北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 276-282. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.011
肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌的临床病理特点及预后
- 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科, 北京大学泌尿外科研究所, 国家泌尿、男性生殖系肿瘤研究中心, 北京 100034
Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of kidney: Clinicopathology and prognosis
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
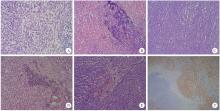
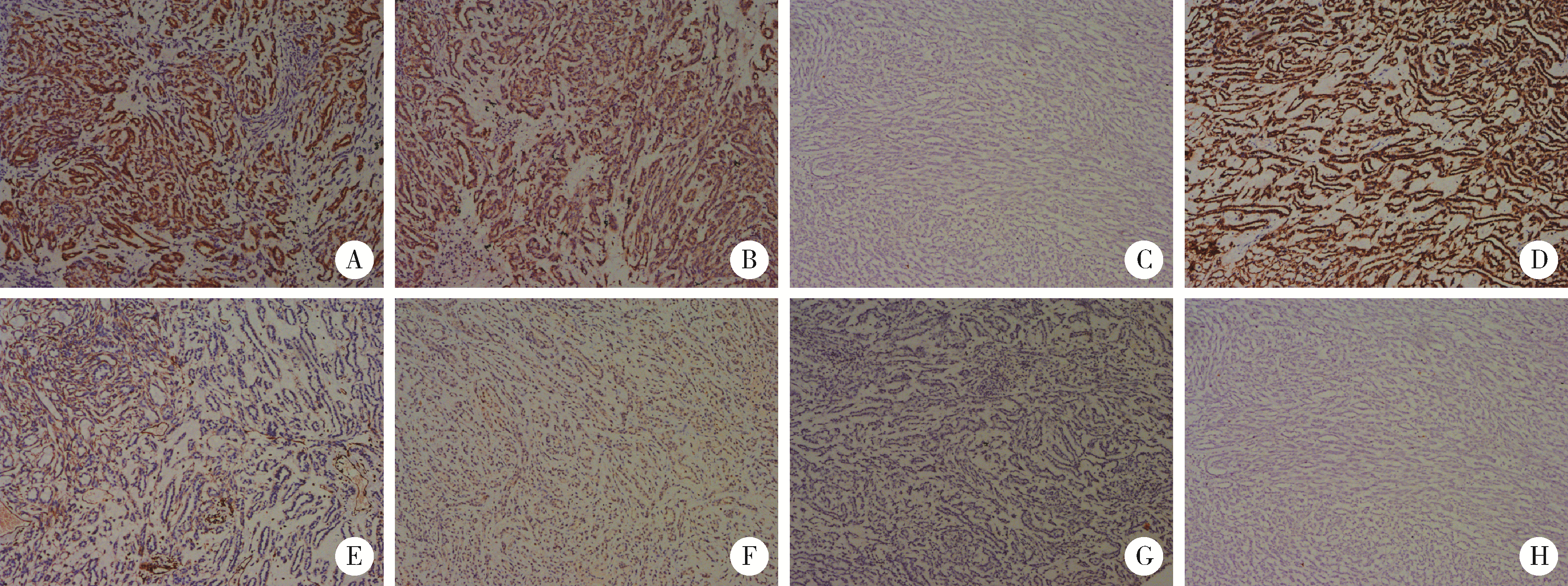
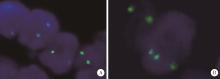
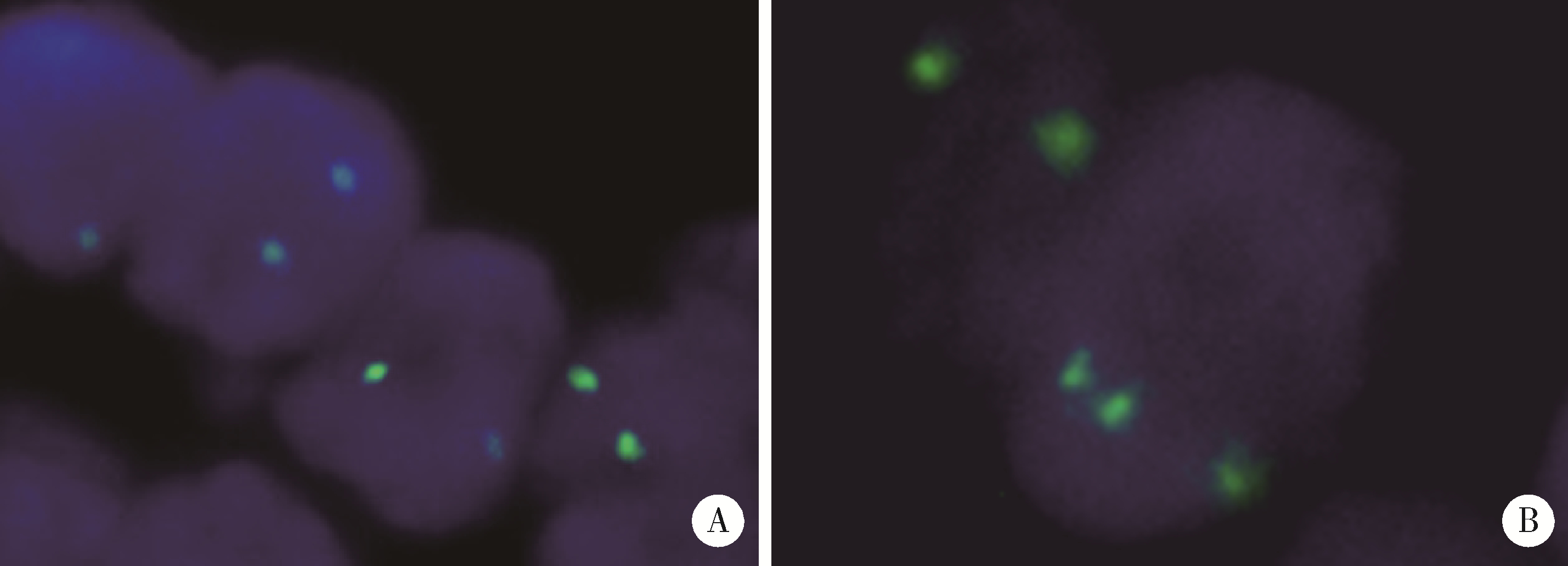
目的: 探讨肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌的临床病理学特征、免疫表型、鉴别诊断及预后。方法: 回顾性分析13例肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌病例, 总结其临床和病理学特点以及免疫组织化学表达情况, 并进行荧光原位杂交检测。结果: 13例患者年龄39~78岁, 平均57.1岁, 其中男性4例, 女性9例, 男女比例为1 ∶2.25, 均无临床症状, 为偶然发现。3例行肾部分切除术, 10例行肾根治切除术; 9例肿瘤位于左侧肾, 4例位于右侧肾, 最大径2~12 cm。大部分病例镜下形态为经典型形态改变, 细胞核分级采用世界卫生组织(World Health Organization, WHO)/国际泌尿病理协会(International Society of Urological Pathology, ISUP)分级系统, 11例为G2, 2例为G3。病理分期PT1a共6例, PT1b共3例, PT2a共2例, PT2b及PT3a各1例。