北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 702-707. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.04.022
下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素
卢汉1,张建运2,杨榕1,徐乐1,李庆祥1,郭玉兴1,*( ),郭传瑸1,*(
),郭传瑸1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心, 国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院病理科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心, 国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室, 北京 100081
Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma
Han LU1,Jian-yun ZHANG2,Rong YANG1,Le XU1,Qing-xiang LI1,Yu-xing GUO1,*( ),Chuan-bin GUO1,*(
),Chuan-bin GUO1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
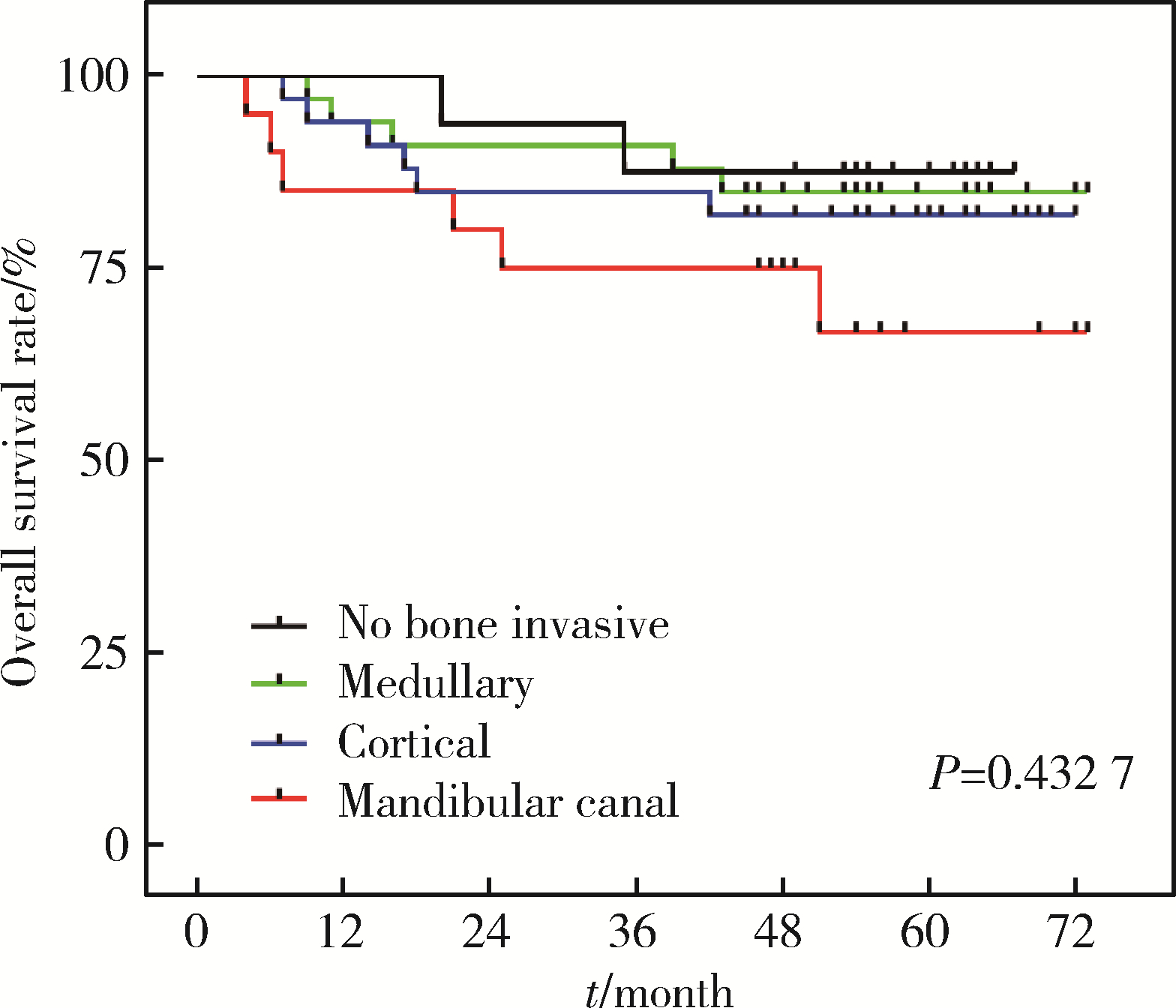
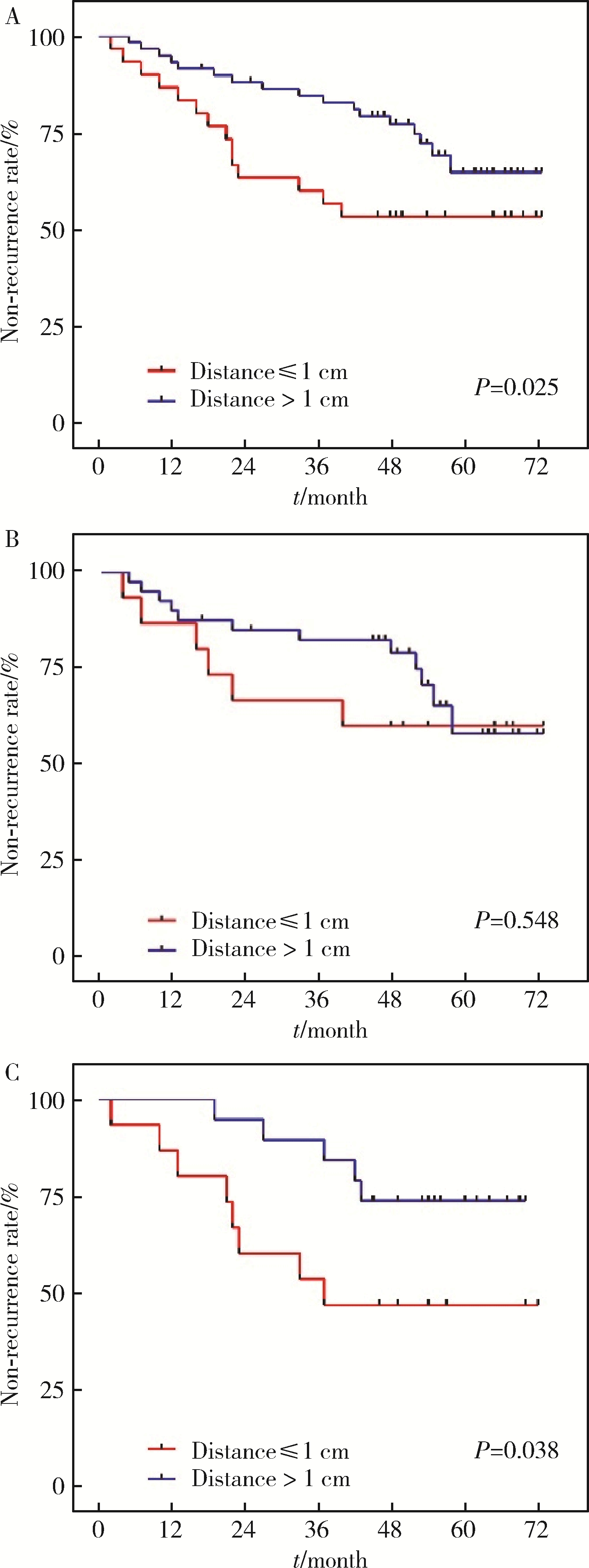
目的: 分析影响下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌(lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma, LGSCC)局部复发和生存的因素, 以及不同骨侵犯深度是否是LGSCC的独立预后因素。方法: 回顾性分析2013年6月至2015年12月于北京大学口腔医院住院治疗的初诊为LGSCC的患者104例, 所有患者随访3年以上。通过术前影像资料(螺旋CT和曲面体层片)评判骨侵犯程度, 分为未侵犯、侵犯骨皮质、侵犯骨髓腔及侵犯下颌管。按照肿瘤中心位置分为下颌骨前段(颏孔前区)和下颌骨后段(颏孔后区)侵犯两类。不同侵犯深度组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U秩和检验, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。