北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1093-1097. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.017
早期胃癌淋巴结转移规律及内镜黏膜下剥离术治疗早期胃癌的疗效评价
武颖超1,蔡云龙2,戎龙2,张继新3,刘金1,汪欣1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院普通外科,北京 100034
2. 北京大学第一医院内镜中心,北京 100034
3. 北京大学第一医院病理科,北京 100034
Characteristics of lymph node metastasis and evaluating the efficacy of endoscopic submucosal dissection in early gastric cancer
Ying-chao WU1,Yun-long CAI2,Long RONG2,Ji-xin ZHANG3,Jin LIU1,Xin WANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of General Surgery, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Endoscopy, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
3. Department of Pathology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
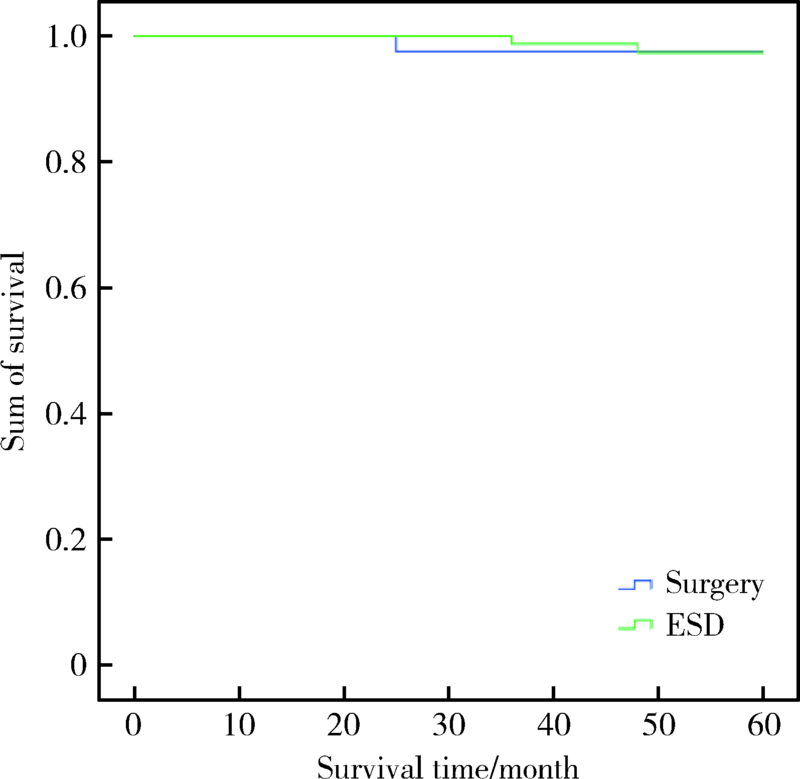
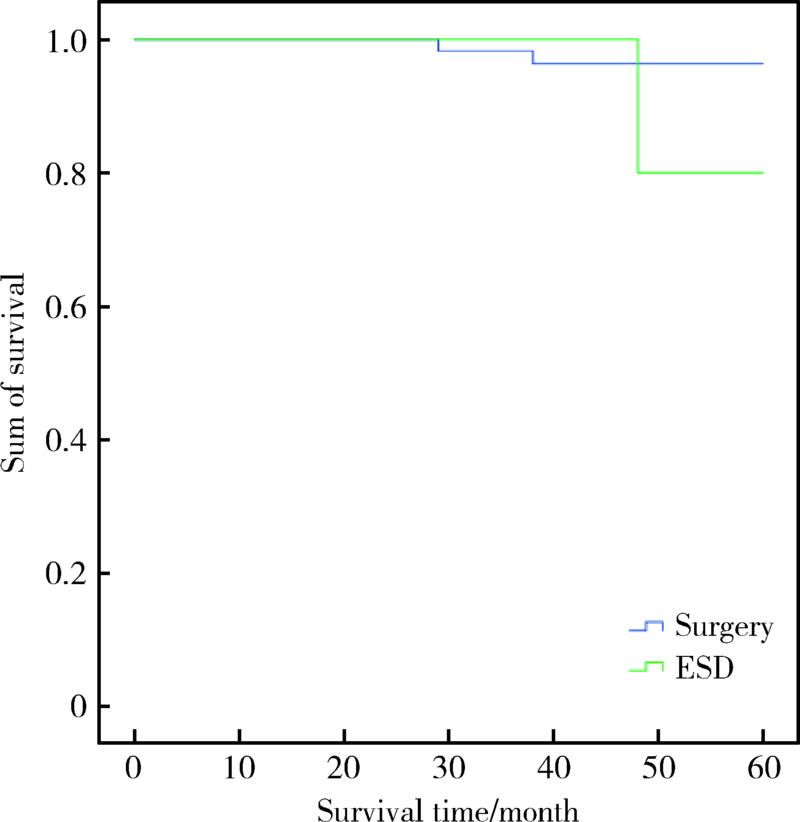
目的:探讨早期胃癌淋巴结转移的规律,并通过与手术治疗对比评价内镜黏膜下剥离术(endoscopic submucosal dissection,ESD)治疗早期胃癌的疗效。方法: 回顾性分析北京大学第一医院2010年1月至2017年12月间收治的320例早期胃癌患者的临床病理资料,其中外科手术治疗198例,ESD治疗122例。分析早期胃癌的淋巴结转移规律,总结符合ESD绝对及扩大适应证的早期胃癌的淋巴结转移情况;进一步比较ESD和手术治疗早期胃癌的远期疗效,从而评价目前ESD治疗早期胃癌的绝对适应证和扩大适应证的合理性。结果:198例早期胃癌患者共有22例淋巴结转移,转移率为11.1%。单因素分析结果显示肿瘤大小(χ2=5.525,P=0.019)、浸润深度(χ2=8.235,P=0.004)、分化程度(χ2=6.323,P=0.012)、脉管浸润(χ2=12.273,P<0.001)与早期胃癌的淋巴结转移有关;多因素分析显示肿瘤浸润深度(Wald=7.575,P=0.006)和分化程度(Wald=6.317,P=0.012)是早期胃癌发生淋巴结转移的独立影响因素。符合ESD绝对适应证和扩大适应证的患者的淋巴结转移率均为0%;符合ESD绝对适应证而行手术和ESD治疗的患者的5年生存率分别为97.6%和97.9%,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.014,P=0.907);符合ESD扩大适应证而行手术和ESD治疗的患者的5年生存率分别为96.5%和91.7%,差异无统计学意义(χ2=1.061,P=0.303)。结论: 早期胃癌的淋巴结转移主要与肿瘤的浸润深度和分化程度密切相关;本组数据显示ESD治疗早期胃癌无论是绝对适应证还是扩大适应证都跟手术疗效相当,但仍需大样本量的研究证实。
中图分类号:
- R735.2
| [1] |
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016,66(2):115-132.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 pmid: 26808342 |
| [2] |
Murakami T. Early cancer of the stomach[J]. World J Surg, 1979,3(6):685-692.
doi: 10.1007/BF01654788 pmid: 532187 |
| [3] |
Guo CG, Zhao DB, Liu Q, et al. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer with signet ring cell carcinoma[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2015,19(11):1958-1965.
doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-2915-z pmid: 26302875 |
| [4] |
Kunisaki C, Akiyama H, Nomura M, et al. Significance of long-term follow-up of early gastric cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2006,13(3):363-369.
pmid: 16485155 |
| [5] |
Ito H, Inoue H, Ikeda H, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and treatment strategies in early gastric cancer: A retrospective cohort study[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2011,30(1):117.
doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-117 |
| [6] |
Hirasawa T, Gotada T, Miyata S, et al. Incidence of lymph node metastasis and the feasibility of endoscopic resection for undifferentiated-type early gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2009,12(3):148-152.
pmid: 19890694 |
| [7] |
Wang HS, Zhang H, Wang C, et al. Expanded endoscopic therapy criteria should be cautiously used in intramucosal gastric cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2016,28(3):348-354.
doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2016.03.09 pmid: 27478320 |
| [8] |
Chen L, Wang YH, Cheng YQ, et al. Risk factors of lymph node metastasis in 1620 early gastric carcinoma radical resections in Jiangsu Province in China: A multicenter clinicopathological study[J]. J Dig Dis, 2017,18(10):556-565.
doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12545 pmid: 28949436 |
| [9] |
Bausys R, Bausys A, Vysniauskaite I, et al. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients: Report from Eastern Europe country-Lithuania[J]. BMC Surg, 2017,17(1):108.
doi: 10.1186/s12893-017-0304-0 pmid: 29169358 |
| [10] |
Hölscher AH, Drebber U, Mönig SP, et al. Early gastric cancer: lymph node metastasis starts with deep mucosal infiltration[J]. Ann Surg, 2009,250(5):791-797.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181bdd3e4 pmid: 19809298 |
| [11] |
Takizawa K, Takashima A, Kimura A, et al. A phase II clinical trial of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer of undifferentiated type: Japan Clinical Oncology Group study JCOG1009/1010[J]. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2013,43(1):87-91.
