北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 498-504. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.015
1990—2019年中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡率分析
- 北京大学公共卫生学院,北京大学儿童青少年卫生研究所,北京 100191
Injury mortality among Chinese aged 5 to 24 years from 1990 to 2019
Yun-fei LIU,Jia-jia DANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ning MA,Di SHI,Yi SONG*( )
)
- Institute of Child and Adolescent Health, School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
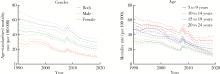
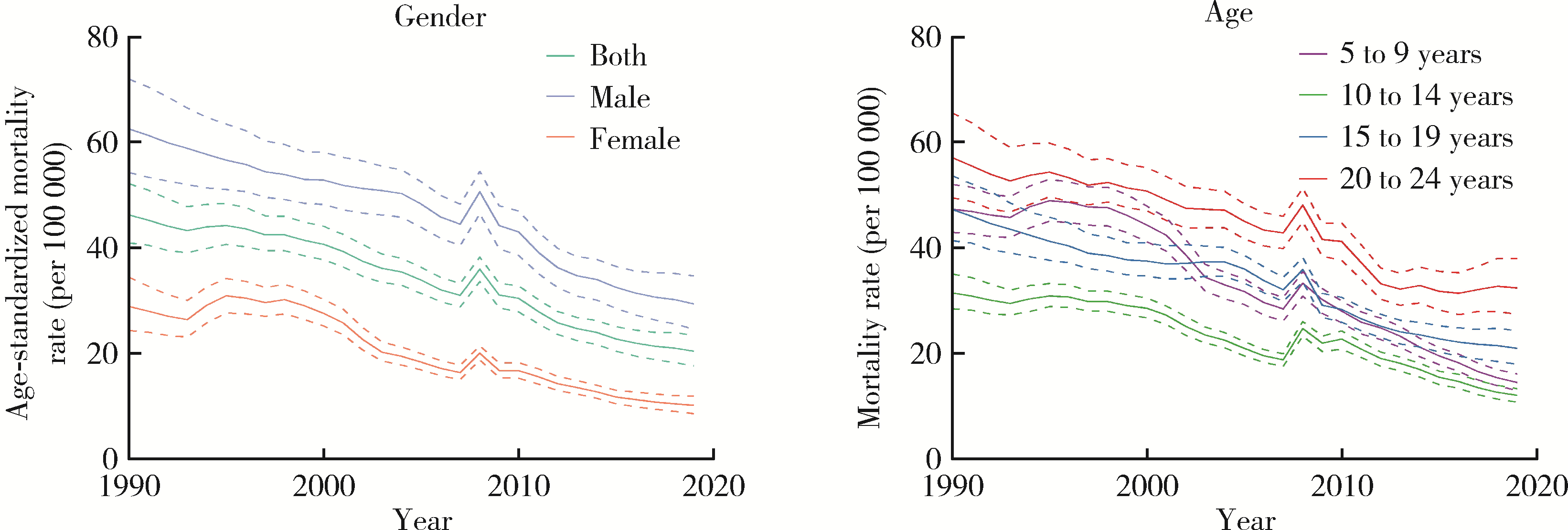
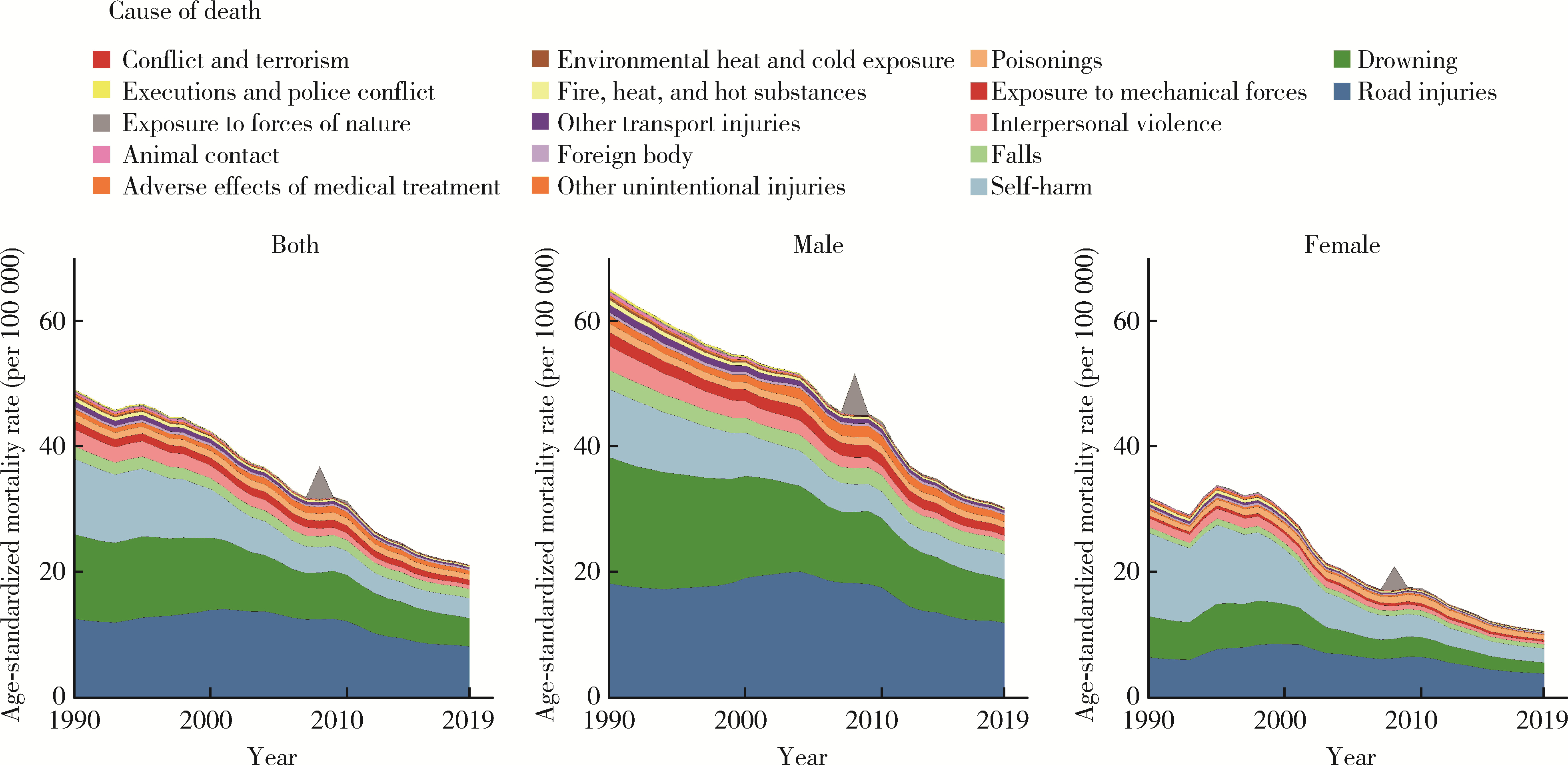
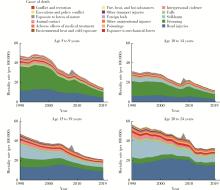
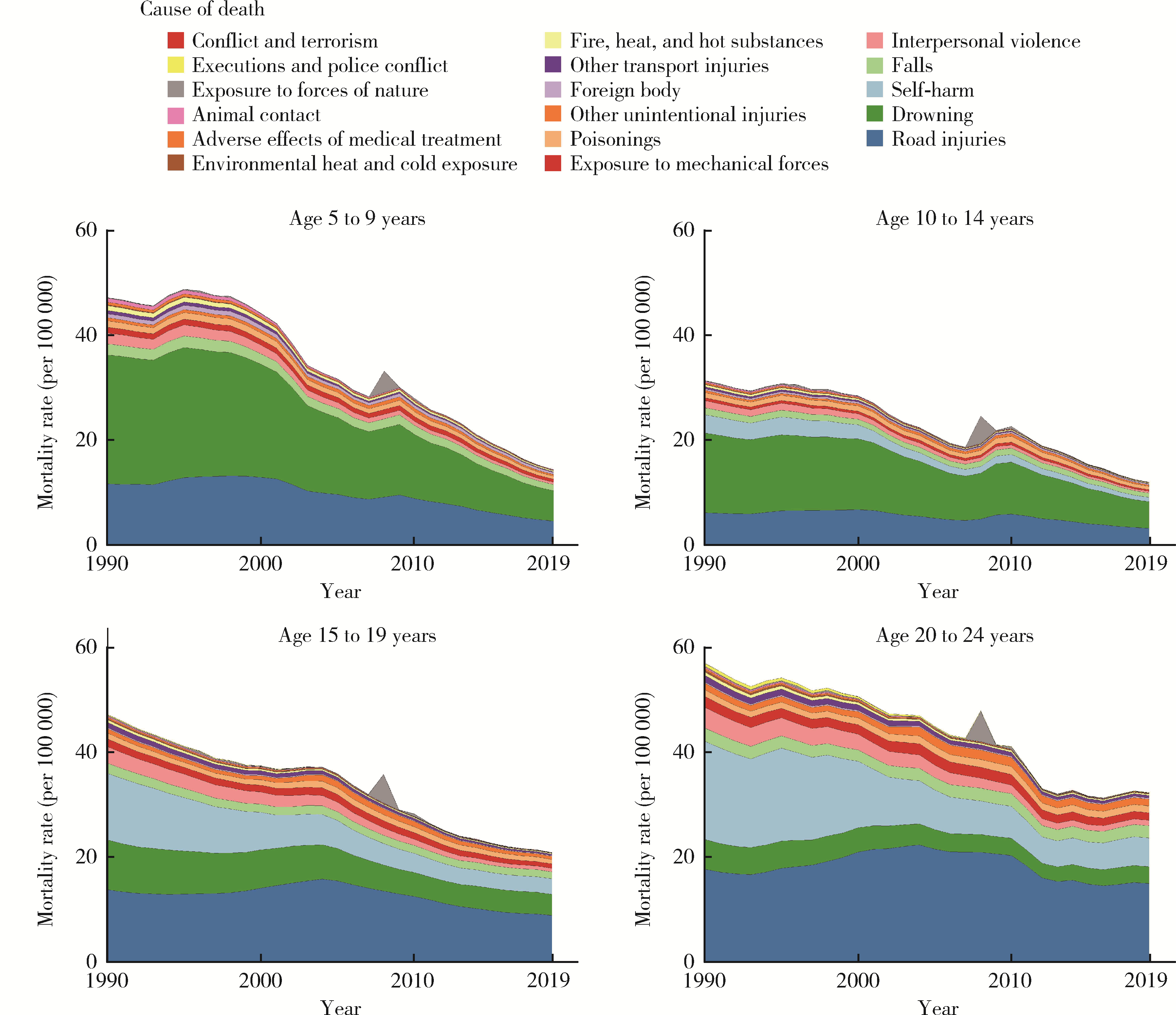
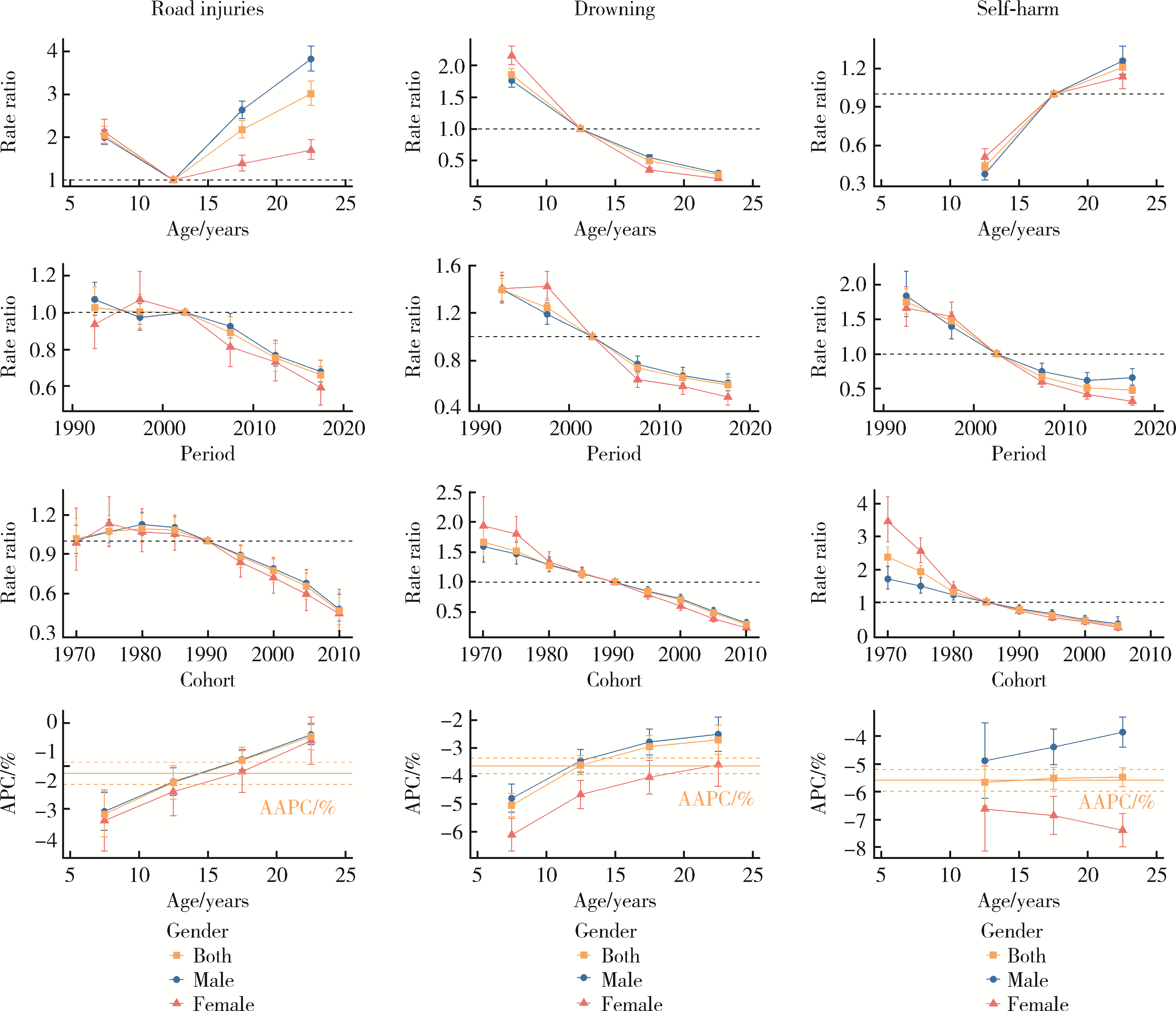
