北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 131-137. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.020
牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点
凌晓彤1,屈留洋1,郑丹妮1,杨静1,闫雪冰2,柳登高1,*( ),高岩3
),高岩3
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院影像科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔材料重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院第一门诊部特诊科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔材料重点实验室,北京 100081
3. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔病理科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
Xiaotong LING1,Liuyang QU1,Danni ZHENG1,Jing YANG1,Xuebing YAN2,Denggao LIU1,*( ),Yan GAO3
),Yan GAO3
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
2. Special Dental Department, The First Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
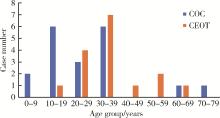
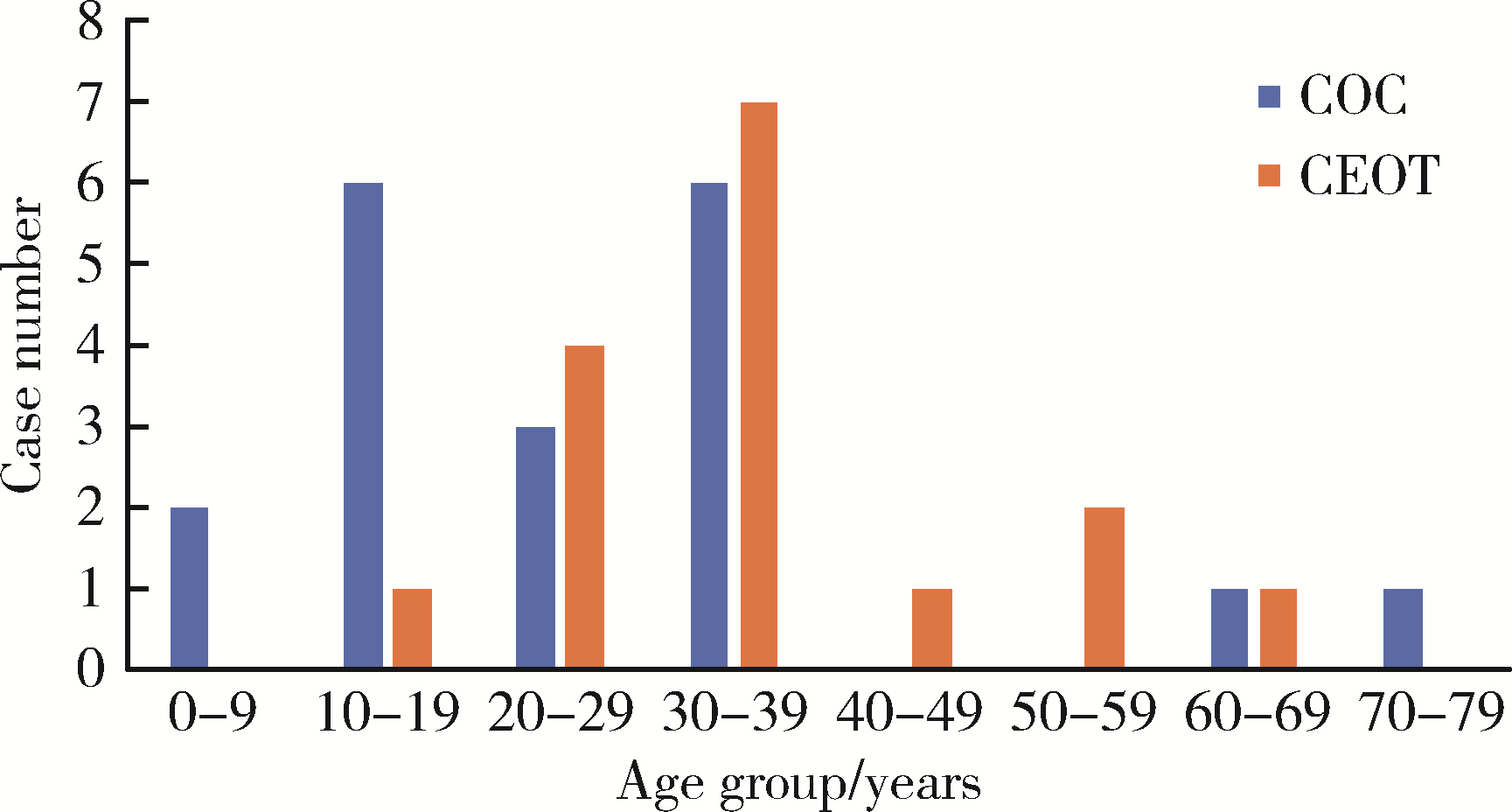
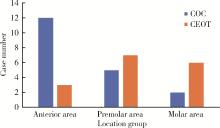
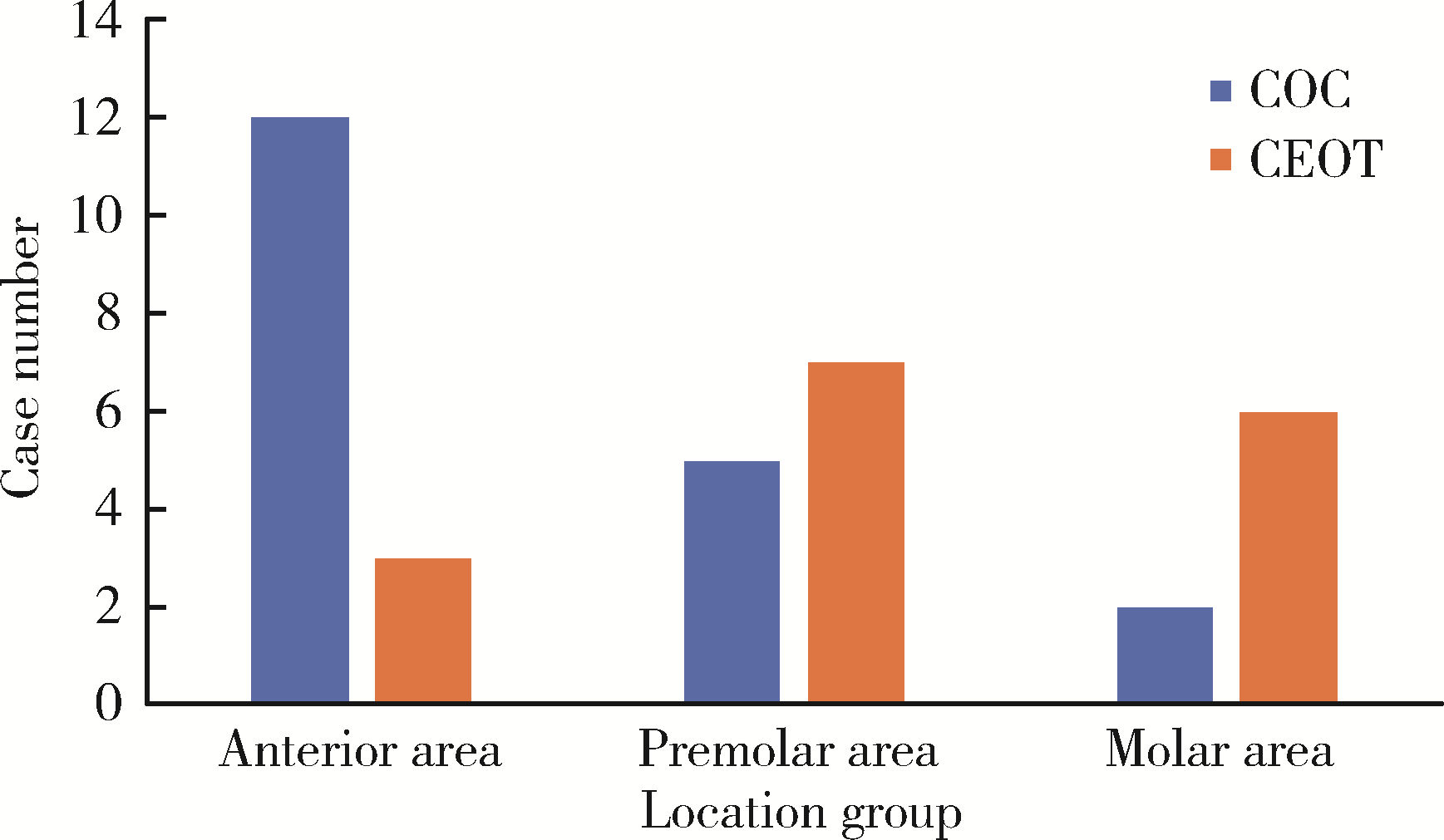
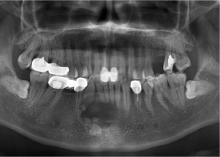
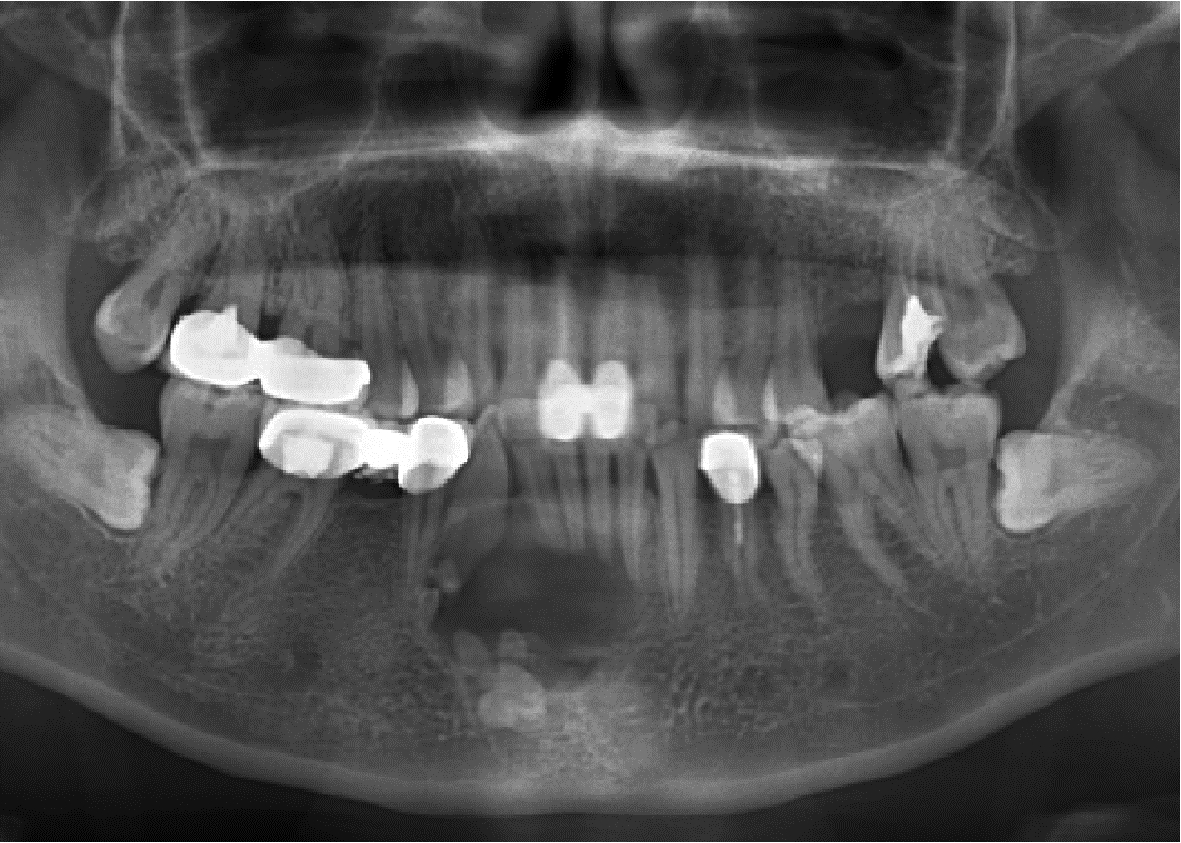
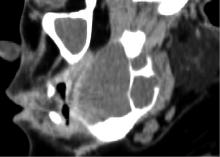
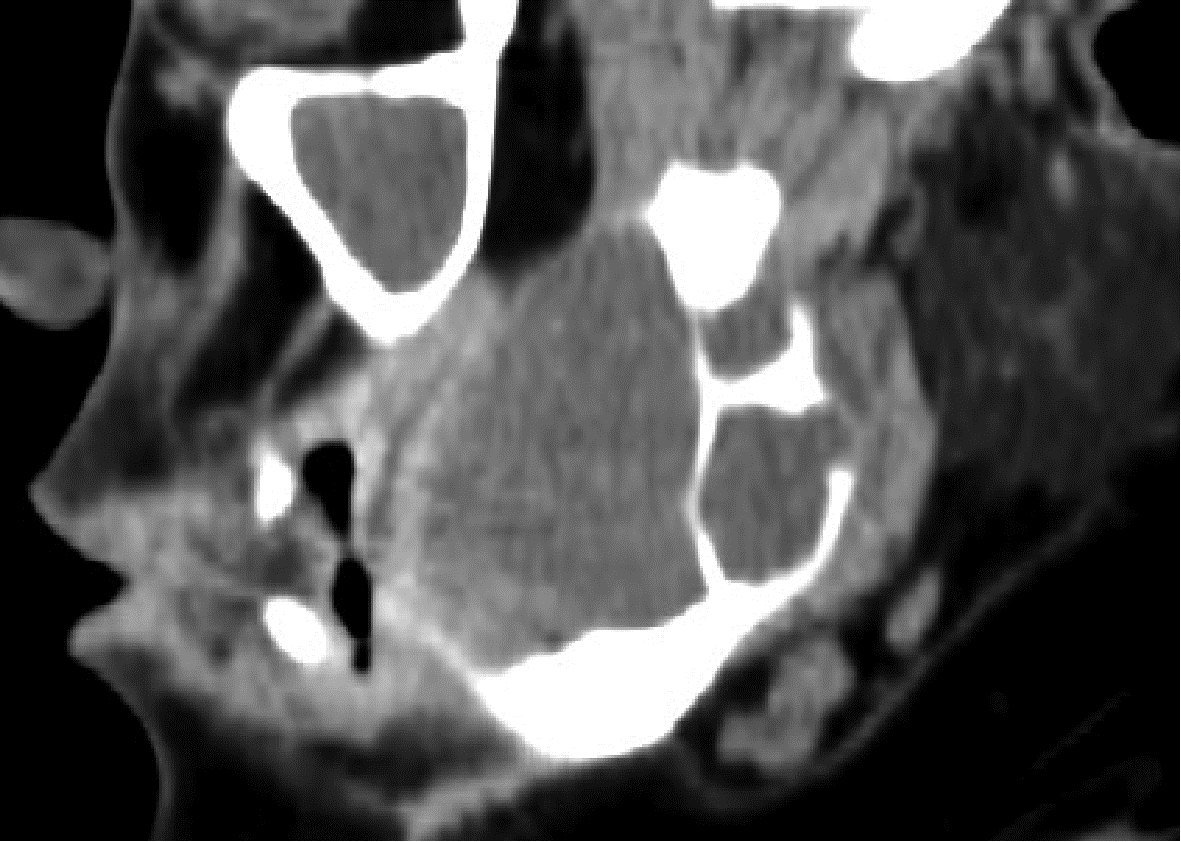
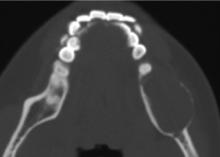
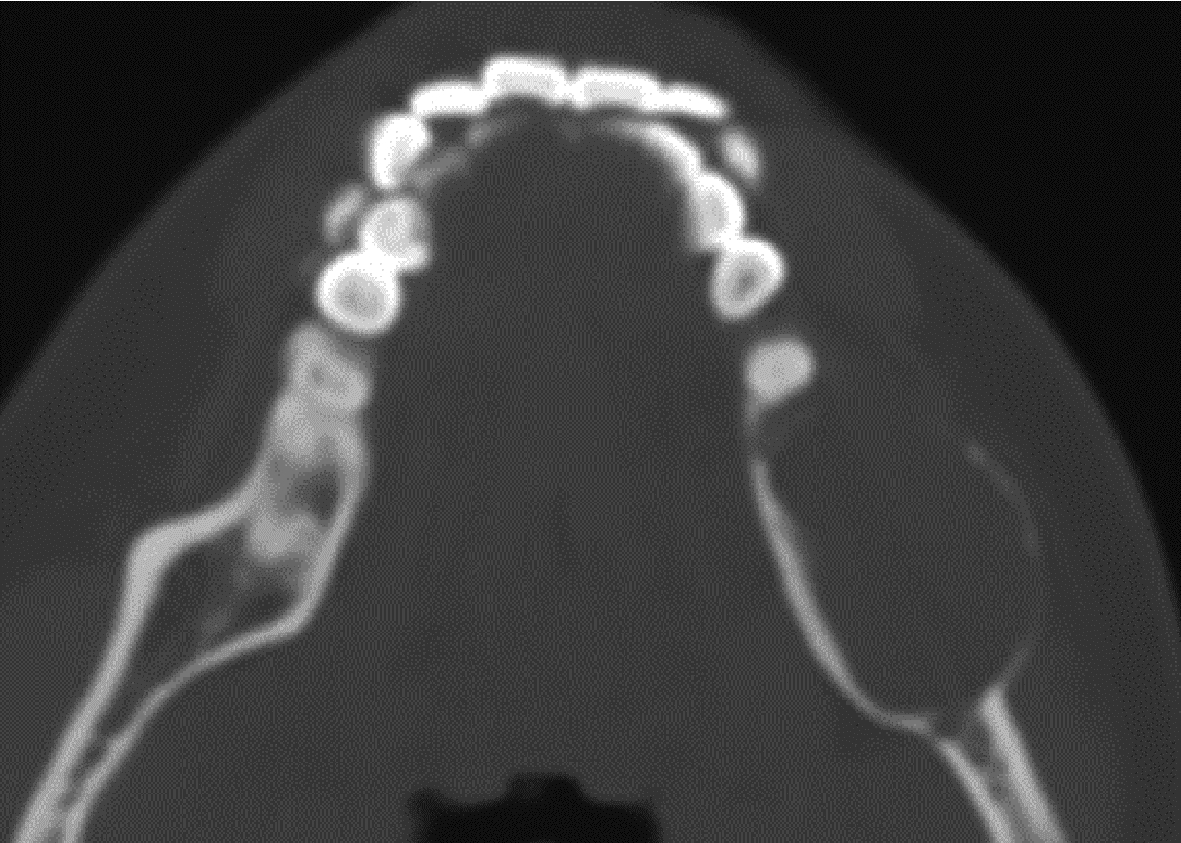
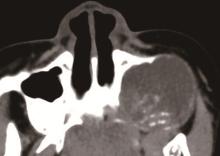
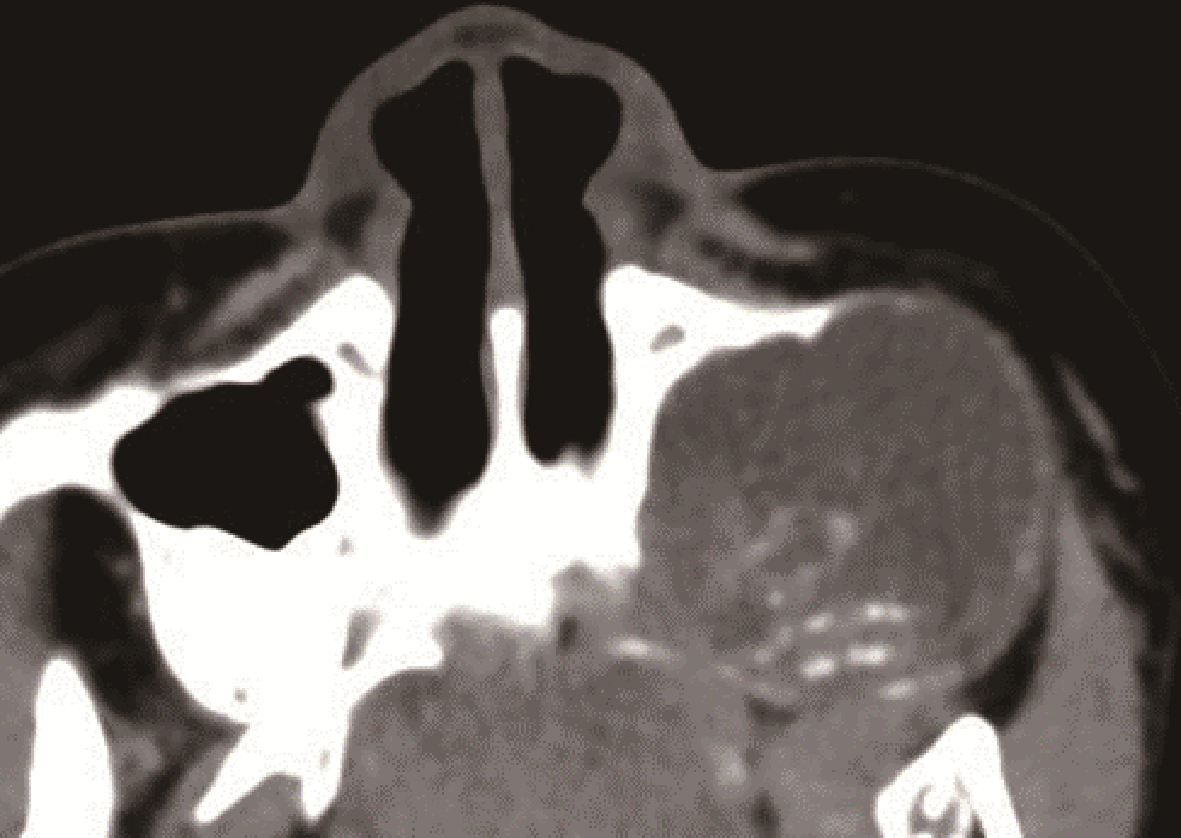
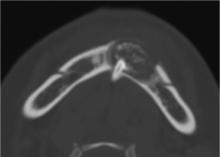
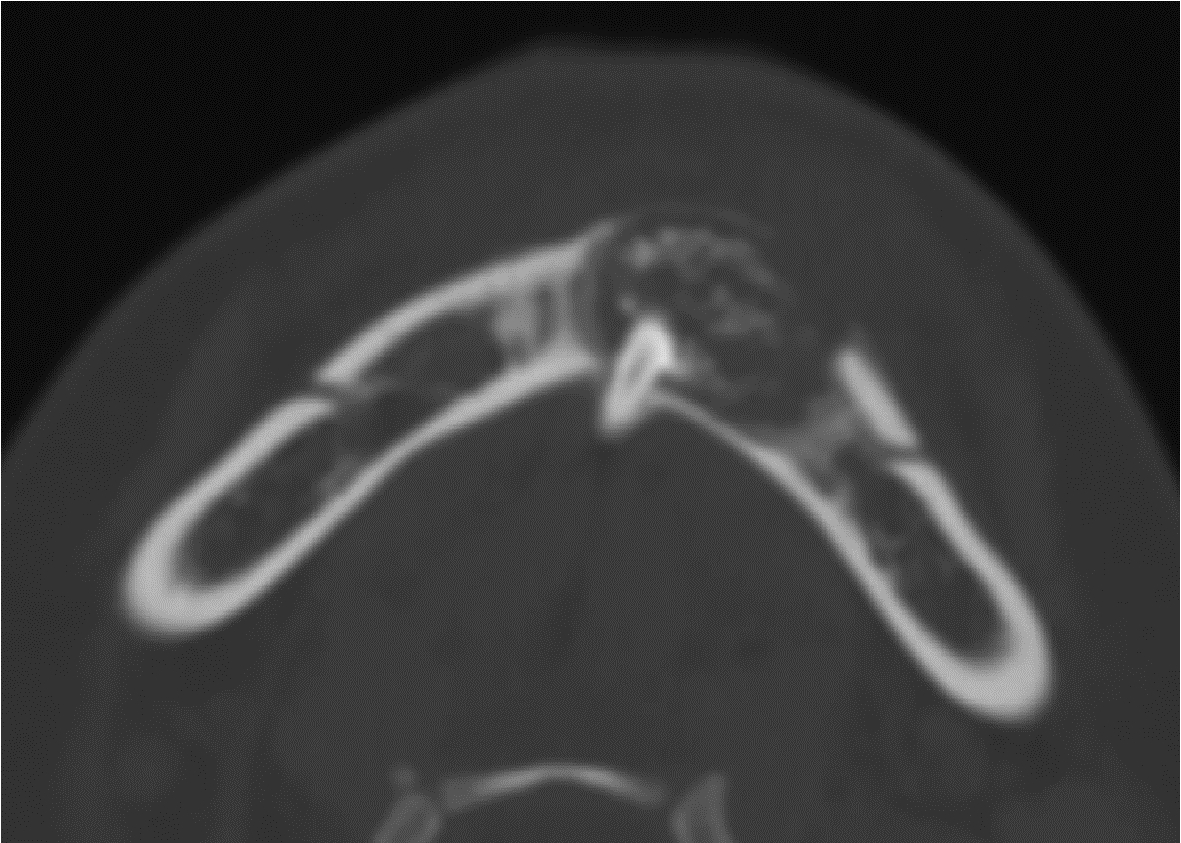
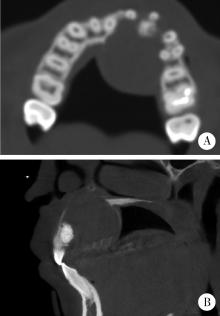
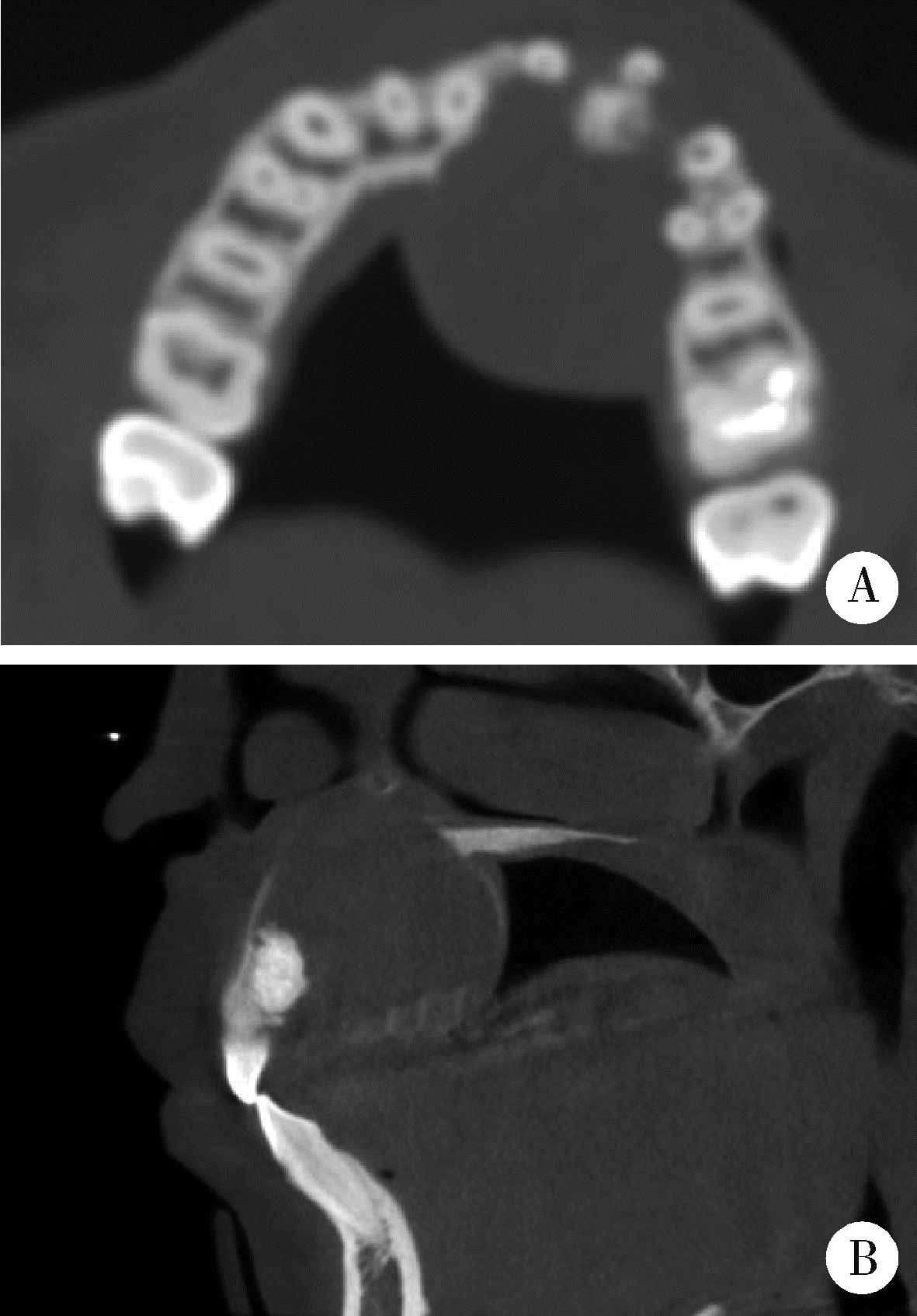
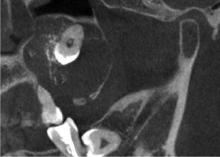
