北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 755-761. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.030
复合树脂与玻璃陶瓷微拉伸粘接强度的体外研究
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙体牙髓科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.中国科学院动物研究所,北京 100101
3.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院第二门诊部,北京 100101
Evaluation of microtensile bond strength between resin composite and glass ceramic
Ren-tao TANG1,Xin-hai LI2,Jiang-li YU3,Lin FENG1,△( ),Xue-jun GAO1
),Xue-jun GAO1
- 1. Department of Cariology and Endodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100101, China
3. Second Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100101, China
摘要:
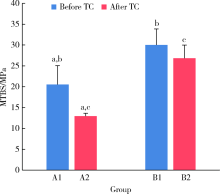
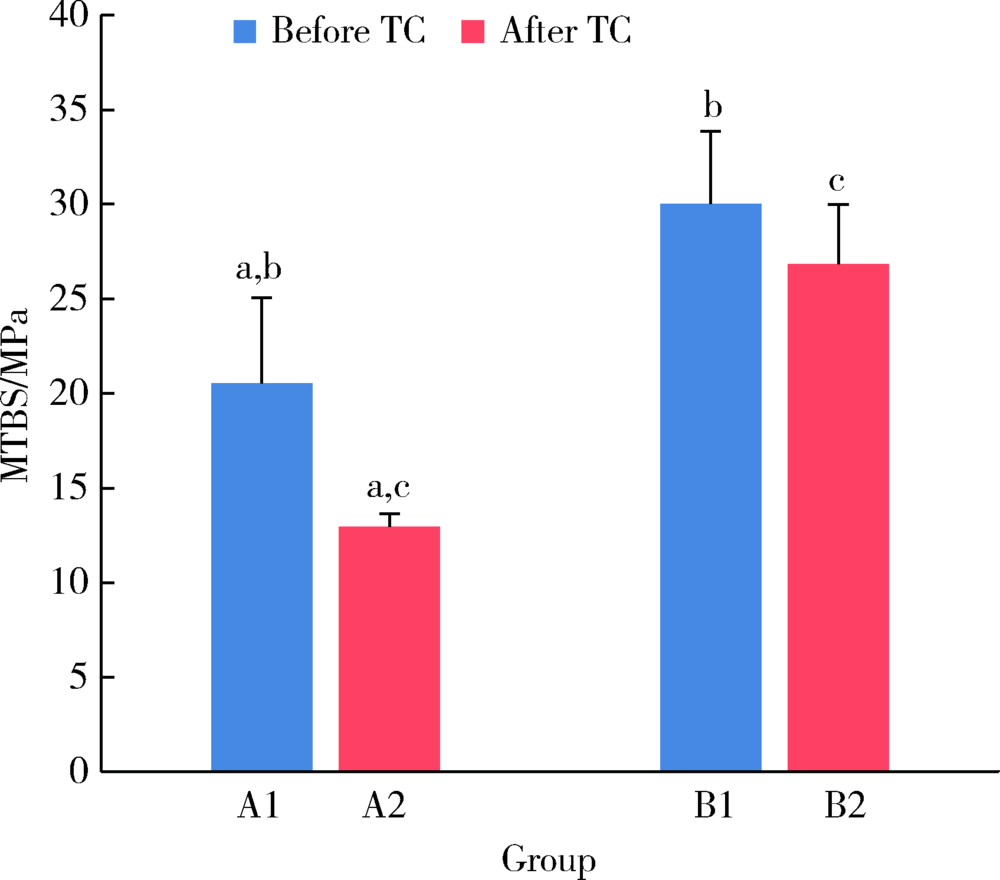
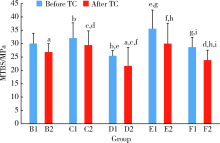
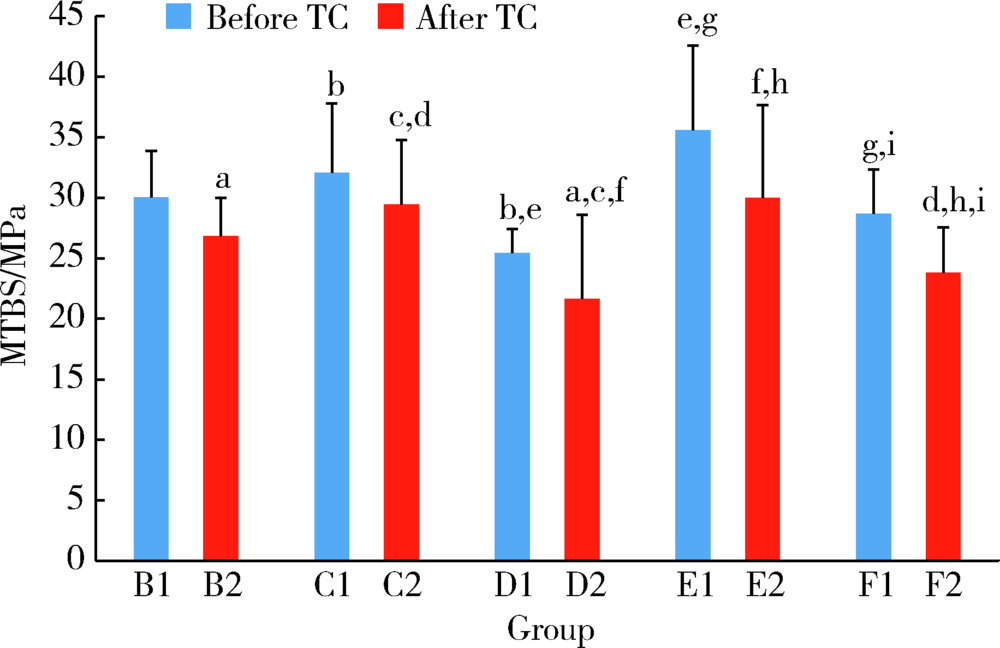
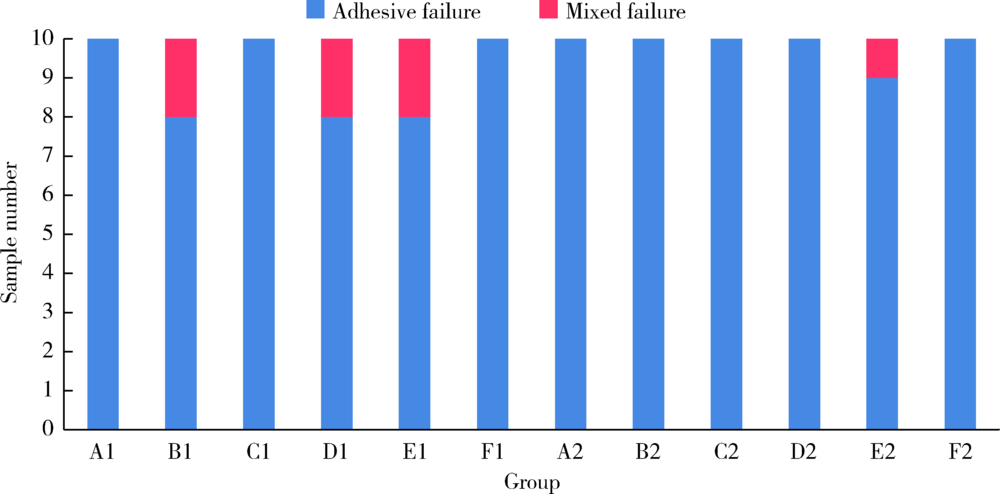
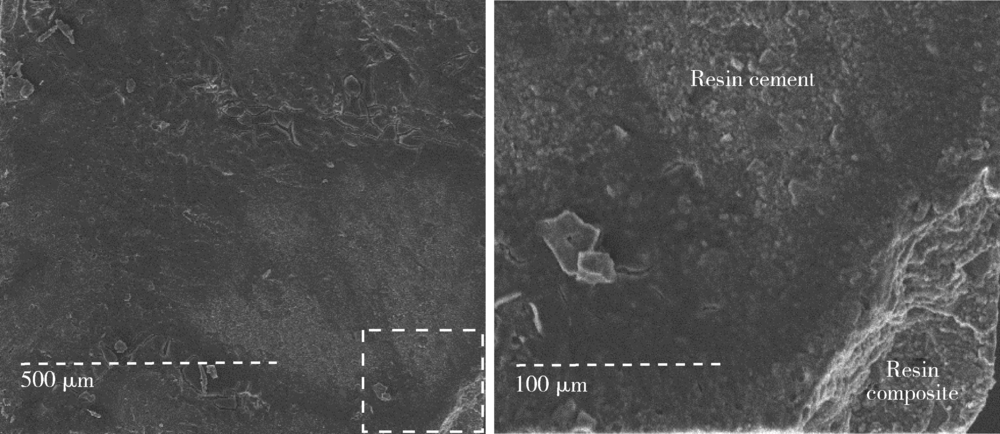
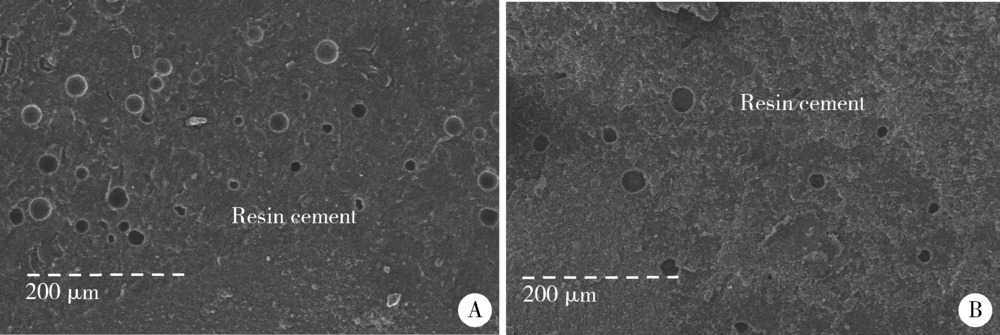