免疫组织化学染色阳性率: 波形蛋白(vimentin)、AE1/AE3、α-甲基脂酰辅酶A消旋酶(α-methylacyl-CoA racemase, αMACR)、细胞角蛋白(cytokeratin, CK)8/18均为100%(13/13), CK7为92.3%(12/13), 上皮细胞膜抗原(epithelial membrane antigen, EMA)为92.3%(12/13), CK20为46.2%(6/13), CD10为30.8%(4/13), 突触素(synaptophysin, Syn)为7.7%(1/13), 嗜铬素(chromogranin A, CgA)、CD57、WT1、Ki-67均为0(0/13)。荧光原位杂交结果显示所有病例均未见7、17号染色体多倍体改变。术后随访6个月至7年6个月, 2例出现肺转移后死亡(1例核分级为G3, 1例伴有坏死), 其余11例无复发和转移。结论: 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌是一种低度恶性的独特类型肾肿瘤, 好发于女性, 年龄分布广泛。目前治疗方法为手术切除, 伴有坏死及高级别形态的病例易发生复发和转移, 虽然大部分病例预后良好, 但术后仍需密切随访。
中图分类号:
- R737.11
| 1 | Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs[R]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2004. |
| 2 | Moch H, Humphrey P, Ulbright T, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs[R]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2016. |
| 3 |
MacLennan GT , Farrow GM , Bostwick DG . Low-grade collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: Report of 13 cases of low-grade mucinous tubulocystic renal carcinoma of possible collecting duct origin[J]. Urology, 1997, 50 (5): 679- 684.
doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00335-X |
| 4 |
Ged Y , Chen YB , Knezevic A , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle-cell carcinoma of the kidney: Clinical features, genomic profiles, and treatment outcomes[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2019, 17 (4): 268- 274.
doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.04.006 |
| 5 |
Xu X , Zhong J , Zhou X , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney: A study of clinical, imaging features and treatment outcomes[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 865263.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.865263 |
| 6 |
Ferlicot S , Allory Y , Comperat E , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: A report of 15 cases and a review of the literature[J]. Virchows Arch, 2005, 447 (6): 978- 983.
doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-0036-x |
| 7 |
Rakozy C , Schmahl GE , Bogner S , et al. Low-grade tubular-mucinous renal neoplasms: Morphologic, immunohistochemical, and genetic features[J]. Mod Pathol, 2002, 15 (11): 1162- 1171.
doi: 10.1097/01.MP.0000031709.40712.46 |
| 8 |
Nathany S , Monappa V . Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: A review of histopathology and clinical and prognostic implications[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2020, 144 (1): 115- 118.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0506-RS |
| 9 | Xiao L , Xiao W , Guo Y , et al. Huge mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney: A case report[J]. Urol Case Rep, 2021, 40, 101914. |
| 10 |
Bajpai M , Pooja S , Tyagi M , et al. Mucinous spindle and tubular renal cell cancer: A rare variant of renal cell cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2022, 18 (4): 1168- 1170.
doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_99_21 |
| 11 | Kuroda N , Hes O , Michal M , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma with Fuhrman nuclear grade 3: A histological, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and FISH study[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2008, 23 (12): 1517- 1523. |
| 12 |
Fuchizawa H , Kijima T , Takada-Owada A , et al. Metastatic mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney responding to nivolumab plus ipilimumab[J]. IJU Case Rep, 2021, 4 (5): 333- 337.
doi: 10.1002/iju5.12342 |
| 13 |
Arafah M , Zaidi SN . Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney with sarcomatoid transformation[J]. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant, 2013, 24 (3): 557- 560.
doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.111066 |
| 14 |
Bulimbasic S , Ljubanovic D , Sima R , et al. Aggressive high-grade mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol, 2009, 40 (6): 906- 907.
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.03.004 |
| 15 |
Pillay N , Ramdial PK , Cooper K , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma with aggressive histomorphology: A sarco-matoid variant[J]. Hum Pathol, 2008, 39 (6): 966- 969.