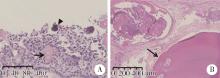
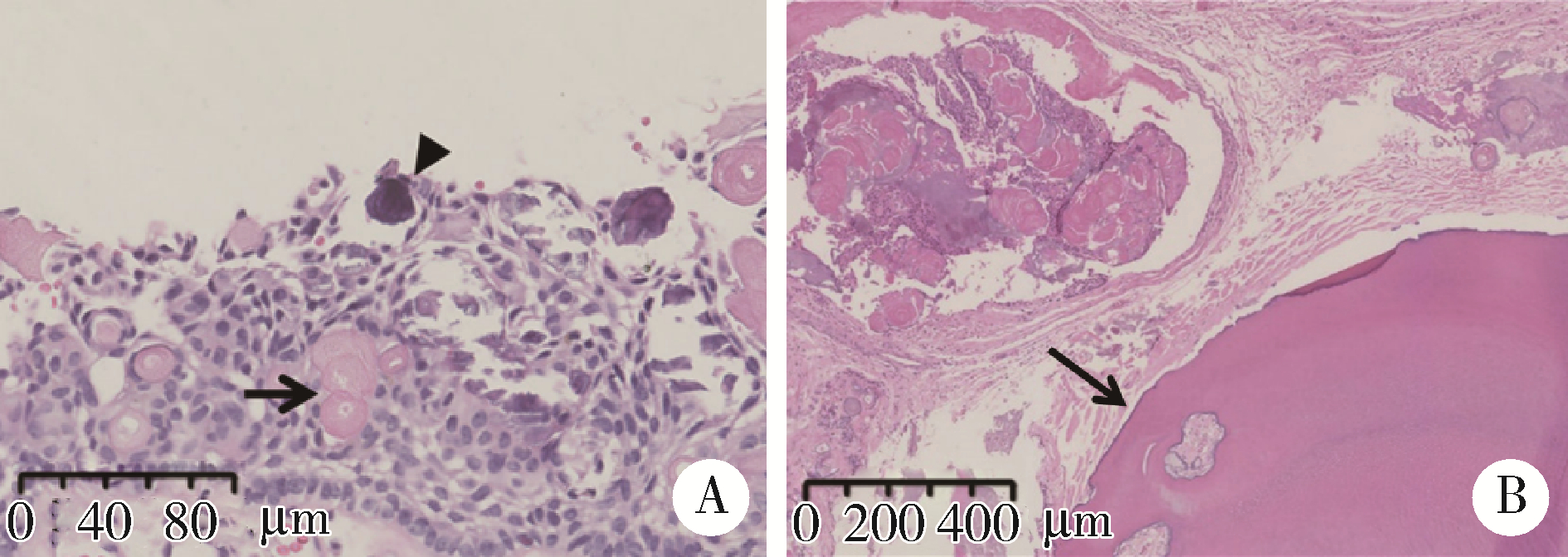
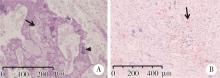
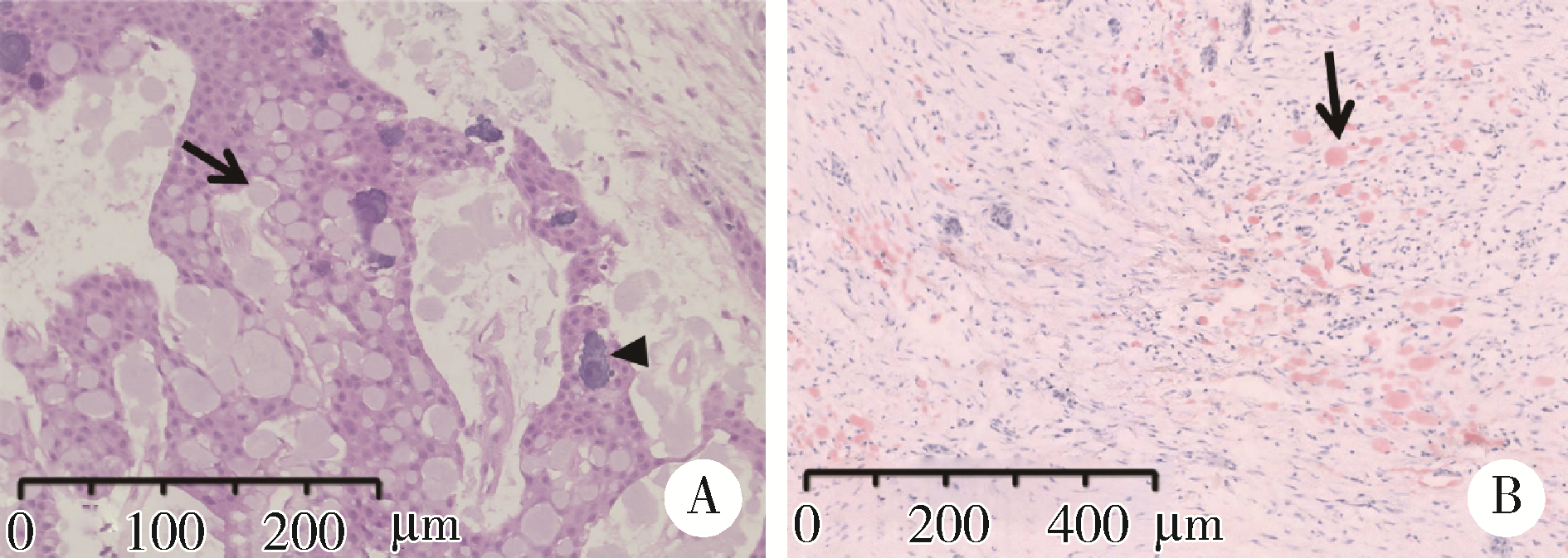
目的: 利用螺旋CT和锥束计算机体层摄影术(cone-beam computed tomography,CBCT)比较分析牙源性钙化囊肿(calcifying odontogenic cyst,COC)与牙源性钙化上皮瘤(calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor,CEOT)的三维影像学特征。方法: 回顾性收集北京大学口腔医院经病理证实的19例COC和16例CEOT的螺旋CT或CBCT影像资料,结合患者的临床与病理表现分析其影像学特征,包括病变位置、大小、膨隆程度、内部结构及牙齿受累情况等,并对病变内钙化特点进行分类。结果: 19例COC患者中,男性12例,女性7例,平均年龄27岁,89.5%(17/19)的病变位于前牙区和前磨牙区,100.0%存在颌骨膨隆,78.9%出现骨皮质不连续。16例CEOT患者中,男性3例,女性13例,平均年龄36岁,81.3%(13/16)的病变位于前磨牙区和磨牙区,56.3%存在颌骨膨隆,93.8%出现骨皮质不连续。根据病变内钙化物的分布特点分为无钙化型(未见钙化影像)、边缘型(钙化影位于病变边缘,且仅在一侧散在分布)、弥散型(多发钙化影广泛分布于病变范围内)、团块型(存在直径大于5 mm的钙化团块)及冠周型(钙化影像聚集于阻生牙周围)。73.7%的COC病变区存在钙化,包括边缘型9例、弥散型3例及团块型2例;42.8%的CEOT病变区存在钙化,包括弥散型2例及冠周型5例。