目的: 分析1990—2019年中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡率情况,为预防伤害相关政策的制定提供理论依据。方法: 使用《2019全球疾病负担》报告提供的中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡数据,描述伤害死亡率在1990—2019年间的变化情况,并使用年龄-时期-队列模型分析道路交通伤害、溺水、自伤等原因导致死亡率变化的年龄、时期和队列效应。结果: 1990—2019年,中国5~24岁人群总体伤害死亡率从46.22[95%不确定性区间(uncertainty interval, UI):40.88~52.12]/10万下降至20.36(95%UI:17.58~23.38)/10万,各亚组变化趋势与总体基本一致。溺水由该人群首位伤害死因下降为第二位,道路交通伤害则成为首位伤害死因,自伤处于伤害死因第三位。各亚组前三位死因与总体基本一致,但排序有所不同。年龄-时期-队列分析结果表明,道路交通伤害、溺水和自伤的死亡率均随着时期的推移和队列年份的增加而下降,其中道路交通伤害死亡风险随年龄增加先降低后升高,溺水死亡风险随年龄增加而降低,自伤死亡风险随年龄增加而升高。结论: 中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡情况在过去30年中整体得到改善,但具体原因导致的伤害死亡在不同亚组中表现有所差异。未来应针对不同亚组伤害的死亡特点,提出针对性政策和干预手段,减少儿童青少年伤害死亡率。
中图分类号:
- R179
