北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 396-401. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.027
67例上颌根尖周囊肿的三维影像特点分析
孟圆1,张丽琪1,赵雅宁1,柳登高1,Δ( ),张祖燕1,高岩2
),张祖燕1,高岩2
- 1.口腔颌面医学影像科, 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.口腔病理科, 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Three-dimentional radiographic features of 67 maxillary radicular cysts
MENG Yuan1,ZHANG Li-qi1,ZHAO Ya-ning1,LIU Deng-gao1,Δ( ),ZHANG Zu-yan1,GAO Yan2
),ZHANG Zu-yan1,GAO Yan2
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
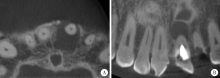
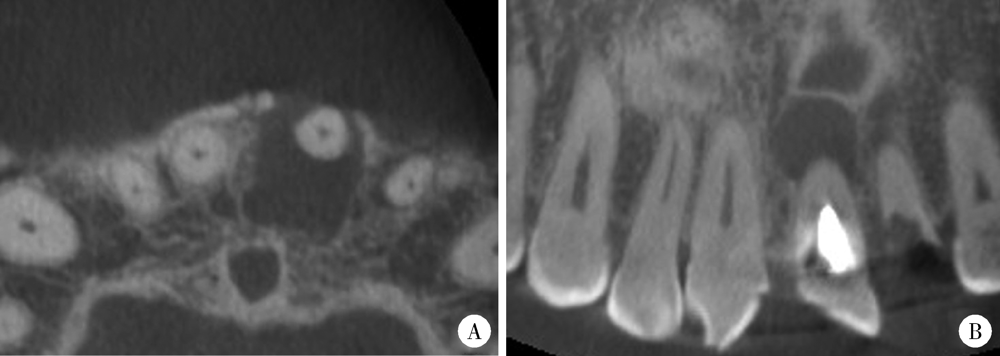
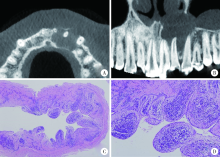
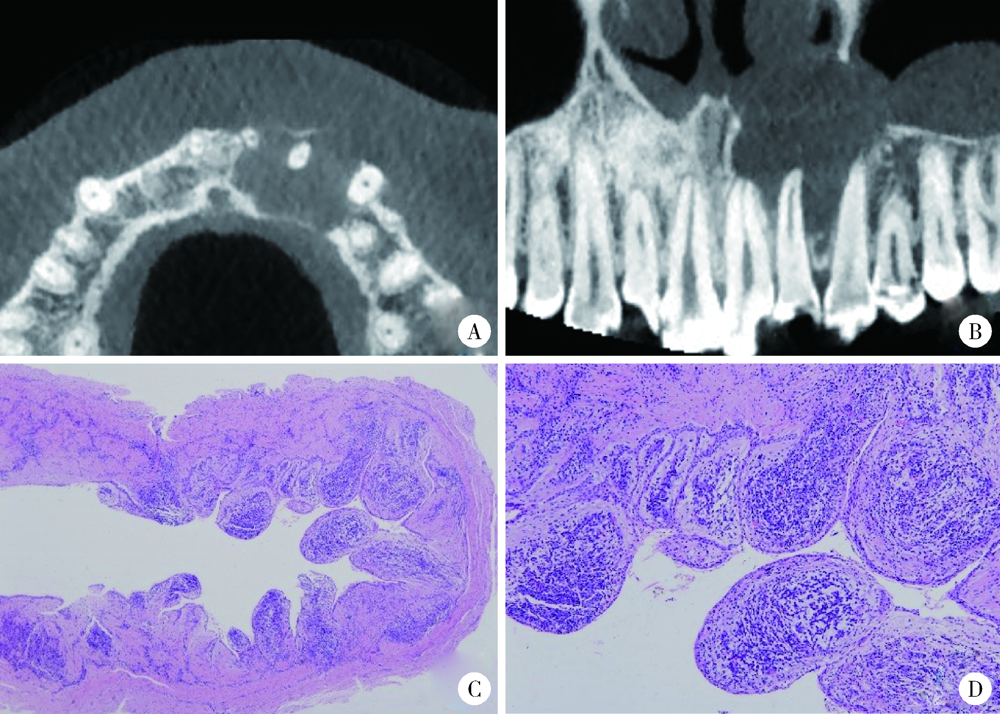
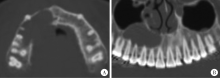
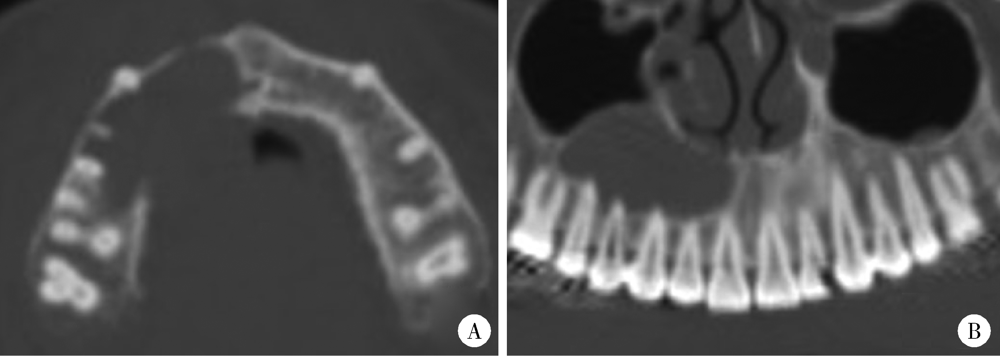
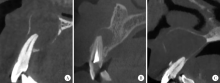
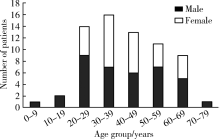
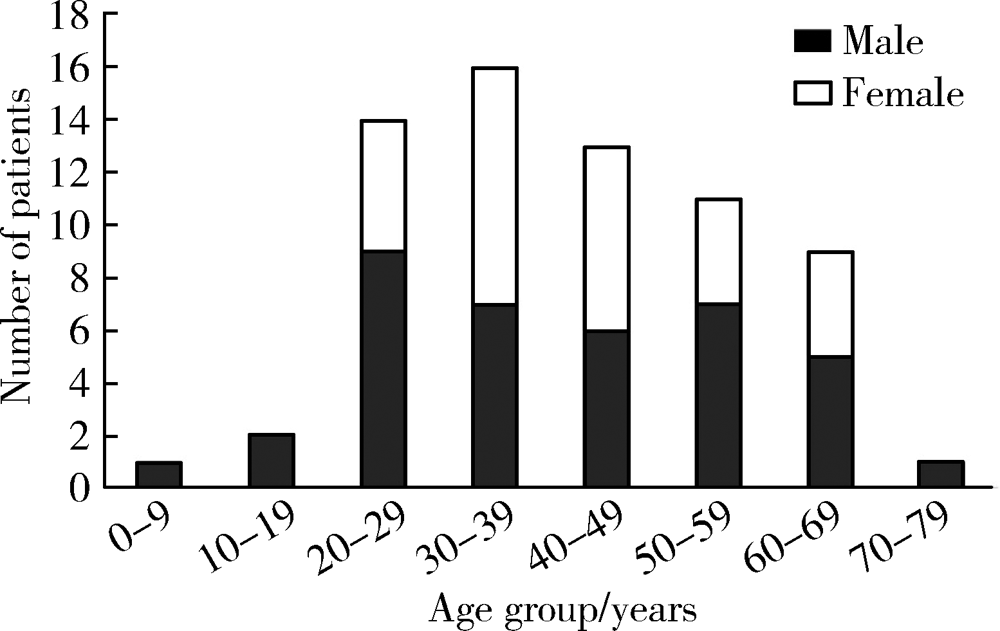
目的: 利用锥形束CT和螺旋CT分析上颌根尖周囊肿的三维影像学特点。方法: 收集2012年12月至2018年1月就诊于北京大学口腔医院并有完整临床资料、病理诊断及锥形束CT或螺旋CT影像的上颌根尖周囊肿患者67例,分析其影像学特点,包括病变大小、形态、膨隆情况、内部结构及与周围组织的关系等。根据病变累及牙的范围分为三型:(1)单牙型:病变仅累及1枚病原牙的根周骨质;(2)邻牙受累型:病变除累及1枚病原牙的根周骨质外,向近中和/或远中累及1枚邻牙牙根;(3)多牙型:病变累及≥4枚相邻牙位的根周骨质。