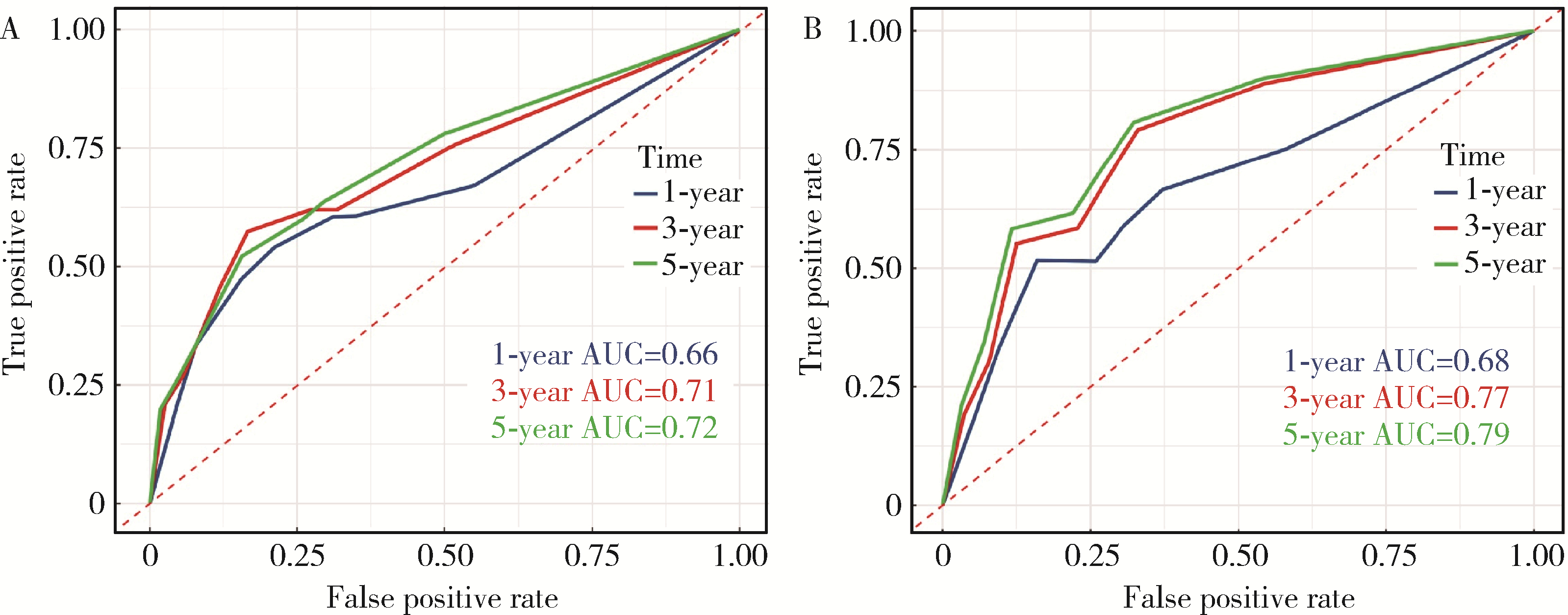
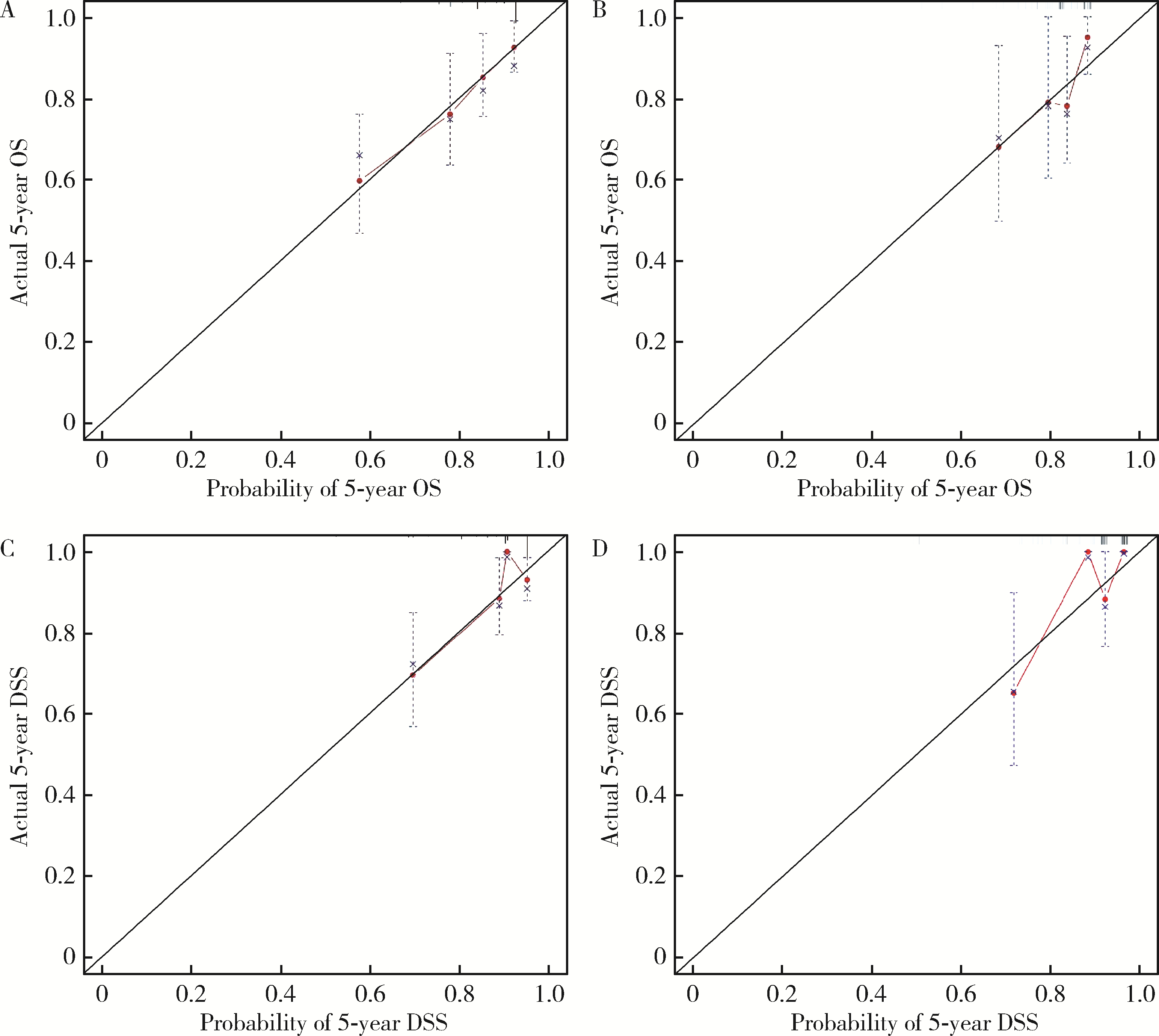
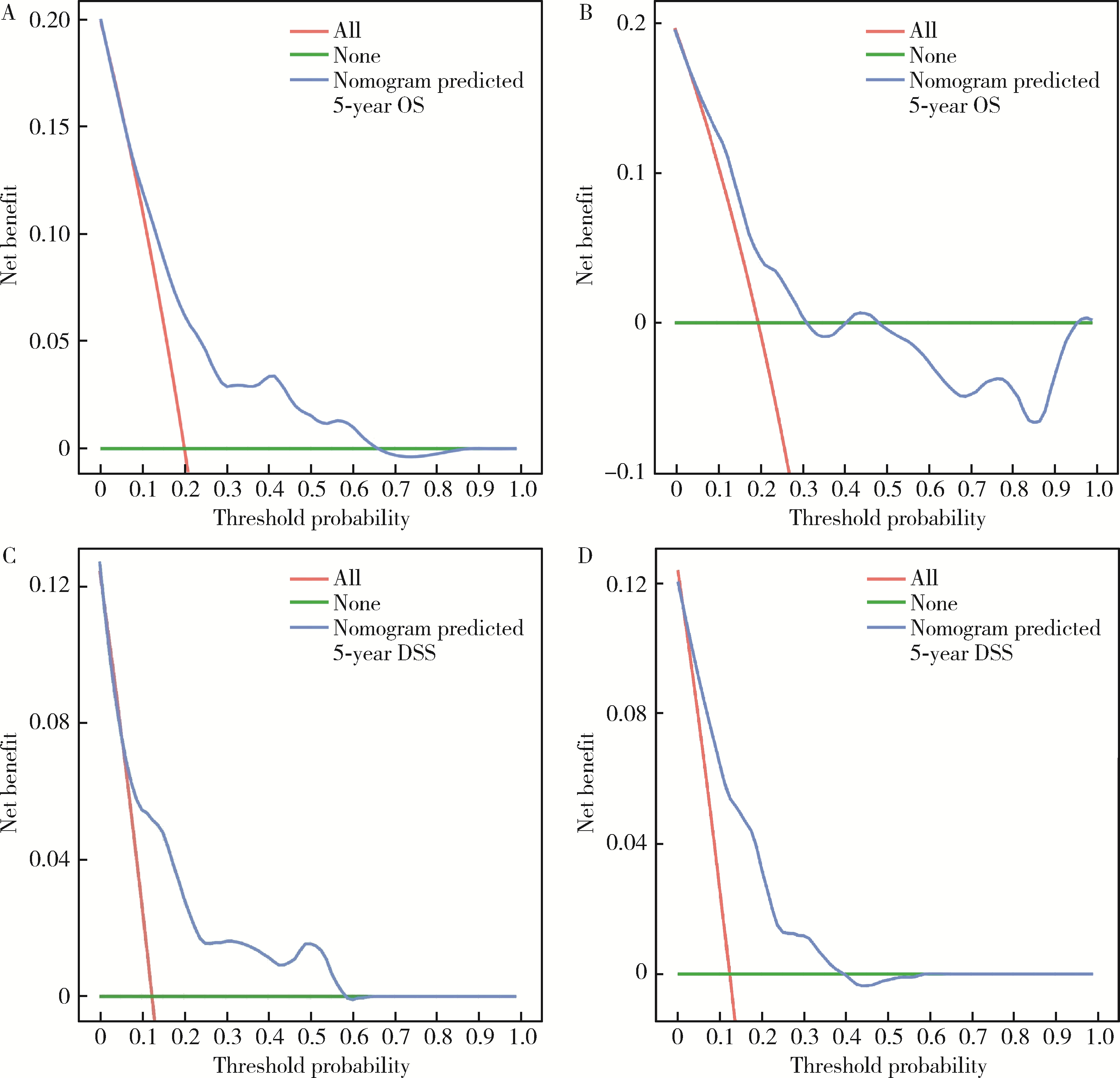
目的: 评估术前炎症生物标志物、预后营养指数和临床病理特征对舌鳞状细胞癌(tongue squamous cell carcinoma, TSCC)患者行根治性切除术后生存结局的预后价值, 并以此构建患者预后预测列线图模型。方法: 回顾性收集2017年1月至2018年7月于北京大学口腔医院接受根治性肿瘤切除术的297例TSCC患者的病例资料, 随机按照7 :3比例分为训练集和验证集。分析患者术前全身炎症反应标志物中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比率(neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, NLR)、淋巴细胞/单核细胞比率(lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, LMR)、血小板/淋巴细胞比率(platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, PLR)、系统免疫炎症指数(systemic immune-inflammation index, SII)、系统性炎症评分(systemic inflammation score, SIS)及预后营养指数(prognostic nutritional index, PNI)与TSCC患者术后总生存期(overall survival, OS)和疾病特异性生存期(disease-specific survival, DSS)的相关性。使用X-tile软件确定连续变量的最佳截断值作为分界点。采用Kaplan-Meier生存分析和多变量Cox回归模型分析影响TSCC患者的独立预后预测因素, 据此构建OS和DSS的生存相关列线图预测模型, 通过训练集和验证集进行模型内部交叉验证和外部验证, 具体通过一致性指数、时间依赖性受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic, ROC)曲线、曲线下面积(area under the curve, AUC)、校准曲线和决策曲线分析对列线图的准确性进行验证。