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.10.006 |
| 16 | Simon RA , di Sant'agnese PA , Palapattu GS , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney with sarcomatoid differentiation[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2008, 1 (2): 180- 184. |
| 17 |
Dhillon J , Amin MB , Selbs E , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney with sarcomatoid change[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33 (1): 44- 49.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181829ed5 |
| 18 |
Fine SW , Argani P , DeMarzo AM , et al. Expanding the histologic spectrum of mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2006, 30, 1554- 1560.
doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213271.15221.e3 |
| 19 |
Reuter VE , Argani P , Zhou M , et al. Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in the kidney tumors: Report from the International Society of Urologic Pathology[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2014, 38 (8): e35- e49.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000258 |
| 20 |
Paner GP , Srigley JR , Radhakrishnan A , et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma of the kidney: Significant immunophenotypic overlap warrants diagnostic caution[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2006, 30 (1): 13- 19.
doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000180443.94645.50 |
| 21 |
Uchida S , Suzuki K , Uno M , et al. Mucin-poor and aggressive mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney: Two case reports[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2017, 7 (5): 777- 782.
doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1400 |
| 22 |
Kuroda N , Nakamura S , Miyazaki E , et al. Low-grade tubular-mucinous renal neoplasm with neuroendocrine differentiation: A histological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study[J]. Pathol Int, 2004, 54 (3): 201- 207.
doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2004.01608.x |
| 23 |
Peckova K , Martinek P , Sperga M , et al. Mucinous spindle and tubular renal cell carcinoma: Analysis of chromosomal aberration pattern of low-grade, high grade, and an overlapping morphologic variant with papillary renal[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2015, 19 (4): 226- 231.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.04.004 |
| 24 |
Kuroda N , Naroda T , Tamura M , et al. High-grade mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: Comparative genomic hybridization study[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2011, 15 (6): 472- 475.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2010.08.003 |
| 25 |
Sadimin ET , Chen YB , Wang L , et al. Chromosomal abnormalities of high-grade mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. Histopathology, 2017, 71 (5): 719- 724.
doi: 10.1111/his.13298 |
| 26 |
Mehra R , Vats P , Cieslik M , et al. Bi-allelic alteration and dysregulation of the Hippo pathway in mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. Cancer Discov, 2016, 6 (11): 1258- 1266.
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0267 |
| 27 |
Ren Q , Wang L , Al-Ahmadie HA , et al. Distinct genomic copy number alterations distinguish mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney from papillary renal cell carcinoma with overlapping histologic features[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2018, 42 (6): 767- 777.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001038 |
| 28 |
邹子归, 王玉红, 周晋星, 等. 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌临床病理分析及全外显子组测序分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2021, 50 (7): 762- 767.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20200922-00731 |
| 29 |
Xu H , Li W , Zhu C , et al. Proteomic profiling identifies novel diagnostic biomarkers and molecular subtypes for mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. J Pathol, 2022, 257 (1): 53- 67.
doi: 10.1002/path.5869 |
| 30 |
Bharti JN , Choudhary GR , Madduri VKS , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: A difficult diagnosis[J]. Urol Ann, 2021, 13 (2): 180- 182.
doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_44_20 |
| 31 |
Thway K , du Parcq J , Larkin JM , et al. Metastatic renal muci-nous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma. Atypical behavior of a rare, morphologically bland tumor[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2012, 16 (5): 407- 410.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2011.04.001 |
| 32 |
Cossu-Rocca P , Eble JN , Delahunt B , et al. Renal mucinous tubular and spindle carcinoma lacks the gains of chromosomes 7 and 17 and losses of chromosome Y that are prevalent in papillary renal cell carcinoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2006, 19 (4): 488- 493.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800565 |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [8] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [9] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [10] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [11] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [12] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [13] | 许云屹,苏征征,郑林茂,张孟尼,谭珺娅,杨亚蓝,张梦鑫,徐苗,陈铌,陈雪芹,周桥. 转录通读环状RNA rt-circ-HS促进低氧诱导因子1α表达和肾癌细胞增殖与侵袭[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 217-227. |
| [14] | 朱晓娟,张虹,张爽,李东,李鑫,徐玲,李挺. 人表皮生长因子受体2低表达乳腺癌的临床病理学特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [15] | 赖玉梅,李忠武,李欢,吴艳,时云飞,周立新,楼雨彤,崔传亮. 68例肛管直肠黏膜黑色素瘤临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
|
||