应用Kaplan-Meier生存分析法绘制生存曲线, 运用COX回归探讨LGSCC预后影响因素的风险比及其95%可信区间(CI)。结果: 随访结果显示, 104例LGSCC患者术后1年、3年和5年生存率分别为91%、84%, 82%。本组有34例(32.7%)发生颈部淋巴结转移, 下颌骨前段和后段颈部淋巴结转移率分别为12.5%(2/16)和36.4%(32/88)。单因素和多因素COX分析显示, N分期和局部复发是影响预后的独立因素(P < 0.05)。结论: 下颌骨侵犯程度越严重, 下颌牙龈癌患者预后越差; N分期和局部复发是下颌牙龈癌的预后风险因素。颈部淋巴结转移与肿瘤原发部位相关, 原发部位位于下颌骨后段的LGSCC可在疾病早期发生颈部淋巴结转移, 应采取更积极的颈部淋巴结清扫策略。
中图分类号:
- R739.8
| 1 |
Montero PH , Patel SG . Cancer of the oral cavity[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2015, 24 (3): 491- 508.
doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2015.03.006 |
| 2 |
Fives C , Nae A , Roche P , et al. Impact of mandibular invasion on prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma four centimeters or less in size[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127 (4): 849- 854.
doi: 10.1002/lary.26211 |
| 3 |
Fried D , Mullins B , Weissler M , et al. Prognostic significance of bone invasion for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma considered T1/T2 by American joint committee on cancer size criteria[J]. Head Neck, 2014, 36 (6): 776- 781.