结果: 单因素Cox回归分析显示, TNM分期、T分期、N分期、分化程度、侵袭深度(depth of invasion, DOI)、肿瘤直径和治疗前PNI水平为影响TSCC预后危险因素; 多因素Cox回归分析显示, 治疗前PNI水平、N分期、DOI和肿瘤直径为患者5年OS或DSS的独立预后因素(P<0.05)。治疗前N分期≥1、PNI≤50.65和DOI>2.4 cm与较差的5年OS显著相关, 而N分期≥1、PNI≤50.65、肿瘤直径>3.4 cm与较差的5年DSS显著相关。基于独立预后因素构建的TSCC术后患者OS和DSS的列线图预测模型的一致性指数分别为0.708 (95%CI, 0.625~0.791)和0.717 (95%CI, 0.600~0.834), 验证集验证结果显示, OS和DSS列线图预测模型的一致性指数为0.659 (95%CI, 0.550~0.767)和0.780 (95%CI, 0.669~0.890)。OS列线图模型和DSS列线图模型的1年、3年和5年的时间依赖性ROC分析(AUC分别为0.66、0.71、0.72和0.68、0.77、0.79)表明模型具有稳定的判别能力。校准曲线显示OS和DSS预测估值与实际观察值之间具有良好的一致性, 决策曲线分析反映模型具有较好的临床应用价值。结论: 治疗前PNI、N分期、DOI和肿瘤直径可能对TSCC患者的OS和DSS有可靠的预测价值, 基于这些参数构建的预后预测列线图在预测TSCC根治性切除术后患者的OS和DSS方面表现出良好的准确性和有效性, 是评估生存结局的有效工具, 有助于选择有针对性的联合治疗来改善患者预后。
中图分类号:
- R739.8
| 1 |
Panarese I , Aquino G , Ronchi A , et al. Oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Prognostic and predictive parameters in the etiopathogenetic route[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2019, 19 (2): 105- 119.
doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1561288 |
| 2 |
Faisal M , Abu Bakar M , Sarwar A , et al. Depth of invasion (DOI) as a predictor of cervical nodal metastasis and local recurrence in early stage squamous cell carcinoma of oral tongue (ESSCOT)[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13 (8): e0202632.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202632 |
| 3 |
Ibrahim SA , Ahmed ANA , Elsersy HA , et al. Elective neck dissection in T1/T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma with N0 neck: Essential or not? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277 (6): 1741- 1752.
doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05866-3 |
| 4 |
Lu Z , Yan W , Liang J , et al. Nomogram based on systemic immune-inflammation index to predict survival of tongue cancer patients who underwent cervical dissection[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10, 341.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00341 |
| 5 |
Jia B , Dao J , Han J , et al. LINC00958 promotes the proliferation of TSCC via miR-211-5p/CENPK axis and activating the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21 (1): 147.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01808-z |
| 6 |
Almangush A , Pirinen M , Youssef O , et al. Risk stratification in oral squamous cell carcinoma using staging of the eighth American Joint Committee on Cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42 (10): 3002- 3017.
doi: 10.1002/hed.26344 |
| 7 |
Wei PY , Li WY , Tai SK . Discrete perineural invasion focus number in quantification for T1-T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160 (4): 635- 641.
doi: 10.1177/0194599818808510 |
| 8 |
Shi J , Bao X , Liu Z , et al. Serum miR-626 and miR-5100 are promising prognosis predictors for oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9 (4): 920- 931.
doi: 10.7150/thno.30339 |
| 9 |
Romani C , Salviato E , Paderno A , et al. Genome-wide study of salivary miRNAs identifies miR-423-5p as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11 (6): 2987- 2999.