目的: 研究复合树脂与玻璃陶瓷的微拉伸粘接强度,以及树脂表面处理和老化对粘接强度的影响。方法: 制备离体牙牙本质块、树脂块及瓷试块,使用树脂水门汀粘固。根据粘固底物(牙本质与瓷或树脂与瓷)、不同树脂表面处理以及是否温度循环老化进行分组。对照组为牙本质与瓷粘固(A1、A2组);实验组为树脂与瓷粘固,对树脂表面不处理(B1、B2组)或分别进行以下处理,即甲基丙烯酸酯单体(C1、C2组)、硅烷化(D1、D2组)、粗化(E1、E2组)、抛光(F1、F2组)处理后再与瓷粘固。将粘固后的试块切为长方体试件,试件制备后即刻(A1~F1组)或经温度循环后(A2~F2组)测试微拉伸粘接强度。扫描电镜观察试件断面形态,采用单因素方差分析对所得数据进行统计学分析。结果: 老化前后,未经表面处理的树脂与瓷的微拉伸粘接强度[B1 (30.02±3.85) MPa,B2 (26.83±3.14) MPa]均高于牙本质与瓷[A1 (20.55±4.51) MPa,A2 (12.94±0.69) MPa](P<0.05)。与未行表面处理(B1、B2组)相比,经表面处理后树脂与瓷(C1~F1、C2~F2组)的粘接强度差异无统计学意义。结论: 树脂与瓷粘固,可获得不低于牙本质与瓷的粘接强度,对树脂进行甲基丙烯酸酯单体处理、硅烷化、粗化或抛光等表面处理不能有效提升树脂与瓷的粘接强度。
中图分类号:
- R783.1
| [1] |
Saygili G, Sahmali S. Effect of ceramic surface treatment on the shear bond strengths of two resin luting agents to all-ceramic materials[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2003,30(7):758-764.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2003.01027.x pmid: 12791165 |
| [2] | Reich S, Wichmann M, Rinne H, et al. Clinical performance of large, all-ceramic CAD/CAM-generated restorations after three years: a pilot study[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 2004,135(5):605-612. |
| [3] |
Otto T, De Nisco S. Computer-aided direct ceramic restorations: a 10-year prospective clinical study of Cerec CAD/CAM inlays and onlays[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2002,15(2):122-128.
pmid: 11951800 |
| [4] | Otto T, Schneider D. Long-term clinical results of chairside Cerec CAD/CAM inlays and onlays: a case series[J]. Int J Prostho-dont, 2008,21(1):53-59. |
| [5] |
Papia E, Larsson C, du Toit M, et al. Bonding between oxide ceramics and adhesive cement systems: a systematic review[J]. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2014,102(2):395-413.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33013 pmid: 24123837 |
| [6] | Tian T, Tsoi JK, Matinlinna JP, et al. Aspects of bonding between resin luting cements and glass ceramic materials[J]. Dental Mater, 2014,30(7):e147-e162. |
| [7] | Ozcan M, Barbosa S, Melo R, et al. Effect of surface conditioning methods on the microtensile bond strength of resin composite to composite after aging conditions[J]. Dental Mater, 2007,23(10):1276-1282. |
| [8] |
Brendeke J, Ozcan M. Effect of physicochemical aging conditions on the composite-composite repair bond strength[J]. J Adhes Dent, 2007,9(4):399-406.
