北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 397-402. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.004
青春期和成年早期自制力与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联:基于全国调查的十年前瞻性队列研究
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院妇幼卫生学系,北京 100191
2. 北京大学人民医院儿科,北京 100044
Association between self-control and co-occurrence of depressive symptoms and overweight or obesity during adolescence and early adulthood: A ten-year prospective cohort study based on national surveys
Jing CHEN1,Rui SHAN1,Wucai XIAO1,Xiaorui ZHANG2,Zheng LIU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Maternal and Child Health, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pediatrics, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
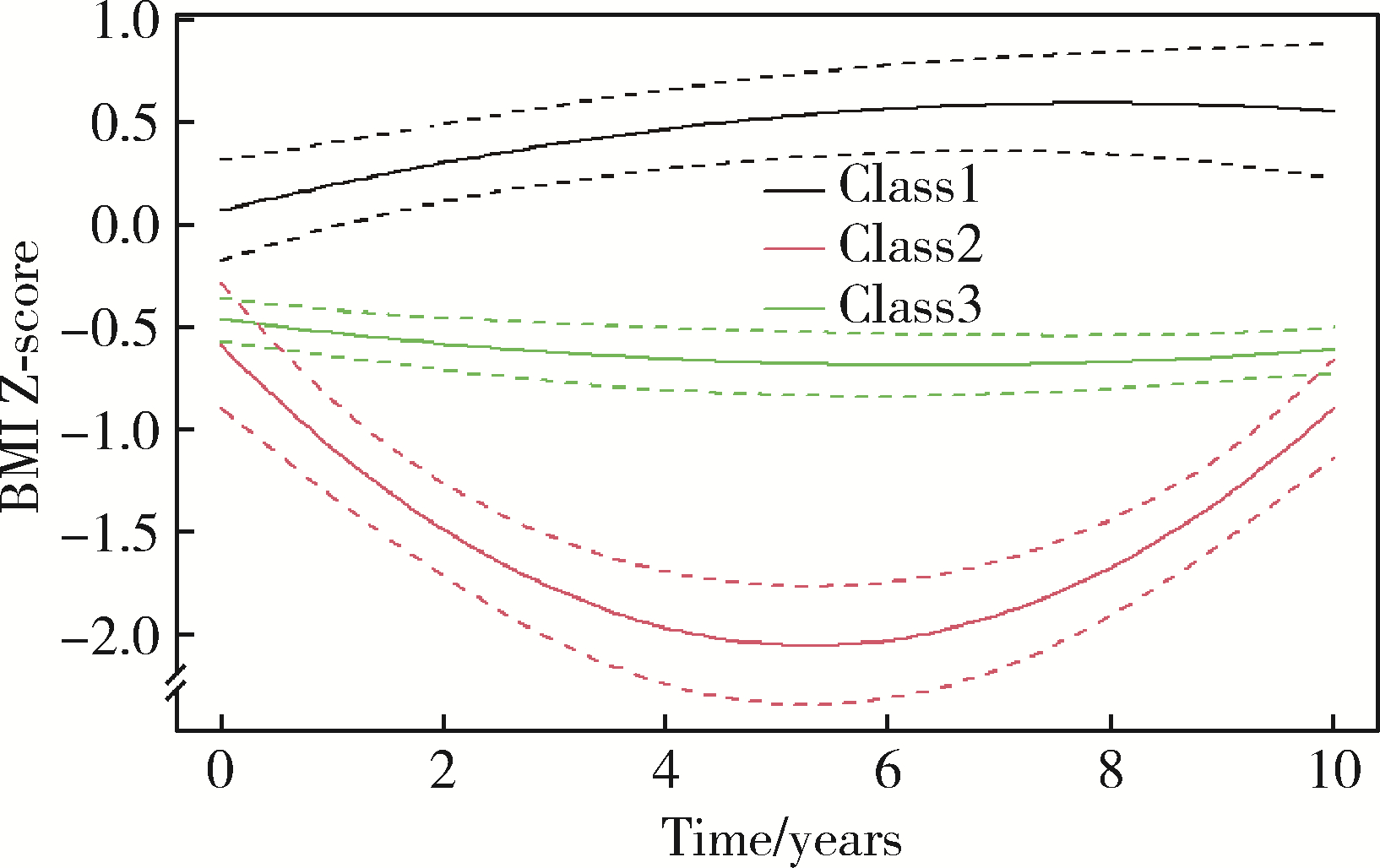
目的: 在我国青春期至成年早期人群中探索自制力与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联,为将来针对不同风险人群开展个性化干预提供依据。方法: 基于一项长达10年的队列研究——中国家庭追踪调查(China family panel studies, CFPS),纳入2010年10~19岁、中国标准下处于正常体质量、无抑郁症状、有自制力得分,且2010—2020年至少有两次抑郁症状得分和体重指数(body mass index, BMI)、每个家庭中唯一或年龄最小的608名青少年作为研究对象。用整个随访期间平均标准化抑郁症状得分和BMI Z评分均处于高水平,或者基于潜分类轨迹模型(latent class trajectory modeling, LCTM)得到的抑郁症状和BMI随时间的轨迹分类同时属于“风险型”,或者最后一次随访调查时有抑郁症状且超重肥胖三种方式定义抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病人群。采用无序多分类Logistic回归模型分析标准化自制力得分与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联。结果: 校正年龄、性别、城乡、每周体力活动时长、父母文化程度、父母超重肥胖和抑郁情况后,无论哪种共病定义方式,当以健康人群为参照组时,自制力得分每升高一个标准差,个体患抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病的风险降低33%(95%CI: 14%~48%,基于整个随访期间平均水平)~78%(95%CI: 6%~95%,基于抑郁症状和BMI随时间变化的联合轨迹)。此外,自制力得分每升高一个标准差,个体仅患抑郁症状和仅超重肥胖的风险分别降低25%(95%CI: 4%~42%,仅基于整个随访期间平均水平)和21% (95%CI: 1%~37%,仅基于抑郁症状和BMI随时间变化的联合轨迹)。本研究主要结果与根据世界卫生组织(World Health Organization, WHO)标准定义个体是否超重肥胖时的敏感性分析结果一致。结论: 青春期和成年早期个体自制力越高,患抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病的风险越低,提示未来可基于自制力开展个性化的抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病干预。
中图分类号:
- R479.4
| 1 |
Sawyer SM , Afifi RA , Bearinger LH , et al. Adolescence: A foundation for future health[J]. Lancet, 2012, 379 (9826): 1630- 1640.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60072-5 |
| 2 |
McGrath JJ , Al-Hamzawi A , Alonso J , et al. Age of onset and cumulative risk of mental disorders: A cross-national analysis of population surveys from 29 countries[J]. Lancet Psychiatry, 2023, 10 (9): 668- 681.
doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(23)00193-1 |
| 3 |
Rao DP , Kropac E , Do MT , et al. Childhood overweight and obesity trends in Canada[J]. Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can, 2016, 36 (9): 194- 198.
doi: 10.24095/hpcdp.36.9.03 |
| 4 |
Shorey S , Ng ED , Wong CHJ . Global prevalence of depression and elevated depressive symptoms among adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Clin Psychol, 2022, 61 (2): 287- 305.
doi: 10.1111/bjc.12333 |
| 5 |
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) . Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390 (10113): 2627- 2642.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 |
| 6 | World Health Organization. Depression and other common mental disorders: Global health estimates[R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2017. |
| 7 |
Chooi YC , Ding C , Magkos F . The epidemiology of obesity[J]. Metabolism, 2019, 92, 6- 10.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.09.005 |
| 8 |
Smith JD , Fu E , Kobayashi MA . Prevention and management of childhood obesity and its psychological and health comorbidities[J]. Annu Rev Clin Psychol, 2020, 16, 351- 378.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-100219-060201 |
| 9 | Jelalian E , Jandasek B , Wolff JC , et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy plus healthy lifestyle enhancement for depressed, overweight/obese adolescents: Results of a pilot trial[J]. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol, 2019, 48 (Suppl 1): S24- S33. |
| 10 | Bräutigam-Ewe M , Lydell M , Månsson J , et al. Dietary advice on prescription: Experiences with a weight reduction programme[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2017, 26 (5/6): 795- 804. |
| 11 |
Couch D , Han GS , Robinson P , et al. Men' s weight loss stories: How personal confession, responsibility and transformation work as social control[J]. Health (London), 2019, 23 (1): 76- 96.
doi: 10.1177/1363459317724855 |
| 12 |
Zhu N , Lu HJ , Chang L . Peer popularity and self-discipline as protective factors against depressive symptoms in Chinese adolescents: Do boys and girls benefit equally[J]. Psych J, 2024, 13 (1): 66- 78.