另外,根据矢状位图像囊肿与牙根长轴的关系分为向心(病原牙牙根长轴指向病变中心)、偏腭(囊肿主体位于病原牙根的腭侧)及偏唇颊(囊肿主体位于病原牙根的唇颊侧)三种。结果: 共纳入67例患者,男性38例,女性29例,年龄13~77岁,其中46例(68.7%)位于上颌前部,65例(97.0%)为类圆形或椭圆形,43例(64.2%)唇颊侧骨板膨隆,37例(55.2%)腭侧骨板膨隆,27例(40.3%)累及鼻底,26例(38.8%)突入上颌窦,9例(13.4%)可见牙根吸收。近远中最大径为(20.89±8.11) mm,唇(颊)腭向最大径为(16.70±5.88) mm。4例患者的病原牙已拔除,其余63例患者根据病变范围分为单牙型14例、邻牙受累型26例、多牙型23例,根据病变与牙长轴关系分为向心46例、偏腭15例、偏唇颊2例。结论: 根尖周囊肿以上颌前部多见,多表现为类圆形或椭圆形,少数病变尺寸较大。根据病变与病原牙的近远中向累及范围分为单牙型、邻牙受累型和多牙型。矢状面上,病变与病原牙长轴多为向心关系,少数偏腭或偏唇颊。
中图分类号:
- R781.34
| [1] | White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology principles and interpretation[M]. 7th ed. Missouri: Mosby Inc., 2014. |
| [2] | Takata T, Slootweg PJ. Odontogenic and maxillofacial bone tumors[M] // El-Naggar AE, Chan JKC, Grandis JR, et al. WHO classification of head and neck tumors. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC, 2017: 203-260. |
| [3] | Kilinc A, Saruhan N, Gundogdu B, et al. Benign tumors and tumorlike lesions of the oral cavity and jaws: an analysis of 709 cases[J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2017,20(1):1448-1454. |
| [4] | 张震康, 俞光岩. 口腔颌面外科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013. |
| [5] | 马绪臣. 口腔颌面医学影像学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2014. |
| [6] | 吴运堂. 口腔颌面骨疾病临床影像诊断学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2005. |
| [7] |
Scarfe WC, Toghyani S, Azevedo B. Imaging of benign odontoge-nic lesions[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2018,56(1):45-62.
pmid: 29157548 |
| [8] |
Barros C, Santos HBP, Cavalcante IL, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of nasopalatine duct cyst: A 47-year retrospective study and review of current concepts[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2018,46(2):264-268.
pmid: 29248496 |
| [9] |
Araujo JP, Lemos CA, Miniello TG, et al. The relevance of clinical and radiographic features of jaw lesions: a prospective study[J]. Braz Oral Res, 2016,30(1):e96-e104.
pmid: 27556683 |
| [10] |
Nunez-Urrutia S, Figueiredo R, Gay-Escoda C. Retrospective clinicopathological study of 418 odontogenic cysts[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2010,15(5):e767-e773.
pmid: 20383117 |
| [11] |
Chen JH, Tseng CH, Wang WC, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of 232 radicular cysts of the jawbone in a population of southern Taiwanese patients[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2018,34(4):249-254.
doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2018.01.011 pmid: 29655415 |
| [12] |
Gondak RO, Rocha AC, Neves Campos JG, et al. Unicystic ameloblastoma mimicking apical periodontitis: a case series[J]. J Endod, 2013,39(1):145-148.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.09.017 pmid: 23228275 |
| [13] | 高岩, 李铁军. 口腔组织学与病理学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013. |
| [14] |
Faitaroni LA, Bueno MR, Carvalhosa AA, et al. Differential diagnosis of apical periodontitis and nasopalatine duct cyst[J]. J Endod, 2011,37(3):403-410.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.11.022 pmid: 21329830 |
| [15] |
Omoregie FO, Sede MA, Ojo AM. Ameloblastomatous change in radicular cyst of the jaw in a Nigerian population[J]. Ghana Med J, 2015,49(2):107-111.
doi: 10.4314/gmj.v49i2.8 pmid: 26339095 |
| [16] | Mass E, Kaplan I, Hirshberg A. A clinical and histopathological study of radicular cysts associated with primary molars[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 1995,24(1):458-461. |
| [17] |
Aboulhosn M, Noujeim Z, Nader N, et al. Decompression and enucleation of a mandibular radicular cyst, followed by bone regeneration and implant-supported dental restoration[J]. Case Rep Dent, 2019,2019:9584235.
doi: 10.1155/2019/9584235 pmid: 30729045 |
| [18] |
Pitcher B, Alaqla A, Noujeim M, et al. Binary decision trees for preoperative periapical cyst screening using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. J Endod, 2017,43(3):383-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2016.10.046 pmid: 28231977 |
| [19] | 孟圆, 张亚琼, 叶欣, 等. 上颌成釉细胞瘤、牙源性角化囊肿及含牙囊肿的螺旋CT和锥形束CT影像分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018,53(10):659-664. |
| [20] |
Guo J, Simon JH, Sedghizadeh P, et al. Evaluation of the reliability and accuracy of using cone-beam computed tomography for diagnosing periapical cysts from granulomas[J]. J Endod, 2013,39(12):1485-1490.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.019 pmid: 24238434 |
| [1] | 薄士仕,高承志. 基于卷积神经网络实现锥形束CT牙齿分割及牙位标定[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 735-740. |
| [2] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [3] | 章锦花,潘洁,孙志鹏,王霄. 不同根管内容物对口腔颌面锥形束CT诊断牙根纵裂准确性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 333-338. |
| [4] | 叶佳学,梁宇红. 牙髓专科医师应用锥形束CT的现况调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 114-119. |
| [5] | 潘孟乔,刘建,徐莉,徐筱,侯建霞,李小彤,王晓霞. 牙周-正畸-正颌联合治疗骨性安氏Ⅲ类错 |
| [6] | 高娟,吕航苗,马慧敏,赵一姣,李小彤. 锥形束CT三维体积测量评估骨性Ⅲ类错 |
| [7] | 刘伟涛,王怡然,王雪东,周彦恒. 锥形束CT研究上颌反复扩缩前方牵引后上颌骨缝的三维变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 346-355. |
| [8] | 康一帆,单小峰,张雷,蔡志刚. 游离腓骨瓣修复重建上颌骨术后腓骨瓣位置变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 938-942. |
| [9] | 王鹏,李大军,刘建彰. 上颌前牙宽度、前牙弓周长与前牙弓深度的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 124-128. |
| [10] | 曹畅,王菲,王恩博,刘宇. β-磷酸三钙用于下颌第三磨牙拔除术后骨缺损修复的自身对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 97-102. |
| [11] | 李丽伟,刘茁,王国良,张华,陈文,马静,张丽,何为,马潞林,王淑敏. 肾癌伴下腔静脉瘤栓合并血栓的多种影像学比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 678-683. |
| [12] | 谢晓艳,贾淑梅,孙志辉,张祖燕. 分辨率设置与锥形束CT检测牙根外吸收的可靠性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 75-79. |
| [13] | 孟沛琦,郭玉兴. 双侧上颌骨二膦酸盐颌骨坏死1例报道[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 1098-1101. |
| [14] | 孙乾,章文博,高敏,于森,毛驰,郭传瑸,俞光岩,彭歆. cN0上颌恶性肿瘤颈淋巴结转移的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 1050-1054. |
| [15] | 赵一姣,刘怡,孙玉春,王勇. 一种基于曲率连续算法的冠、根三维数据融合方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 719-723. |
|
||