另外,6例COC病变中存在牙瘤样影像,9例无钙化的CEOT中8例为朗格汉斯(Langerhans)型,病变较小(近远中径平均为17.8 mm),不含阻生牙,且无牙根吸收。结论: COC好发于颌骨前部,膨隆明显,而CEOT好发于颌骨后部,多存在骨皮质不连续。两者的钙化特点差异较大,COC病变区钙化影像发生率高,多沿病变边缘散在分布,位于病变一侧,远离阻生牙,部分病变与牙瘤共同发生;CEOT逾半数无钙化且病变较小,其余病变中钙化物影像多围绕在阻生牙周围。
中图分类号:
- R739.8
| 1 |
Lee SK , Kim YS . Current concepts and occurrence of epithelial odontogenic tumors: Ⅱ. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor versus ghost cell odontogenic tumors derived from calcifying odontogenic cyst[J]. Korean J Pathol,, 2014, 48 (3): 175- 187.
doi: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.3.175 |
| 2 | 马绪臣. 口腔颌面医学影像学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2006. |
| 3 |
Philipsen HP , Reichart PA . Adenomatoid odontogenic tumour: Facts and figures[J]. Oral Oncol, 1999, 35 (2): 125- 131.
doi: 10.1016/S1368-8375(98)00111-0 |
| 4 | Bansal SP , Shaikh S , Arvandekar AS , et al. Analysis of 55 cases of adenomatoid odontogenic tumor in an Indian population and review of literature[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2022, 27 (1): e85- e93. |
| 5 |
陈菲, 张庆庆, 陆东辉, 等. 牙源性钙化囊性瘤临床病理研究[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2012, 28 (8): 891- 894.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7399.2012.08.014 |
| 6 |
付文荣, 程正江. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤3例临床病理观察[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2014, 21 (4): 231- 233.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2014.04.012 |