doi: 10.7150/thno.45157 |
| 10 |
Zhang J , Hu Z , Horta CA , et al. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by tumor microenvironmental signals and its implication in cancer therapeutics[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2023, 88, 46- 66.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.12.002 |
| 11 |
Mariani P , Russo D , Maisto M , et al. Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an independent prognostic factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2022, 51 (1): 39- 51.
doi: 10.1111/jop.13264 |
| 12 |
Kumarasamy C , Tiwary V , Sunil K , et al. Prognostic utility of platelet-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancers: A detailed PRISMA compliant systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13 (16): 4166.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13164166 |
| 13 |
Xu X , Jing J . Inflammation-related parameter serve as prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 900305.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.900305 |
| 14 |
Wang Y , Lyu J , Jia H , et al. Clinical utility of the systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after radical radiotherapy[J]. Future Oncol, 2021, 17 (20): 2647- 2657.
doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0304 |
| 15 |
Wang D , Hu X , Xiao L , et al. Prognostic nutritional index and systemic immune-inflammation index predict the prognosis of patients with HCC[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 25 (2): 421- 427.
doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04492-7 |
| 16 |
Murthy P , Zenati MS , Al Abbas AI , et al. Prognostic value of the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) after neoadjuvant therapy for patients with resected pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2020, 27 (3): 898- 906.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-08094-0 |
| 17 |
Chang Y , An H , Xu L , et al. , Systemic inflammation score predicts postoperative prognosis of patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 2015, 113 (4): 626- 633.
doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.241 |
| 18 |
Kim MG , Choi YS , Youn SM , et al. Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors in oral tongue cancer: A 20-year retrospective study at the National Cancer Center, South Korea[J]. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 48 (4): 192- 200.
doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.4.192 |
| 19 |
Wolfer S , Elstner S , Schultze-Mosgau S . Degree of keratinization is an independent prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 76 (2): 444- 454.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2017.06.034 |
| 20 |
Ravasco P , Monteiro-Grillo I , Vidal PM , et al. Nutritional deterioration in cancer: The role of disease and diet[J]. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol), 2003, 15 (8): 443- 450.
doi: 10.1016/S0936-6555(03)00155-9 |
| 21 |
Jiang Y , Xu D , Song H , et al. Inflammation and nutrition-based biomarkers in the prognosis of oesophageal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMJ Open, 2021, 11 (9): e048324.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048324 |
| 22 |
Kono T , Sakamoto K , Shinden S , et al. Pre-therapeutic nutri-tional assessment for predicting severe adverse events in patients with head and neck cancer treated by radiotherapy[J]. Clin Nutr, 2017, 36 (6): 1681- 1685.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.10.021 |
| 23 |
Yoshimura T , Suzuki H , Takayama H , et al. Prognostic value of inflammatory biomarkers in aged patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13, 996757.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.996757 |
| 24 |
Kubota K , Ito R , Narita N , et al. Utility of prognostic nutritional index and systemic immune-inflammation index in oral cancer treatment[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22 (1): 368.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09439-x |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [3] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [4] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [5] | 张铨,宋海峰,马冰磊,张喆楠,周朝晖,李傲林,刘军,梁磊,朱时雨,张骞. 术前预后营养指数可作为预测非转移性肾细胞癌预后的指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 149-155. |
| [6] | 左美妮,杜依青,于路平,戴翔,徐涛. 代谢综合征与肾透明细胞癌患者预后的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 636-643. |
| [7] | 丁婷婷,曾楚雄,胡丽娜,余明华. 基于癌症基因组图谱数据库结直肠癌免疫细胞浸润预测模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 203-208. |
| [8] | 王文鹏,王捷夫,胡均,王俊锋,刘嘉,孔大陆,李健. 结直肠间质瘤临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 353-361. |
| [9] | 刘余庆,卢剑,郝一昌,肖春雷,马潞林. 经皮肾镜取石术后尿脓毒血症的相关危险因素及预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 507-513. |
|
||