doi: 10.1002/pchj.708 |
| 13 |
Tsur AM , Akavian I , Landau R , et al. Adolescent body mass index and early chronic kidney disease in young adulthood[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2024, 178 (2): 142- 150.
doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5420 |
| 14 |
Twig G , Yaniv G , Levine H , et al. Body-mass index in 2.3 million adolescents and cardiovascular death in adulthood[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016, 374 (25): 2430- 2440.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1503840 |
| 15 | Xie Y , Hu J . An introduction to the China family panel studies (CFPS)[J]. Chin Sociol Rev, 2014, 47 (1): 3- 29. |
| 16 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. WS/T 456—2014学龄儿童青少年营养不良筛查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. |
| 17 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. WS/T 586—2018学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. |
| 18 | 章婕, 吴振云, 方格, 等. 流调中心抑郁量表全国城市常模的建立[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2010, 24 (2): 139- 143. |
| 19 |
Lennon H , Kelly S , Sperrin M , et al. Framework to construct and interpret latent class trajectory modelling[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8 (7): e020683.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020683 |
| 20 | World Health Organization. Growth reference data for 5-19 years[EB/OL]. [2024-01-15]. http://www.who.int/growthref/en/. |
| 21 | World Health Organization. BMI-for-age (5-19 years). Growth reference 5-19 years[EB/OL]. [2024-01-15]. http://www.who.int/growthref/who2007_bmi_for_age/en/. |
| 22 |
Kemps E , Goossens L , Petersen J , et al. Evidence for enhancing childhood obesity treatment from a dual-process perspective: A systematic literature review[J]. Clin Psychol Rev, 2020, 77, 101840.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101840 |
| 23 |
Pines AR , Sacchet MD , Kullar M , et al. Multi-unit relations among neural, self-report, and behavioral correlates of emotion regulation in comorbid depression and obesity[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 14032.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32394-2 |
| 24 |
Rios-Leyvraz M , Ortega N , Chiolero A . Reliability of self-reported height and weight in children: A school-based cross-sectional study and a review[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 15 (1): 75.
doi: 10.3390/nu15010075 |
| 25 |
Field AE , Aneja P , Rosner B . The validity of self-reported weight change among adolescents and young adults[J]. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2007, 15 (9): 2357- 2364.
doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.279 |
| [1] | 侯天姣,周治波,王竹青,王梦莹,王斯悦,彭和香,郭煌达,李奕昕,章涵宇,秦雪英,武轶群,郑鸿尘,李静,吴涛,朱洪平. 转化生长因子β信号通路与非综合征型唇腭裂发病风险的基因-基因及基因-环境交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 384-389. |
| [2] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [3] | 吴一凡,玉应香,谢岚,张志达,常翠青. 不同体重指数青年男性的静息能量消耗特点及预测方程评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 247-252. |
| [4] | 陈楚云,孙蓬飞,赵静,贾佳,范芳芳,王春燕,李建平,姜一梦,霍勇,张岩. 北京社区人群促红细胞生成素相关因素及其与10年心血管疾病风险的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1068-1073. |
| [5] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [6] | 王婷,李乔晟,刘皓冉,简伟研. 人格特征、城乡差异与抑郁症状变化的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [7] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [8] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [9] | 张紫薇,花语蒙,刘爱萍. 中国中老年人群抑郁症状、缺血性心血管疾病10年风险对心血管疾病的联合影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 465-470. |
| [10] | 马涛,李艳辉,陈曼曼,马莹,高迪,陈力,马奇,张奕,刘婕妤,王鑫鑫,董彦会,马军. 青春期启动提前与儿童肥胖类型的关联研究: 基于横断面调查和队列调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [11] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [12] | 郭子宁, 梁志生, 周仪, 张娜, 黄捷. 基于国际疾病分类的心血管疾病亚型的基因组学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 453-459. |
| [13] | 吴俊慧,陈泓伯,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,王梦莹,王斯悦,王小文,王伽婷,于欢,胡永华. 2015—2017年北京市2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 518-522. |
| [14] | 王梦莹,李文咏,周仁,王斯悦,刘冬静,郑鸿尘,李静,李楠,周治波,朱洪平,吴涛,胡永华. WNT代谢通路相关基因与中国人群非综合征型唇腭裂发病风险的交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 815-820. |
| [15] | 那晓娜,朱珠,陈阳阳,王东平,王浩杰,宋阳,马晓川,王培玉,刘爱萍. 身体活动、静坐行为的时间分布与肥胖的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 486-491. |
|
||