| 7 | Sonone A , Sabane VS , Desai R . Calcifying ghost cell odontogenic cyst: Report of a case and review of literature[J]. Case Rep Dent, 2011, 2011, 328743. |
| 8 |
刘梅, 孙国文, 唐恩溢, 等. 牙源性钙化囊肿的临床病理分析[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2020, 36 (1): 96- 99.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2020.01.021 |
| 9 |
陶谦, 梁培盛. 2017版WHO牙源性肿瘤新分类之述评[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2017, 25 (12): 749- 754.
doi: 10.12016/j.issn.2096-1456.2017.12.001 |
| 10 | Soluk-Tekkesin M , Wright JM . The World Health Organization classification of odontogenic lesions: A summary of the changes of the 2022 (5th) edition[J]. Turk Patoloji Derg, 2022, 38 (2): 168- 184. |
| 11 |
Buchner A . The central (intraosseous) calcifying odontogenic cyst: An analysis of 215 cases[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1991, 49 (4): 330- 339.
doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(91)90365-S |
| 12 | Ahmad SA , Popli DB , Sircar K , et al. Calcifying odontogenic cyst: Report of an uncommon entity with a brief literature review[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol, 2022, 26 (1): 131. |
| 13 | Chandran A , Nachiappan S , Selvakumar R , et al. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic cyst of maxilla: Report of a case and review and discussion on the terminology and classification[J]. J Microsc Ultrastruct, 2020, 9 (2): 98- 102. |
| 14 |
de Arruda JAA , Schuch LF , Abreu LG , et al. A multicenter study of 268 cases of calcifying odontogenic cysts and a literature review[J]. Oral Dis, 2018, 24 (7): 1282- 1293.
