北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 753-757. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.028
扫频光学相干断层扫描根管内窥影像系统的建立及其在根裂诊断的应用
戚苈源1,陈晨2,姜岚2,李嘉男3,△( ),梁宇红1,4,△(
),梁宇红1,4,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院?口腔医院,牙体牙髓科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院?口腔医院第一门诊部, 北京 100034
3. 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室, 西安 710000
4. 北京大学国际医院口腔科, 北京 102206
Construction of swept source optical coherence tomography imaging system for root canal endoscopy and application in diagnosis of root fractures
Li-yuan QI1,Chen CHEN2,Lan JIANG2,Jia-nan LI3,△( ),Yu-hong LIANG1,4,△(
),Yu-hong LIANG1,4,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Cariology and Endodontology,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology,Beijing 100081,China
2. First Clinical Division,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology,Beijing 100034,China
3. State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics,Xian Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Xian,Shanxi 710000,China
4. Department of Stomatology,Peking University International Hospital,Beijing 102206,China
摘要:
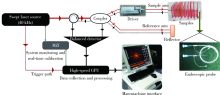
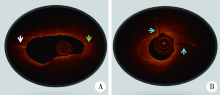
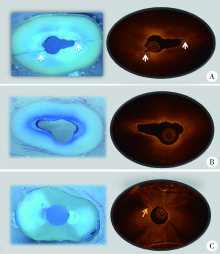
目的:建立扫频光学相干断层扫描(swept source-optical coherence tomography, SS-OCT)根管内窥影像系统,并评价该系统应用于诊断模拟根管内壁裂的准确性。方法:自主研发基于压电调谐滤波器并应用傅里叶(Fourier)域锁模技术构建的40 kHz超高速扫频激光光源系统(专利号200620135940.2),利用超微型梯度折射率透镜(专利号201320241218.7)制作极细根管内窥探头(直径0.86 mm),实现实时成像传输。构建的SS-OCT根管内窥影像系统扫频光源中心波长为1 310 nm,带宽为100 nm; 扫描图像的横向和纵向分辨率分别为25 μm和15 μm。利用人离体下颌前磨牙牙根制作人工模拟根裂(内壁裂),并制备高度1 mm的牙根横断面切盘。立体显微镜下观察发现,41个待测样本中有27个根管内壁裂样本(宽度在52~284 μm),另14个样本无根裂。应用上述构建的SS-OCT根管内窥影像系统扫描待测样本,重建图像的层厚为30 μm,层间距为30 μm。对1名口腔放射科医师和1名牙体牙髓科医师进行培训,判读SS-OCT扫描重建图像,判读根管内壁裂的有无及具体位置,评价两名观察者的自身一致性和观察者之间的一致性。以立体显微镜(组织学)检查结果作为金标准,评价应用SS-OCT根管内窥影像系统诊断模拟根管内壁裂的准确性。结果:两位观察者自身一致性的Kappa值分别为1.000和0.709,观察者之间的Kappa值为0.792。应用SS-OCT根管内窥影像系统扫描后27个根裂样本均被正确诊断,灵敏度为1.000,14个无根裂的样本有12个被正确判读,特异度为0.857, 2个无根裂样本被判读为有根裂,为假阳性。阳性预测值、阴性预测值分别为0.931、1.000,准确性为0.951。结论:扫频光学相干断层扫描根管内窥影像系统应用于观察根管内壁裂有临床应用前景。
中图分类号:
- R781
| [1] | Fercher AF, Drexler W, Hitzenberger CK , et al. Optical coherence tomography-principles and applications[J]. Rep Prog Phys, 2003,66(2):239. |
| [2] | Oliveira BPD , CÂmara AC, Duarte DA, et al. Detection of apical root cracks using spectral domain and swept-source optical co-herence tomography [J]. Int Endod J, 2017,43(7):1148-1151. |
| [3] | Lavinsky F, Lavinsky D . Novel perspectives on swept-source optical coherence tomography[J]. Int J Retina Vitreous, 2016,2(1):25. |
| [4] | Ha FJ, Giblett JP, Nerlekar N , et al. Optical coherence tomography guided percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Heart Lung Circ, 2017,26(12):1267-1276. |
| [5] | Colston B, Everett M, Da Silva LB , et al. Imaging of hard-and soft-tissue structure in the oral cavity by optical coherence tomography[J]. Applied Optics, 1998,37(16):3582-3585. |
| [6] | Baumgartner A, Dichtl S, Hitzenberger CK , et al. Polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography of dental structures[J]. Caries Res, 1999,34(1):59-69. |
| [7] | Shemesh H, van Soest G, Wu MK , et al. Diagnosis of vertical root fractures with optical coherence tomography[J]. J Endod, 2008,34(6):739-742. |
| [8] | Zain E, Zakian CM, Chew HP . Influence of the loci of non-cavitated fissure caries on its detection with optical coherence tomography[J]. J Dent, 2018,71(4):31-37. |
| [9] | Majkut P, Sadr A, Shimada Y , et al. Validation of optical coherence tomography against micro-computed tomography for evaluation of remaining coronal dentin thickness[J]. J Endod, 2015,41(8):1349-1352. |
| [10] | Han SH, Sadr A, Tagami J , et al. Non-destructive evaluation of an internal adaptation of resin composite restoration with swept-source optical coherence tomography and micro-CT[J]. Dent Mater, 2015,32(1):e1-e7 |