| 1 | The United Nations. Goal 4: Reduce child mortality[EB/OL]. (2008-05-20)[2021-10-09]. https://www.un.org/millenniumgoals/childhealth.shtml. |
| 2 | The United Nations. Goal 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages[EB/OL]. (2015-09-25)[2021-10-12]. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/health/. |
| 3 | World Health Organization. Children: Improving survival and well-being[EB/OL]. (2020-09-08)[2021-10-25]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/children-reducing-mortality. |
| 4 | World Health Organization. Adolescent and young adult health[EB/OL]. (2021-01-18)[2021-10-25]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/adolescents-health-risks-and-solutions. |
| 5 | Unicef. Mortality among children, adolescents and youth aged 5-24[EB/OL]. (2020-09-17)[2021-10-09]. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-survival/child-and-youth-mortality-age-5-24/. |
| 6 |
叶鹏鹏, 金叶, 段蕾蕾. 不同儿童发展纲要时期下中国儿童伤害死亡率变化趋势[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40 (11): 1356- 1362.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.11.004 |
| 7 |
Vos T , Lim SS , Abbafati C , et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396 (10258): 1204- 1222.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9 |
| 8 |
Rosenberg PS , Check DP , Anderson WF , et al. A web tool for age-period-cohort analysis of cancer incidence and mortality rates[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2014, 23 (11): 2296- 2302.
doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0300 |
| 9 |
Ward JL , Viner RM . The impact of income inequality and national wealth on child and adolescent mortality in low and middle-income countries[J]. BMC Public Health, 2017, 17 (1): 429.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4310-z |
| 10 |
Bishai D , Quresh A , James P , et al. National road casualties and economic development[J]. Health Econ, 2006, 15 (1): 65- 81.
doi: 10.1002/hec.1020 |
| 11 |
Miovsky M , Gavurova B , Ivankova V , et al. Fatal injuries and economic development in the population sample of Central and Eastern European Countries: The perspective of adolescents[J]. Int J Public Health, 2020, 65 (8): 1403- 1412.
doi: 10.1007/s00038-020-01449-5 |
| 12 |
Wang L , Ning P , Yin P , et al. Road traffic mortality in China: Analysis of national surveillance data from 2006 to 2016[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2019, 4 (5): e245- e255.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30057-X |
| 13 | World Health Organization. Road traffic injuries[EB/OL]. (2021-06-21)[2021-10-28]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries. |
| 14 |
Simons A , Govender R , Saunders CJ , et al. Childhood vulnerability to drowning in the Western Cape, South Africa: Risk differences across age and sex[J]. Child Care Health Dev, 2020, 46 (5): 607- 616.
doi: 10.1111/cch.12786 |
| 15 | 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 国务院关于加强道路交通安全工作的意见[EB/OL]. (2012-07-27)[2022-03-20]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2012-07/27/content_4157.htm. |
| 16 |
Wang L , Cheng X , Yin P , et al. Unintentional drowning mortality in China, 2006-2013[J]. Inj Prev, 2019, 25 (1): 47- 51.
doi: 10.1136/injuryprev-2017-042713 |
| 17 | World Health Organization. Drowning[EB/OL]. (2021-04-27)[2021-10-28]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drowning. |
| 18 | World Health Organization. Global report on drowning: Preventing a leading killer[EB/OL]. (2014-11-17)[2021-10-28]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/global-report-on-drowning-preventing-a-leading-killer. |
| 19 | 刘辉. 我国儿童伤害主要发生原因及其预防措施的研究进展[J]. 职业与健康, 2021, 37 (8): 1141- 1143.1141-1143, 1148 |
| 20 | 李胜, 刘应焱, 王红英, 等. 2005—2019年中国溺水死亡现状及趋势分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48 (15): 2705- 2709.2705-2709, 2715 |
| 21 | World Health Organization. Suicide[EB/OL]. (2021-06-17)[2021-10-28]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/suicide. |
| 22 |
Ho TC , Gifuni AJ , Gotlib IH . Psychobiological risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors in adolescence: A consideration of the role of puberty[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2022, 27 (1): 606- 623.
doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01171-5 |
| 23 | 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 关于印发健康中国行动: 儿童青少年心理健康行动方案(2019—2022年)的通知[EB/OL]. (2019-12-27)[2022-03-21]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-12/27/content_5464437.htm. |
| 24 |
徐荣彬, 温勃, 宋逸, 等. 1990—2016年中国青少年死亡率及主要死因变化[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2018, 52 (8): 802- 808.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2018.08.006 |
| 25 |
Alonge O , Hyder AA . Reducing the global burden of childhood unintentional injuries[J]. Arch Dis Child, 2014, 99 (1): 62- 69.
doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304177 |
| [1] | 王敏, 李倩. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性影响因素的路径分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 809-814. |
| [2] | 王裕新, 曹茹, 黄婧, Pitakchon Ponsawansong, Benjawan Tawatsupa, 潘小川, Tippawan Prapamontol, 李国星. 不同表观温度水平下大气细颗粒物暴露对人群非意外死亡的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 820-827. |
| [3] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [4] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [5] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [6] | 费秀文,刘斯,汪波,董爱梅. 成人及儿童组织坏死性淋巴结炎临床特征及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [7] | 沈鹤军,侍崇艳,郑清,黄玉,景涛. 我国高中生静坐时长与健康素养现状及其影响因素调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 239-246. |
| [8] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [9] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [10] | 弭小艺,侯杉杉,付子苑,周末,李昕璇,孟召学,蒋华芳,周虹. 中文版童年不良经历问卷在学龄前儿童父母中应用的信效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [11] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [12] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [13] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [14] | 郑丹枫,李君禹,李佳曦,张英爽,钟延丰,于淼. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸椎旁肌的病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 283-291. |
| [15] | 赵亚楠,范慧芸,王翔宇,罗雅楠,张嵘,郑晓瑛. 孤独症患者过早死亡风险及死亡原因[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 375-383. |
|
||