doi: 10.1002/hed.23367 |
| 4 | 万艳, 尚政军. 牙龈癌的流行病学危险因素研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2013, 29 (7): 402- 404. |
| 5 | Yoshida S , Shimo T , Murase Y , et al. The prognostic implications of bone invasion in gingival squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Anticancer Res, 2018, 38 (2): 955- 962. |
| 6 |
Ebrahimi A , Murali R , Gao K , et al. The prognostic and staging implications of bone invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer, 2011, 117 (19): 4460- 4467.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.26032 |
| 7 |
Lee KC , Chuang SK , Philipone EM , et al. Which clinicopathologic factors affect the prognosis of gingival squamous cell carcinoma: A population analysis of 4 345 cases[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 77 (5): 986- 993.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2019.01.007 |
| 8 |
Okura M , Yanamoto S , Umeda M , et al. Prognostic and staging implications of mandibular canal invasion in lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2016, 5 (12): 3378- 3385.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.899 |
| 9 | Brierley J , Gospodarowicz MK , Wittekind C . TNM classification of malignant tumours[M]. 8ed Chichester, West Sussex, UK & Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2017. |
| 10 |
Smits RWH , Ten Hove I , Dronkers EAC , et al. Evaluation of bone resection margins of segmental mandibulectomy for oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 47 (8): 959- 964.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2018.03.006 |
| 11 |
Ahmad JG , Namin AW , Jorgensen JB , et al. Mandibular invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma: Clinicopathologic features of 74 cases[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160 (6): 1034- 1041.
doi: 10.1177/0194599818821859 |
| 12 | Singh A , Mair M , Singhvi H , et al. Incidence, predictors and impact of positive bony margins in surgically treated T4 stage cancers of the oral cavity[J]. Oral Oncol, 2019, 90 (3): 8- 12. |
| 13 |
Cariati P , Serrano AC , Solis JF , et al. Intraoperative cytological examination of bone medullary. A useful technique to predict the extension of bone invasion in segmental mandibulectomy[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40 (5): 743- 746.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.07.005 |
| 14 |
Haase C , Lethaus B , Knuchel-Clarke R , et al. Development of a rapid analysis method for bone resection margins for oral squamous cell carcinoma by immunoblotting[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2018, 12 (2): 210- 220.
doi: 10.1007/s12105-017-0856-4 |
| 15 |
Niu LX , Feng ZE , Wang DC , et al. Prognostic factors in mandi-bular gingival squamous cell carcinoma: A 10-year retrospective study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 46 (2): 137- 143.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2016.09.014 |
| 16 |
Nieberler M , Haussler P , Kesting MR , et al. Intraoperative cell isolation for a cytological assessment of bone resection margins in patients with head and neck cancer[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 55 (5): 510- 516.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2017.02.006 |
| 17 |
Nieberler M , Haussler P , Kesting MR , et al. Clinical impact of intraoperative cytological assessment of bone resection margins in patients with head and neck carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2016, 23 (11): 3579- 3586.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5208-1 |
| 18 |
Gou L , Yang W , Qiao X , et al. Marginal or segmental mandibulectomy: treatment modality selection for oral cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 47 (1): 1- 10.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2017.07.019 |
| 19 |
Namin AW , Bollig CA , Harding BC , et al. Implications of tumor size, subsite, and adjuvant therapy on outcomes in pT4aN0 oral cavity carcinoma[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck surg, 2020, 162 (5): 683- 692.
doi: 10.1177/0194599820904679 |
| 20 | 李传真, 郭传瑸. 口腔颌面部鳞癌原发灶部位对颈淋巴结转移区域的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46 (3): 469- 473. |
| 21 |
Brockhoff HC , Kim RY , Braun TM , et al. Correlating the depth of invasion at specific anatomic locations with the risk for regional metastatic disease to lymph nodes in the neck for oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Head Neck, 2017, 39 (5): 974- 979.
doi: 10.1002/hed.24724 |
| 22 |
Wang Y , Li Q , Xu L , et al. Cancer stemness of CD10-positive cells regulated by Hedgehog pathway promotes the resistance to cisplatin in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oral Dis, 2021, 27 (6): 1403- 1411.
doi: 10.1111/odi.13673 |
| 23 |
Li Q , Wang Y , Xu L , et al. High level of CD10 expression is associated with poor overall survival in patients with head and neck cancer[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2021, 50 (7): 857- 864.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2020.07.037 |
| 24 |
Nassiri AM , Campbell BR , Mannion K , et al. Survival outcomes in T4aN0M0 mandibular gingival squamous cell carcinoma treated with surgery alone[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160 (5): 870- 875.
doi: 10.1177/0194599818821892 |
| 25 |
Hasegawa T , Yanamoto S , Otsuru M , et al. Multi-center retrospective study of the prognosis and treatment outcomes of Japanese oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with single lymph node metastasis and extra nodal extension[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2018, 117 (8): 1736- 1743.
doi: 10.1002/jso.25083 |
| 26 |
Lubek J , El-Hakim M , Salama AR , et al. Gingival carcinoma: Retrospective analysis of 72 patients and indications for elective neck dissection[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 49 (3): 182- 185.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2010.04.005 |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [8] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [9] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [10] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [12] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [13] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [14] | 朱晓娟,张虹,张爽,李东,李鑫,徐玲,李挺. 人表皮生长因子受体2低表达乳腺癌的临床病理学特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [15] | 赖玉梅,李忠武,李欢,吴艳,时云飞,周立新,楼雨彤,崔传亮. 68例肛管直肠黏膜黑色素瘤临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
|
||