| [11] | Yoshioka T, Sakaue H, Ishimura H , et al. Detection of root surface fractures with swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT)[J]. Photomed Laser Surg, 2013,31(1):23-27. |
| [12] | 陈晨, 章文欣, 戚苈源 , 等. 光学相干断层扫描技术诊断牙根裂的实验研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(3):547-552. |
| [13] | Wang P, Yan X, Liu D , et al. Detection of dental root fractures by using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2011,40(5):290-298. |
| [14] | Li G . Patient radiation dose and protection from cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Imaging Sci Dent, 2013,43(2):63-69. |
| [15] | Paul RA, Tamse A, Rosenberg E . Cracked and broken teeth definitions, differential diagnosis and treatment[J]. Refuat Hapeh Vehashinayim, 2007,24(2):7-12. |
| [16] | Huang D, Swanson EA, Lin CP , et al. Optical coherence tomography[J]. Science, 1991,254(5035):1178-1181 |
| [17] | Bahcall JK, Barss JT . Fiberoptic endoscope usage for intracanal visualization[J]. J Endod, 2001,27(2):128-129. |
| [18] | Hassan B, Metska ME, Ozok AR , et al. Detection of vertical root fractures in endodontically treated teeth by a cone beam computed tomography scan[J]. J Endod, 2009,35(5):719-722. |
| [19] | Özer SY . Detection of vertical root fractures of different thicknesses in endodontically enlarged teeth by cone beam computed tomography versus digital radiography[J]. J Endod, 2010,36(7):1245-1249. |
| [20] | Patel S, Brady E, Wilson R , et al. The detection of vertical root fractures in root filled teeth with periapical radiographs and CBCT scans[J]. Int Endod J, 2013,46(12):1140-1152. |
| [21] | Chavda R, Mannocci F, Andiappan M , et al. Comparing the in vivo diagnostic accuracy of digital periapical radiography with cone-beam computed tomography for the detection of vertical root fracture[J]. J Endod, 2014,40(10):1524-1529. |
| [22] | Makeeva IM, Byakova SF, Novozhilova NE , et al. Detection of artificially induced vertical root fractures of different widths by cone beam computed tomography in vitro and in vivo[J]. Int Endod J, 2016,49(10):980-989. |
| [1] | 胡玉如,刘娟,李文静,赵亦兵,李启强,路瑞芳,孟焕新. Ⅲ期或Ⅳ期牙周炎患者龈沟液中有机酸浓度与牙周炎的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 332-337. |
| [2] | 任晓萌,李凯一,李春蕾. 基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
| [3] | 张晗,秦亦瑄,韦帝远,韩劼. 牙周炎患者种植修复维护治疗依从性的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [4] | 赵菡,卫彦,张学慧,杨小平,蔡晴,宁成云,徐明明,刘雯雯,黄颖,何颖,郭亚茹,江圣杰,白云洋,吴宇佳,郭雨思,郑晓娜,李文静,邓旭亮. 口腔硬组织修复材料仿生设计制备和临床转化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 4-8. |
| [5] | 殳畅,韩烨,孙雨哲,杨再目,侯建霞. Ⅲ期牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗前后炎症性贫血相关指标的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 45-50. |
| [6] | 何佩瑶,包旭东. 常温流动牙胶封闭剂GuttaFlow2单尖充填弯曲根管的封闭效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 99-105. |
| [7] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [8] | 赵晓一,刘畅,钱锟,潘洁. 成熟恒牙牙髓切断术的疗效及影像学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 138-143. |
| [9] | 陈晨,梁宇红. 复杂根管上颌磨牙的根管治疗3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 190-195. |
| [10] | 董佳芸,李雪芬,路瑞芳,胡文杰,孟焕新. 血管化骨瓣重建颌骨种植体周软组织病理学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 25-31. |
| [11] | 邢海霞,王琳,乔迪,刘畅,潘洁. 干燥综合征口腔疾病的治疗特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 929-933. |
| [12] | 叶雨阳,岳林,邹晓英,王晓燕. 成牙本质方向分化牙髓干细胞外泌体形态及微小RNA表达谱特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [13] | 裴喜燕,阳雯,欧阳翔英,孙凤. 牙周内窥镜下根面清创与牙周翻瓣术疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 716-720. |
| [14] | 章锦花,潘洁,孙志鹏,王霄. 不同根管内容物对口腔颌面锥形束CT诊断牙根纵裂准确性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 333-338. |
| [15] | 俞光岩,宿骞,张艳,吴立玲. 唾液腺疾病与全身系统性疾病的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 1-7. |
|
||