pmid: 23166384 |
| [12] | 日本胃癌學會. 胃癌治療ガイドライン[M]. 5 版. 東京: 金原出版株式会社, 2018: 20-24. |
| [13] |
Hasuike N, Ono H, Boku N, et al. A non-randomized confirmatory trial of an expanded indication for endoscopic submucosal dissection for intestinal-type gastric cancer (cT1a): The Japan Clinical Oncology Group study (JCOG0607)[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2018,21(1):114-123.
doi: 10.1007/s10120-017-0704-y pmid: 28224238 |
| [14] |
Gotoda T. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2007,10(1):1-11.
doi: 10.1007/s10120-006-0408-1 |
| [15] |
Yamamoto Y, Fujisaki J, Hirasawa T, et al. Therapeutic outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection of undifferentiated-type intramucosal gastric cancer without ulceration and preoperatively diagnosed as 20 millimetres or less in diameter[J]. Dig Endosc, 2010,22(2):112-118.
doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2010.00945.x pmid: 20447204 |
| [16] |
Abdelfatah MM, Barakat M, Lee H, et al. The incidence of lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer according to the expanded criteria in comparison with the absolute criteria of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2018,87(2):338-347.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.09.025 pmid: 28966062 |
| [17] |
Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, et al. Incidence of lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: estimation with a large number of cases at two large centers[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2000,3(4):219-225.
doi: 10.1007/pl00011720 pmid: 11984739 |
| [18] |
Kang HJ, Kim DH, Jeon TY, et al. Lymph node metastasis from intestinal-type early gastric cancer: experience in a single institution and reassessment of the extended criteria for endoscopic submucosal dissection[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2010,72(3):508-515.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.03.1077 pmid: 20554277 |
| [1] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [2] | 罗靓,李云,王红彦,相晓红,赵静,孙峰,张晓盈,贾汝琳,李春. 抗内皮细胞抗体检测在早期流产中的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1039-1044. |
| [3] | 侯卫华,宋书杰,石中月,金木兰. 幽门螺杆菌阴性早期胃癌的临床病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 292-298. |
| [4] | 刘菊梅,梁丽,张继新,戎龙,张梓怡,吴悠,赵旭东,李挺. 411例早期胃癌及癌前病变内镜黏膜下剥离术标本的病理学评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 299-307. |
| [5] | 柯杨,王敏敏,刘萌飞,刘芳芳,刘英,何忠虎. 肿瘤早期预警生物标志物的研究与思考[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 810-813. |
| [6] | 罗采南,李正芳,武丽君,陈海娟,杨春梅,徐文晖,刘小玲,唐薇,乔平,热娜·白合提亚. 类风湿关节炎不同分类标准的多中心临床比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 897-901. |
| [7] | 杨阳,刘毅强,王晓红,季科,李忠武,白健,杨爱蓉,胡颖,韩海勃,李子禹,步召德,吴晓江,张连海,季加孚. 单中心大样本Epstein-Barr病毒相关性胃癌亚型的临床病理及分子特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 451-458. |
| [8] | 刘鑫,张静,王晔,张贺军,丁士刚,周丽雅. 早期胃癌白光内镜下特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 302-306. |
| [9] | 张智勇,孟甜,陈全,刘文曙,陈宇寰. 种植体早期失败病例回顾性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1088-1091. |
| [10] | 刘梦珂,王露辰,胡凡磊. 血清基质金属蛋白酶3水平与早期类风湿关节炎病情评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 981-985. |
| [11] | 王明,李辉,王静,高嵩. 利用X射线衍射增强成像技术诊断肝纤维化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 899-904. |
| [12] | 李健男,冯芝恩,王琳,王衣祥,郭传瑸. 乏氧诱导因子-1α在口腔鳞状细胞癌颈淋巴转移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 26-32. |
| [13] | 孙乾,章文博,高敏,于森,毛驰,郭传瑸,俞光岩,彭歆. cN0上颌恶性肿瘤颈淋巴结转移的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 1050-1054. |
| [14] | 林天歆. 膀胱癌的淋巴结清扫范围[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 565-568. |
| [15] | 高翔,陈香梅,张婷,张静,陈茉,郭正阳,石岩岩,鲁凤民,丁士刚. 巨噬细胞加帽蛋白与胃癌细胞增殖及迁移能力的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 489-494. |
|
||