pmid: 17847643 |
| [9] |
Sharif MO, Catleugh M, Merry A, et al. Replacement versus repair of defective restorations in adults: resin composite [J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2014(2): CD005971.
doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009961.pub2 pmid: 25922858 |
| [10] |
Melo MA, Moyses MR, Santos SG, et al. Effects of different surface treatments and accelerated artificial aging on the bond strength of composite resin repairs[J]. Braz Oral Res, 2011,25(6):485-491.
pmid: 22147227 |
| [11] |
Cho SD, Rajitrangson P, Matis BA, et al. Effect of Er, Cr:YSGG laser, air abrasion, and silane application on repaired shear bond strength of composites[J]. Oper Dent, 2013,38(3):E58-E66.
doi: 10.2341/11-054-L |
| [12] |
Blum IR, Lynch CD, Wilson NH. Factors influencing repair of dental restorations with resin composite[J]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent, 2014,6:81-87.
doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S53461 pmid: 25378952 |
| [13] |
Barcellos DC, Miyazaki Santos VM, Niu L, et al. Repair of composites: Effect of laser and different surface treatments[J]. Int J Adhes Adhes, 2015,59:1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2015.01.008 |
| [14] |
Padipatvuthikul P, Mair LH. Bonding of composite to water aged composite with surface treatments[J]. Dent Mater, 2007,23(4):519-525.
pmid: 16765431 |
| [15] |
Loomans BAC, Vivan Cardoso M, Roeters FJM, et al. Is there one optimal repair technique for all composites?[J]. Dent Mater, 2011,27(7):701-709.
pmid: 21571359 |
| [16] |
Goyal S. Silanes: Chemistry and applications[J]. J Indian Prosthodont Soc, 2006,6(1):14-18.
doi: 10.4103/0972-4052.25876 |
| [17] |
Dal Piva AMDO, Tribst JPM, de Carvalho PCK, et al. Effect of surface treatments on the bond repair strength of resin composite to different artificial teeth[J]. Appl Adhes Sci, 2018,6(1):1-7.
doi: 10.1186/s40563-017-0102-z |
| [18] |
Sirin Karaarslan E, Ozsevik AS, Cebe MA, et al. Bond strength of repaired composite resins: surface treatments, adhesive systems, and composite type[J]. J Adhes Sci Technol, 2016,30(5):520-533.
doi: 10.1080/01694243.2015.1111187 |
| [19] |
Alqarni D, Nakajima M, Hosaka K, et al. The repair bond strength to resin matrix in cured resin composites after water aging[J]. Dent Mater J, 2019,38(2):233-240.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2018-044 pmid: 30449829 |
| [20] |
Flury S, Dulla FA, Peutzfeldt A. Repair bond strength of resin composite to restorative materials after short-and long-term storage[J]. Dent Mater, 2019,35(9):1205-1213.
pmid: 31146960 |
| [21] |
Monticelli F, Osorio R, Mazzitelli C, et al. Limited decalcification diffusion of self-adhesive cements into dentin[J]. J Dent Res, 2008,87(10):974-979.
pmid: 18809754 |
| [22] |
Demunck J. Bonding of an auto-adhesive luting material to enamel and dentin[J]. Dent Mater, 2004,20(10):963-971.
pmid: 15501325 |
| [23] |
Fukuda R, Yoshida Y, Nakayama Y, et al. Bonding efficacy of polyalkenoic acids to hydroxyapatite, enamel and dentin[J]. Biomaterials, 2003,24(11):1861-1867.
doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(02)00575-6 pmid: 12615476 |
| [24] |
Al-Assaf K, Chakmakchi M, Palaghias G, et al. Interfacial characteristics of adhesive luting resins and composites with dentine[J]. Dent Mater, 2007,23(7):829-839.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2006.06.023 pmid: 16934865 |
| [25] | Reis A, Grandi V, Carlotto L, et al. Effect of smear layer thickness and acidity of self-etching solutions on early and long-term bond strength to dentin[J]. J Dentistry, 2005,33(7):549-559. |
| [26] |
Youm S, Jung K, Son S, et al. Effect of dentin pretreatment and curing mode on the microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements[J]. J Adv Prosthodont, 2015,7(4):317-322.
doi: 10.4047/jap.2015.7.4.317 pmid: 26330979 |
| [27] |
Cornelio RB, Wikant A, Mjosund H, et al. The influence of bis-EMA vs bis GMA on the degree of conversion and water susceptibility of experimental composite materials[J]. Acta Odontol Scand, 2014,72(6):440-447.
pmid: 24255958 |
| [28] |
Yoon TH, Lee YK, Lim BS, et al. Degree of polymerization of resin composites by different light sources[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2002,29(12):1165-1173.
pmid: 12472853 |
| [29] |
Vankerckhoven H, Lambrechts P, van Beylen M, et al. Unreac-ted methacrylate groups on the surfaces of composite resins[J]. J Dent Res, 1982,61(6):791-795.
pmid: 7045184 |
| [30] |
Goncalves F, Kawano Y, Pfeifer C, et al. Influence of BisGMA, TEGDMA, and BisEMA contents on viscosity, conversion,and flexural strength of experimental resins and composites[J]. Eur J Oral Sci, 2009,117(4):442-446.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2009.00636.x pmid: 19627357 |
| [31] |
Imbery TA, Gray T, Delatour F, et al. Evaluation of flexural, diametral tensile, and shear bond strength of composite repairs[J]. Oper Dent, 2014,39(6):E250-E260.
doi: 10.2341/13-299-L pmid: 25084105 |
| [32] |
Matinlinna JP, Lassila LV, Ozcan M, et al. An introduction to silanes and their clinical applications in dentistry[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2004,17(2):155-164.
pmid: 15119865 |
| [1] | 李伟伟,陈虎,王勇,孙玉春. 氧化锆陶瓷表面硅锂喷涂层的摩擦磨损性能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 94-100. |
| [2] | 杨洋,浦婷婷,陈立,谭建国. 比较两种改良式印章法辅助后牙树脂牙合贴面修复的形态准确性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 977-982. |
| [3] | 李媛,林红,张铁军. 对比传统成像与数字成像对牙科复合树脂X射线阻射性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 995-1001. |
| [4] | 穆海丽,田福聪,王晓燕,高学军. 玻璃体和通用型复合树脂耐磨性的临床对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 120-125. |
| [5] | 李秋菊,宫玮玉,董艳梅. 生物活性玻璃预处理对牙本质粘接界面耐久性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 931-937. |
| [6] | 于鹏,王晓燕. 填料折射率与比例对复合树脂折射率和透明度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 790-793. |
| [7] | 朱晓鸣,齐璇,李德利,张玉玮,李和平,谭建国. 不同温度新型大气压冷等离子体处理对牙本质粘接强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 43-48. |
| [8] | 李贝贝,邸萍. CAD/CAM钛合金表面处理工艺联合树脂粘接剂对硬质复合树脂粘接强度和耐久性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 111-114. |
| [9] | 张皓羽,姜婷,程明轩,张玉玮. 类瓷树脂及玻璃陶瓷牙合贴面疲劳实验前后的磨耗及表面粗糙度的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 73-77. |
| [10] | 王月,梁宇红. 次氯酸钠溶液表面处理对牙本质粘接强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 105-109. |
| [11] | 郭惠杰,高承志, 林斐,刘伟,岳林. 唾液污染对复合树脂间粘接强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 96-100. |
| [12] | 林斐, 刘伟, 闫鹏, 岳林. 复合树脂间粘接的微拉伸强度研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 124-128. |
| [13] | 蔡雪, 聂杰, 王祖华, 田洪琰, 赵莹, 王晓燕. 洞缘形态对复合树脂颜色匹配的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 120-123. |
| [14] | 田福聪,王晓燕,高学军. 不同粘接系统用于楔状缺损直接修复的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(1): 58-61. |
| [15] | 袁慎坡, 林红, 潘硕, 娄丽丽, 徐永祥. Polident义齿清洁剂对义齿基托树脂性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(6): 946-949. |
|
||