doi: 10.1111/odi.12906 |
| 15 |
Rojo R , Prados-Frutos JC , Gutierrez Lázaro I , et al. Calcifying odontogenic cysts[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 118 (2): 122- 124.
doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2016.10.007 |
| 16 |
Chindasombatjaroen J , Poomsawat S , Boonsiriseth K . Two unique cases of calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor in the maxillary posterior region[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2014, 118 (4): 497- 504.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.06.006 |
| 17 | Santos HBP , de Morais EF , Moreira DGL , et al. Calcifying odontogenic cyst with extensive areas of dentinoid: uncommon case report and update of main findings[J]. Case Rep Pathol, 2018, 2018, 8323215. |
| 18 | Gamoh S , Akiyama H , Furukawa C , et al. Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor accompanied by a dentigerous cyst: A case report[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14 (5): 5785- 5790. |
| 19 |
Hirshberg A , Kaplan I , Buchner A . Calcifying odontogenic cyst associated with odontoma: A possible separate entity (odontocalcifying odontogenic cyst)[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1994, 52 (6): 555- 558.
doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(94)90087-6 |
| 20 |
Vizuete-Bolaños MX , Salgado-Chavarria F , Ramírez-Martínez CM , et al. Compound odontoma associated with a calcifying odontogenic cyst. Case report and systematic review[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 123 (3): e97- e105.
doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2021.10.008 |
| 21 |
张艳宁, 侯亚丽, 于美清, 等. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤1例临床病理分析及文献复习[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2021, 37 (3): 431- 433.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2021.03.032 |
| 22 | Mujib BR , Kulkarni PG , Lingappa A , et al. An atypical presentation of Pindborg tumor in anterior maxilla[J]. Dent Res J (Isfahan), 2012, 9 (4): 495- 498. |
| 23 |
Ibituruna ACH , Costa ARGF , Paulo LFB , et al. Multiple calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor: Case report and review of the literature[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2019, 128 (3): 268- 272.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.03.018 |
| 24 |
Zhang A , Chaw SY , Talacko AA , et al. Central calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumour in the posterior maxilla: A case report[J]. Aust Dent J, 2016, 61 (3): 381- 385.
doi: 10.1111/adj.12384 |
| 25 | 王凯利, 郑广宁, 刘莉, 等. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤2例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2016, 34 (1): 104- 107. |
| 26 |
Vered M , Wright JM . Update from the 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of head and neck tumors: Odontogenic and maxillofacial bone tumours[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2022, 16 (1): 63- 75.
doi: 10.1007/s12105-021-01404-7 |
| 27 |
王丽, 汪说之, 陈新明, 等. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤中朗格汉斯细胞的研究[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2005, 21 (6): 645- 648.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7651.2005.06.016 |
| 28 |
Hong SP , Ellis GL , Hartman KS . Calcifying odontogenic cyst. A review of ninety-two cases with reevaluation of their nature as cysts or neoplasms, the nature of ghost cells, and subclassification[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol, 1991, 72 (1): 56- 64.
doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(91)90190-N |
| 29 | 刘轶芳. 245例颌骨良恶性肿瘤的CT影像学特征的对比研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020. |
| 30 | 叶婷婷, 陈蔚华, 裴婧, 等. 青少年牙本质生成性影细胞瘤1例[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2022, 38 (10): 995- 996. |
| 31 | 王予江, 李琳琳. 外周型牙源性钙化囊性瘤病例报道[C]//中华口腔医学会口腔颌面外科专业委员会. 第十四次中国口腔颌面外科学术会议论文汇编. 重庆: [出版者不详], 2018: 1. |
| [1] | 段登辉,WANGHom-Lay,王恩博. 可吸收胶原膜在颊侧袋形瓣引导性骨再生手术中的作用: 一项回顾性影像学队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1097-1104. |
| [2] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [3] | 温奥楠,刘微,柳大为,朱玉佳,萧宁,王勇,赵一姣. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
| [4] | 杨刚,胡文杰,曹洁,柳登高. 牙周健康的上颌前牙唇侧嵴顶上牙龈的三维形态分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 990-994. |
| [5] | 高璐,谷岩. 中国人群腭中缝形态特点分期与Demirjian牙龄的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 133-138. |
| [6] | 邱天成,刘筱菁,薛竹林,李自力. 基于三维动态照相机的正常人面部表情可重复性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1107-1111. |
| [7] | 贾鹏程,杨刚,胡文杰,赵一姣,刘木清. 根尖片评估单根牙骨内牙根表面积的准确性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 91-97. |
| [8] | 马静,江久汇. 骨性Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类高角错牙合患者下切牙区的牙槽骨形态分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 98-103. |
| [9] | 徐筱,徐莉,江久汇,吴佳琪,李小彤,靖无迪. 锥形束CT评判安氏Ⅲ类错牙合上前牙骨开裂与骨开窗的准确性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 104-109. |
| [10] | 曹婕1,孟焕新. 锥形束CT用于评估牙槽骨骨缺损的情况和骨再生区域骨密度的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 110-116. |
| [11] | 常大桐,周彦恒,刘伟涛. 上颌反复快速扩缩对上气道影响的锥束CT研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 685-690. |
| [12] | 陈全,张晓1张智勇,高巍,刘文曙,孟甜,陈宇寰,王慧丽. 上颌窦前外侧壁骨内血管孔道位置锥形束CT影像判断分析及其临床应对措施[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 540-546. |
| [13] | 赵一姣,王斯维,刘怡,王勇. 基于影像学牙周膜解剖特征快速提取活体牙三维牙根形态的方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 54-059. |
| [14] | 苏征,白雨豪,侯晓玫. 不同技术对弯曲根管根尖气锁去除效果的锥形束CT研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 76-080. |
| [15] | 温馥嘉,陈贵,刘怡. 基于锥形束CT的强支抗内收上前牙病例牙根及牙槽骨的形态学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 702-708. |
|
||